A&A 429, L33-L36 (2005)
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:200400101
Using close stars as probes of hot accretion flow in Sgr A*
S. Nayakshin
Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik,
Karl-Schwarzschild-Str.1, 85741 Garching, Germany
Received 20 October 2004 / Accepted 6 November 2004
Abstract
The extremely hot and tenuous accretion flow in the immediate vicinity of Sgr A* is believed to be invisible (too dim) in the X-ray band, except for short X-ray flares. Here we point out that during pericenter passages, close brightest stars irradiate the inner region of the accretion flow, providing a plenty of optical/UV photons. These seed photons are
Compton up-scattered by the hot electrons of the accretion flow to higher frequencies, some into the X-ray band, potentially making the innermost accretion flow much brighter in X-rays than usual. We propose to use coordinated near infra-red and X-ray observations of close star passages to put constraints onto Sgr A* accretion theories. The absence of a noticeable change in the steady emission of Sgr A* as observed by Chandra in the year 2002, when the star named S2 passed through a pericenter of its orbit, already rules out the hotter of the "standard'' Advection-Dominated Accretion Flows. The less dense accretion flows, in particular the model of Yuan et al. (2003), passes the test and is constrained to accretion rates no larger than 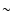 few
few 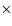 10
10
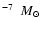 year-1.
year-1.
Key words: accretion, accretion disks - black hole physics - Galaxy: center - radiation
mechanisms: general
Sgr A* is the super massive black hole (SMBH) in the center of our Galaxy (Ghez et al. 2003a; Schödel et al. 2002; Reid et al. 1999). The gas from the winds of the surrounding young massive stars should be able to maintain the accretion rate on the SMBH at a sizable fraction of the Bondi
accretion rate if the SMBH can accept the gas at this rate. The Bondi accretion rate is estimated to be 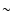
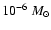 year-1 (Baganoff et al. 2003), whereas the linear polarization measurements at a range of radio wavelengths constrain the accretion rate onto the SMBH to a value of
year-1 (Baganoff et al. 2003), whereas the linear polarization measurements at a range of radio wavelengths constrain the accretion rate onto the SMBH to a value of 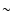 10-8-
10-8-
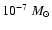 year-1 (e.g., Bower et al. 2003). The latter estimate is based on somewhat uncertain assumptions about the magnetic field equipartition and absence of many magnetic field reversals
(Ruszkowski & Begelman 2002).
year-1 (e.g., Bower et al. 2003). The latter estimate is based on somewhat uncertain assumptions about the magnetic field equipartition and absence of many magnetic field reversals
(Ruszkowski & Begelman 2002).
It would certainly be beneficial to have another physically
independent method to constrain the properties of the accretion flow
near the event horizon. Unfortunately, in the X-ray band, it appears
that the quiescent Sgr A* emission is resolved
(Baganoff et al. 2003) and can be explained by thermal bremsstrahlung
from the capture radius region (Quataert 2002). The inner flow may
thus be simply invisible to the observer unless there is a sizable
X-ray emission from a jet (e.g., Yuan et al. 2002), or during strong
X-ray flares (Baganoff et al. 2001).
In this letter we note that comptonization of the radiation of the
closest of the observed bright stars by the hot accretion flow may be
used to this effect. These stars produce as much as
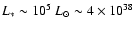 erg/s in optical-UV radiation, the amount far greater than the total bolometric luminosity of Sgr A*,
erg/s in optical-UV radiation, the amount far greater than the total bolometric luminosity of Sgr A*,
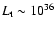 erg/s. In a single
Compton scattering, the photon energy on average increases by a factor
erg/s. In a single
Compton scattering, the photon energy on average increases by a factor 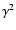 ,
where
,
where 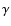 is
the Lorenz
is
the Lorenz 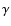 -factor of the electron taking part in the
up-scattering. Averaged over a relativistic Maxwellian electron
distribution with temperature
-factor of the electron taking part in the
up-scattering. Averaged over a relativistic Maxwellian electron
distribution with temperature 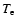 ,
the average boost factor becomes
,
the average boost factor becomes
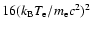 ,
where
,
where 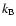 is the Boltzmann constant, and
is the Boltzmann constant, and 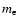 is the electron mass. The typical frequency of a photon emitted by the star is around
is the electron mass. The typical frequency of a photon emitted by the star is around
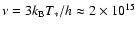 Hz, where
T* = 30 000 Kelvin is the stellar temperature, and h is the Planck constant. Chandra frequency band is centered around
Hz, where
T* = 30 000 Kelvin is the stellar temperature, and h is the Planck constant. Chandra frequency band is centered around
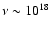 Hz. Therefore electrons with temperature of
Hz. Therefore electrons with temperature of
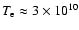 K are the most efficient in scattering of S2 radiation into the Chandra band.
K are the most efficient in scattering of S2 radiation into the Chandra band.
Such high temperature electrons are present in both the canonical ADAF (without winds) model, e.g. Narayan (2002), and even more so in the less dense but hotter Non-Radiative Accretion Flows (NRAFs) that incorporate effects of gas outflows. Since Sgr A* is very dim in X-rays in its normal "quiescent'' state, e.g.
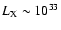 erg s-1, there is then a hope of detecting a comptonized "echo'' of a close star passage.
erg s-1, there is then a hope of detecting a comptonized "echo'' of a close star passage.
2 Analytical estimates
We shall rely on the accretion flow models by Narayan (2002) and Yuan et al. (2003), who used
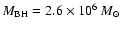 .
Recently, Sgr A* mass has been determined to be larger, e.g.
.
Recently, Sgr A* mass has been determined to be larger, e.g.
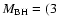 -
-
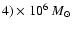 (Ghez et al. 2003a; Genzel et al. 2003). We thus use an intermediate value of
(Ghez et al. 2003a; Genzel et al. 2003). We thus use an intermediate value of
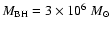 .
.
The Thomson optical depth,
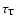 ,
of the hot accretion flow in
Sgr A* is quite small:
,
of the hot accretion flow in
Sgr A* is quite small:
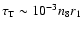 ,
where
,
where
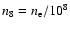 is the typical electron density in units of
108 cm-3, and
is the typical electron density in units of
108 cm-3, and
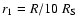 .
(Note that further out the
optical depth of the flow is even smaller.) Therefore, only the first
order scattering of the stellar photons need be considered.
.
(Note that further out the
optical depth of the flow is even smaller.) Therefore, only the first
order scattering of the stellar photons need be considered.
At the moment of the closest approach to the SMBH, the star S2 in particular, was
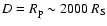 away from Sgr A*, where
away from Sgr A*, where
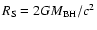 is the Schwarzschild radius of the SMBH, D is the current distance between the star and Sgr A*, and
is the Schwarzschild radius of the SMBH, D is the current distance between the star and Sgr A*, and 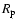 is the pericenter distance of the orbit. The radiation energy density near the SMBH is thus
is the pericenter distance of the orbit. The radiation energy density near the SMBH is thus
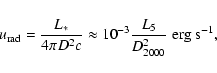 |
(1) |
where
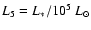 ,
,
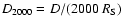 .
.
We now introduce
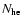 as the total number of electrons in the hot accretion flow that are able to up-scatter an optical/UV photon with frequency
as the total number of electrons in the hot accretion flow that are able to up-scatter an optical/UV photon with frequency
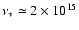 Hz into the Chandra band,
Hz into the Chandra band,
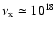 Hz. The corresponding mass of the accretion flow ions, assumed to be all protons for simplicity, is clearly
Hz. The corresponding mass of the accretion flow ions, assumed to be all protons for simplicity, is clearly
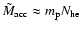 ,
where
,
where 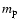 is the proton mass. Since scattering conserves number of photons, we can estimate the X-ray luminosity of the up-comptonized S2 emission as
is the proton mass. Since scattering conserves number of photons, we can estimate the X-ray luminosity of the up-comptonized S2 emission as
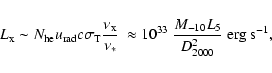 |
(2) |
where
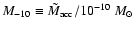 .
Recall that
quiescent X-ray luminosity of Sgr A* is
.
Recall that
quiescent X-ray luminosity of Sgr A* is
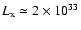 erg/s. Thus, if the region of accretion flow with
erg/s. Thus, if the region of accretion flow with
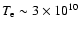 K had a mass of around
K had a mass of around
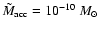 or larger, the up-comptonized S2 emission would have been measurable in 2002 by Chandra.
or larger, the up-comptonized S2 emission would have been measurable in 2002 by Chandra.
We can relate the accretion flow mass
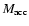 at a given dimensionless radius r to the accretion rate as
at a given dimensionless radius r to the accretion rate as
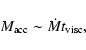 |
(3) |
where
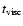 is the viscous time estimated in
is the viscous time estimated in 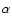 -viscosity accretion flows as
-viscosity accretion flows as
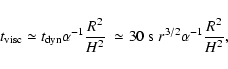 |
(4) |
where
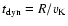 is the local dynamical time and H is the geometrical thickness of the accretion flow. For flows considered here
is the local dynamical time and H is the geometrical thickness of the accretion flow. For flows considered here
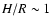 .
For example, with an accretion rate of
.
For example, with an accretion rate of
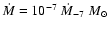 year-1, we have
year-1, we have
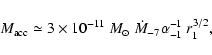 |
(5) |
where
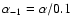 .
Requiring
.
Requiring
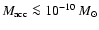 ,
we have
,
we have
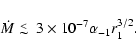 |
(6) |
This is a realistic range of accretion rates for Sgr A* (Yuan et al. 2003; Narayan 2002).
3 Calculation of the comptonized spectrum
The estimates above are useful but nonetheless a more careful
calculation is required as an accretion flow spans a range of
temperatures and its density profile may be changing in a non-trivial
way due to, e.g., outflows. For definitiveness, we shall use the
accretion flow structure as available in models of Narayan (2002)
and Yuan et al. (2003).
The electron temperature is at most equal to the local virial
temperature, e.g. temperature at which the thermal energy of the gas
is equal to the gravitational potential energy:
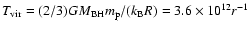 K. Thus,
K. Thus,
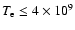 K for
K for
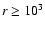 .
Accordingly, we do not consider
Compton scattering in the outer,
.
Accordingly, we do not consider
Compton scattering in the outer,
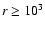 ,
regions of the flow.
In practice
,
regions of the flow.
In practice 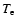 is still smaller than
is still smaller than
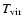 ,
and hence it is
only the inner few hundred Schwarzschild radii of the flow that are important. Since these radii are much smaller than S2 pericenter distance,
,
and hence it is
only the inner few hundred Schwarzschild radii of the flow that are important. Since these radii are much smaller than S2 pericenter distance,
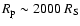 ,
we can safely assume that
,
we can safely assume that
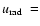 const. in this optically thin region.
const. in this optically thin region.
The emitted comptonized spectrum is calculated as
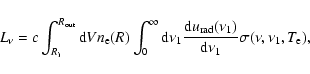 |
(7) |
where d
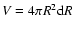 is the volume element,
is the volume element, 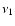 is the
frequency of the photon before scattering and
is the
frequency of the photon before scattering and 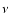 is that after the
scattering, and
is that after the
scattering, and
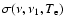 is the cross section for
such a scattering averaged over the electron distribution function
with temperature
is the cross section for
such a scattering averaged over the electron distribution function
with temperature 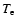 .
The cross section is taken from
Nagirner & Poutanen (1994). We assume also that the bolometric luminosity of S2
is
.
The cross section is taken from
Nagirner & Poutanen (1994). We assume also that the bolometric luminosity of S2
is
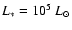 and the spectrum is that of a blackbody at
temperature
T = 30 000 Kelvin.
and the spectrum is that of a blackbody at
temperature
T = 30 000 Kelvin.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{fig1.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2005/02/aagj201/Timg66.gif) |
Figure 1:
The up-comptonized emission of the close star S2 during its closest approach to Sgr A* in 2002 for five different accretion flows, as marked in the figure. The spectrum of the star illuminating the inner 100 Schwarzschild radii of the flow is also shown for comparison. The Chandra data with uncertainties (Baganoff et al. 2003) are shown
with the bow-tie. |
| Open with DEXTER |
Figure 1 shows several examples of the expected
up-comptonized spectrum calculated for several different accretion
flow models. The dash-multiple-dot curve labelled by "Illuminating
rad''. is the stellar radiation incident on the inner
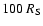 sphere, plotted as a reference scale. The bow-tie is the Chandra
data on emission of Sgr A* with the spectral uncertainty
(Baganoff et al. 2003).
sphere, plotted as a reference scale. The bow-tie is the Chandra
data on emission of Sgr A* with the spectral uncertainty
(Baganoff et al. 2003).
The solid curve is the simplest "cut-off'' ADAF model used by
Narayan (2002) to illustrate the need for a two-temperature nature
of the accretion flow in Sgr A*. In this model the electron temperature
at large radii follows the virial gas temperature but is capped at
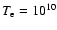 K at smaller radii. We assumed
K at smaller radii. We assumed
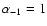 and
accretion rate of
and
accretion rate of
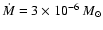 year-1, the
lower of the values used by Narayan (2002) (see his Eq. (3)). The
model clearly over-predicts the emission in the X-ray band. This
occurs despite the fact that electrons never reach the temperature of
year-1, the
lower of the values used by Narayan (2002) (see his Eq. (3)). The
model clearly over-predicts the emission in the X-ray band. This
occurs despite the fact that electrons never reach the temperature of
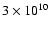 K. The electrons in the tail of the Maxwellian
distribution produce the Chandra band X-rays, and since the
accretion rate is an order of magnitude higher than the critical one
estimated in Eq. (6), the model manages to emit a
measurable X-ray flux.
K. The electrons in the tail of the Maxwellian
distribution produce the Chandra band X-rays, and since the
accretion rate is an order of magnitude higher than the critical one
estimated in Eq. (6), the model manages to emit a
measurable X-ray flux.
Next we test the more refined ADAF models by Narayan (2002). These
employ a self-consistent description of the electron-ion Coulomb
energy exchange rather than the simple temperature cutoff. In
particular, we approximate the electron temperature profiles in his
Fig. 5 as
![\begin{displaymath}%
T_{\rm e} = \cases{T_0 \left[r/3\right]^{-1/2},\hskip 0.5cm...
... vir}(r)\\
T_{\rm vir}(r), \hskip 1.3cm \hbox{otherwise},\\ }
\end{displaymath}](/articles/aa/full/2005/02/aagj201/img72.gif) |
(8) |
where T0 is the electron temperature at r=3. In particular, we
consider two values of T0 that are approximately consistent with
Fig. 5 of Narayan (2002):
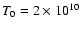 and
and
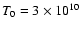 .
Both models are for
.
Both models are for
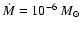 year-1 and
year-1 and
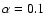 .
The higher initial electron
temperature model is probably ruled out by the existing Chandra
data on Sgr A* that show no noticeable variation in the X-ray flux
during 2002 (Baganoff 2004, private communication). The lower
temperature model may be however below what could have been
detected by Chandra.
.
The higher initial electron
temperature model is probably ruled out by the existing Chandra
data on Sgr A* that show no noticeable variation in the X-ray flux
during 2002 (Baganoff 2004, private communication). The lower
temperature model may be however below what could have been
detected by Chandra.
Finally, we also test the more recent and more physically complete
NRAF models for Sgr A* by Yuan et al. (2003). Their Fig. 2 shows the
electron temperature and the density profiles for one particular set
of parameters that fit Sgr A* broad band spectrum quite well. Due to
strong thermally driven outflows, the radial profile of density is
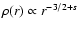 ,
with s = 0.27. Note that for ADAFs
s=0. The temperature profile in Yuan et al. (2003) is quite close to a
power-law with
,
with s = 0.27. Note that for ADAFs
s=0. The temperature profile in Yuan et al. (2003) is quite close to a
power-law with
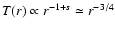 .
The
accretion rate close to the SMBH in this model is
.
The
accretion rate close to the SMBH in this model is
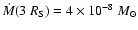 year-1.
year-1.
Yuan et al. (2003) also include a non-thermal component in the electron
distribution. As we find that the latter does not produce a dominant
contribution to the up-comptonized S2 emission in the Chandra
band, and since we do not have access to the exact model by Yuan et al. (2003), we set the minimum and maximum 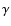 -factors as following:
-factors as following:
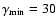 and
and
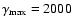 ,
in a rough agreement with Fig. 2 of Yuan et al. (2003).
,
in a rough agreement with Fig. 2 of Yuan et al. (2003).
Figure 1 shows the resulting comptonized spectrum (fine
dotted curves) at the pericenter of S2 orbit for the Yuan et al. (2003)
model. The higher of the curves includes both thermal and non-thermal
electrons, whereas the other one includes scattering due to the
thermal electrons only. In both cases the resulting X-ray emission is
about a factor of 10 below the quiescent X-ray emission of Sgr A*, so
that the model of Yuan et al. (2003) clearly passes the test.
The trajectory of S2 is calculated based on the best fit to its orbit by Ghez et al. (2003a). The background optical-UV radiation energy density near Sgr A* location is assumed to be dominated by the whole of the Sgr A* star cluster, whose luminosity is of order
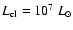 ,
and whose size is
,
and whose size is
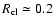 parsec (Genzel et al. 2003). Thus,
parsec (Genzel et al. 2003). Thus,
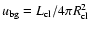 .
We assume a spectrum identical to that of S2 for simplicity. The background is quite negligible in comparison with the radiation energy density
.
We assume a spectrum identical to that of S2 for simplicity. The background is quite negligible in comparison with the radiation energy density
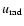 of S2 during its pericenter passage (Eq. (1)).
of S2 during its pericenter passage (Eq. (1)).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{fig2.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2005/02/aagj201/Timg86.gif) |
Figure 2:
The lightcurve of the optical/UV radiation of the close star S2 up-comptonized by the accretion flow into the X-ray band. The upper panel shows the lightcurve on time scales of tens of years, while the lower one shows the emission during 2002 when S2 passes through the pericenter of its orbit. The filled triangles mark the epochs when Chandra observed the Galactic Center region (Park et al. 2004; Eckart et al. 2004). The y-coordinate of the triangles in the figure is arbitrary. |
| Open with DEXTER |
Since the cooling time of the hot electrons due to inverse Compton effect is very long compared to the local dynamical time (Chang & Choi 2003), it can be neglected. The X-ray lightcurve is then
![\begin{displaymath}%
L_{\rm x} = L_{\rm x, p} \;\left[\frac{R_{\rm p}}{D}\right]^2,
\end{displaymath}](/articles/aa/full/2005/02/aagj201/img87.gif) |
(9) |
where D is the current distance between the SMBH and S2. The
resulting X-ray lightcurve, normalized to the maximum reached at the
pericenter,
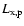 ,
is plotted in Fig. 2. The upper
panel shows the lightcurve on the scales of tens of years, whereas the
lower panel concentrates on that during the year 2002 only. Clearly
the duration of the event is several months. Very luckily, Chandra observed Sgr A* (filled triangles in Fig. 2)
on many occasions in 2002 (e.g. see Park et al. 2004). It is thus possible
that a careful analysis of Chandra 2002 data would be able to
constrain the amount of an extra up-comptonized X-ray flux to a small
fraction of the quiescent X-ray luminosity of Sgr A*. Such an analysis
may be facilitated by the fact that the lightcurve of the event is
well determined due to small overall errors in the trajectory of the
star S2 (Ghez et al. 2003b; Schödel et al. 2002).
,
is plotted in Fig. 2. The upper
panel shows the lightcurve on the scales of tens of years, whereas the
lower panel concentrates on that during the year 2002 only. Clearly
the duration of the event is several months. Very luckily, Chandra observed Sgr A* (filled triangles in Fig. 2)
on many occasions in 2002 (e.g. see Park et al. 2004). It is thus possible
that a careful analysis of Chandra 2002 data would be able to
constrain the amount of an extra up-comptonized X-ray flux to a small
fraction of the quiescent X-ray luminosity of Sgr A*. Such an analysis
may be facilitated by the fact that the lightcurve of the event is
well determined due to small overall errors in the trajectory of the
star S2 (Ghez et al. 2003b; Schödel et al. 2002).
5 Discussion
We have shown that up-comptonization of the optical/UV radiation of
the star S2, which famously passed through the pericenter of its orbit
only 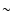 2000 Schwarzschild radii away from Sgr A* (Schödel et al. 2002),
constrains the properties of the accretion flow in the immediate
vicinity of the SMBH. These constraints are completely independent
from those due to the rotation measure limits in the radio wavelengths
(Bower et al. 2003), and are thus complimentary to those results. We urge
the observers to search the Chandra 2002 data for signatures of
the transient brightening with the lightcurve shown in Fig. 2. Such an analysis may perhaps yield much tighter constraints on the amplitude of the effect than Fig. 1 indicates.
2000 Schwarzschild radii away from Sgr A* (Schödel et al. 2002),
constrains the properties of the accretion flow in the immediate
vicinity of the SMBH. These constraints are completely independent
from those due to the rotation measure limits in the radio wavelengths
(Bower et al. 2003), and are thus complimentary to those results. We urge
the observers to search the Chandra 2002 data for signatures of
the transient brightening with the lightcurve shown in Fig. 2. Such an analysis may perhaps yield much tighter constraints on the amplitude of the effect than Fig. 1 indicates.
Future observations of close star passages may be more constraining
that that from the year 2002 if (i) the star approaching the SMBH is
brighter and/or closer to Sgr A* than
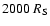 ;
(ii) if more
sensitive and well planned X-ray observations of the close stellar
passage are made. In addition, interaction of stellar winds with the
surrounding hot accretion flow may yield observable signatures in a
range of wavelengths depending on the stellar mass loss rate and the
outflow velocity and (unfortunately) not well constrained details of
presumably collisionless wind/accretion flow shocks (e.g., see Loeb 2004).
;
(ii) if more
sensitive and well planned X-ray observations of the close stellar
passage are made. In addition, interaction of stellar winds with the
surrounding hot accretion flow may yield observable signatures in a
range of wavelengths depending on the stellar mass loss rate and the
outflow velocity and (unfortunately) not well constrained details of
presumably collisionless wind/accretion flow shocks (e.g., see Loeb 2004).
The idea of using the close star passages to constrain the properties
of the accretion flow around Sgr A* is not new. Chang & Choi (2003) noted
that the inverse Compton effect will provide an additional cooling of
the hot electrons. However the corresponding relative change in the
electron temperature is only 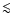 10-4 and appears very hard to
observe in any wavelength. Here we showed that the up-comptonized S2 radiation itself, on the over hand, is much easier to observe since
Sgr A* quiescent X-ray luminosity is very small. In addition,
Nayakshin & Sunyaev (2003) and Cuadra et al. (2003) have shown that passages of close
stars could also be used to constrain the properties of a cold
geometrically thin "inactive''accretion disk around Sgr A*. The fact
that no near infra-red "echoes'' or stellar eclipses were observed up
to date probably indicates that such a disk does not presently exist
in Sgr A*.
10-4 and appears very hard to
observe in any wavelength. Here we showed that the up-comptonized S2 radiation itself, on the over hand, is much easier to observe since
Sgr A* quiescent X-ray luminosity is very small. In addition,
Nayakshin & Sunyaev (2003) and Cuadra et al. (2003) have shown that passages of close
stars could also be used to constrain the properties of a cold
geometrically thin "inactive''accretion disk around Sgr A*. The fact
that no near infra-red "echoes'' or stellar eclipses were observed up
to date probably indicates that such a disk does not presently exist
in Sgr A*.
Concluding, we note that close stellar passages are of
significant value for solving the riddle of Sgr A* and collisionless
gas accretion onto SMBHs in general through a variety of physical
processes.
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges useful discussions with Fred Baganoff and Henk Spruit.
- Baganoff,
F. K., Bautz, M. W., Brandt, W. N., et al.
2001, Nature, 413, 45 [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Baganoff,
F. K., Maeda, Y., Morris, M., et al. 2003, ApJ, 591,
891 [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Bower, G. C.,
Wright, M. C. H., Falcke, H., & Backer, D. C.
2003, ApJ, 588, 331 [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Chang, H., &
Choi, C. 2003, A&A, 410, 519 [EDP Sciences] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Cuadra, J.,
Nayakshin, S., & Sunyaev, R. 2003, A&A, 411, 405 [EDP Sciences] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Eckart, A.,
Baganoff, F. K., Morris, M., et al. 2004, ArXiv
Astrophysics e-prints
- Genzel, R.,
Schödel, R., Ott, T., et al. 2003, ApJ, 594, 812 [CrossRef]
- Ghez, A. M.,
Becklin, E., Duchêne, G., et al. 2003a, Astron. Nachr.,
Vol. 324, No. S1, Special Suppl., The central 300 parsec of the
Milky Way, ed. A. Cotera, H. Falcke,
T. R. Geballe, & S. Markoff
[arXiv:astro-ph/0303151]
- Ghez, A. M.,
Duchêne, G., Matthews, K., et al. 2003b, ApJ, 586,
L127 [CrossRef]
- Loeb, A. 2004, MNRAS,
350, 725 [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Nagirner,
D. I., & Poutanen, J. 1994, Single Compton scattering
(Amsterdam: Harwood Academic Publishers)
(In the text)
- Narayan, R. 2002,
in Lighthouses of the universe: the most luminous celestial objects
and their use for cosmology, ed. M. Gilfanov, R. Sunyaev,
& E. Churazov (Berlin: Springer), 405
(In the text)
- Nayakshin, S., &
Sunyaev, R. 2003, MNRAS, 343, L15 [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Park, S., Muno,
M. P., Baganoff, F. K., et al. 2004, ApJ, 603,
548 [CrossRef]
- Quataert, E.
2002, ApJ, 575, 855 [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Reid, M. J.,
Readhead, A. C. S., Vermeulen, R. C., &
Treuhaft, R. N. 1999, ApJ, 524, 816 [CrossRef]
- Ruszkowski,
M., & Begelman, M. C. 2002, ApJ, 573, 485 (In the text)
- Schödel,
R., Ott, T., Genzel, R., et al. 2002, Nature, 419, 694 [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F., Markoff, S.,
& Falcke, H. 2002, A&A, 383, 854 [EDP Sciences] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Yuan, F., Quataert, E.,
& Narayan, R. 2003, ApJ, 598, 301 [CrossRef] (In the text)
Copyright ESO 2004
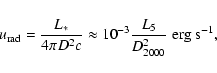
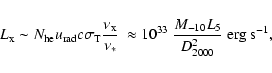
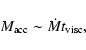
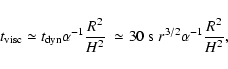
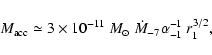
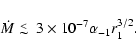
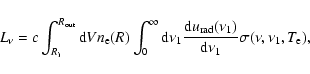
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{fig1.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2005/02/aagj201/Timg66.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}%
T_{\rm e} = \cases{T_0 \left[r/3\right]^{-1/2},\hskip 0.5cm...
... vir}(r)\\
T_{\rm vir}(r), \hskip 1.3cm \hbox{otherwise},\\ }
\end{displaymath}](/articles/aa/full/2005/02/aagj201/img72.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{fig2.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2005/02/aagj201/Timg86.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}%
L_{\rm x} = L_{\rm x, p} \;\left[\frac{R_{\rm p}}{D}\right]^2,
\end{displaymath}](/articles/aa/full/2005/02/aagj201/img87.gif)