All Tables
- Table 1:
The barium syndrome among YSyS. The spectral type of the
cool component is taken from Mürset & Schmid (1999), or references therein.
In column labelled ``nebula'', ``y'' means that an optical nebula has been
detected, and ``PN'' that, based on its emission line spectrum, the star has traditionally been
included in planetary nebulae catalogues, even though no optical nebula may be visible. The column labelled "P'' lists the orbital period, from Mürset & Schmid (1999).
- Table 2:
Stars classified as metal-deficient barium stars by
Mennessier et al. (1997). The absolute magnitude MV is a
maximum likelihood estimate obtained by Mennessier et al. (1997),
except for the additional stars where it is derived from a straight
inversion of the Hipparcos parallax (BD
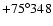 ), from a spectroscopic
estimate of gravity and an educated guess for the mass (BD +
), from a spectroscopic
estimate of gravity and an educated guess for the mass (BD +
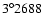 )
or from
a fit to the M 92 isochrone (CS stars). The column labelled "Ba'' indicates
whether detailed chemical analyses have confirmed the Ba nature of the
star.
)
or from
a fit to the M 92 isochrone (CS stars). The column labelled "Ba'' indicates
whether detailed chemical analyses have confirmed the Ba nature of the
star.
- Table 3:
Averaged absolute abundances (in the scale where
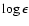 (H) = 12) and normalized abundances [X/Fe] for HD 148897 (relative to the Sun; Grevesse & Sauval 1998). The standard deviations
(H) = 12) and normalized abundances [X/Fe] for HD 148897 (relative to the Sun; Grevesse & Sauval 1998). The standard deviations 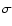 and the number of lines used in the analysis (n) are also
given. Two sets of abundances from Luck (1991) are given:
one is based on a "photometric
and the number of lines used in the analysis (n) are also
given. Two sets of abundances from Luck (1991) are given:
one is based on a "photometric 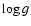 '' (derived from the absolute
magnitude, the effective temperature and an estimate for the stellar
mass) and the other on the "spectroscopic
'' (derived from the absolute
magnitude, the effective temperature and an estimate for the stellar
mass) and the other on the "spectroscopic 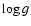 '' (Fe I/Fe II ionization balance).
'' (Fe I/Fe II ionization balance).
- Table 4:
Abundances for HD 139409, in the scale where
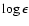 (H) = 12, and
normalized with respect to the solar abundances (Grevesse & Sauval 1998).
The standard deviations
(H) = 12, and
normalized with respect to the solar abundances (Grevesse & Sauval 1998).
The standard deviations 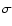 and the number N of lines used in the analysis are also given.
and the number N of lines used in the analysis are also given.
- Table 5:
Binary properties of confirmed or suspected metal-deficient barium stars. The
column labeled "Ba'' indicates whether detailed chemical analyses have
confirmed the Ba nature of the star. The columns labeled
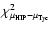 and Prob(
and Prob(
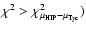 provide the
provide the 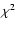 (and its associated probability) involved in the comparison of Hipparcos and Tycho-2 proper motions
(see text for details). The column "Bin.'' has been set to "y'' if the first kind risk of rejecting the null hypothesis that the Tycho and Hipparcos proper motions are equal is smaller than 10%. The column labeled IAD indicates whether the signature of an orbital motion is present in the Hipparcos Intermediate Astrometric Data, according
to the various tests described in the text. The column labeled
(and its associated probability) involved in the comparison of Hipparcos and Tycho-2 proper motions
(see text for details). The column "Bin.'' has been set to "y'' if the first kind risk of rejecting the null hypothesis that the Tycho and Hipparcos proper motions are equal is smaller than 10%. The column labeled IAD indicates whether the signature of an orbital motion is present in the Hipparcos Intermediate Astrometric Data, according
to the various tests described in the text. The column labeled
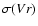 provides the radial-velocity standard deviation,
provides the radial-velocity standard deviation, 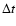 and N correspond to the time span and number of observations, respectively. The columns labeled P and "Ref'' list the orbital period (when available) and the reference for the radial velocity and/or orbital data. The
column "Binary'' gives the final binarity diagnostics.
and N correspond to the time span and number of observations, respectively. The columns labeled P and "Ref'' list the orbital period (when available) and the reference for the radial velocity and/or orbital data. The
column "Binary'' gives the final binarity diagnostics.
- Table 6:
Orbital elements for BD +04
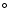 2466.
2466.
- Table 7:
Individual CORAVEL radial velocities and associated errors for HIP 34795, HIP 58596, HIP 76605, BD +
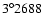 and BD +04
and BD +04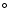 2466. The last column indicates which
one of the two CORAVEL spectrovelocimeters has been used (NO = CORAVEL north
at the Observatoire de Haute Provence; SO = CORAVEL south on the Danish 1.54-m telescope
at ESO).
2466. The last column indicates which
one of the two CORAVEL spectrovelocimeters has been used (NO = CORAVEL north
at the Observatoire de Haute Provence; SO = CORAVEL south on the Danish 1.54-m telescope
at ESO).