- ... from a homeoidal expansion
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- All Appendices are only available in electronic form at http://www.edpsciences.org
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
pairs
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- In the self-gravitating case
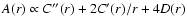 and
and
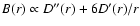 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... motions
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- A bar over a quantity means average over
phase-space velocities. In particular,
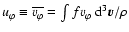 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... function
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The Lambert
function is defined by the identity
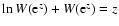 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.