 |
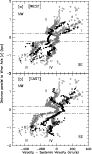
Figure 1:
a) BLUE-shifted outflow (solid dots) measured
parallel to the minor axis at
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
In the text
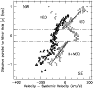 |
Figure 2:
Red-shifted outflow (dots) measured parallel to the
minor axis at
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
In the text
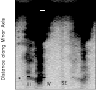 |
Figure 3:
H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
In the text
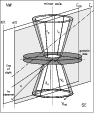 |
Figure 4:
Illustration of an idealized outflow cone on the SE and NW side of
the galactic disk. E |
| Open with DEXTER | |
In the text
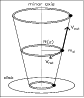 |
Figure 5: Momentum conservation of outflow material moving outwards along the cone walls (a tangential element is shown). The arrow indicates the trajectory of the outflowing material. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
In the text
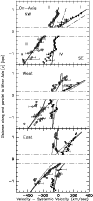 |
Figure 6:
Illustration of the agreement between the observation and the
adopted cone model (Table 2). The displayed data are the averages of the
velocities determined from the H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
In the text
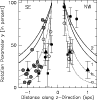 |
Figure 7:
Values of the rotation parameter |
| Open with DEXTER | |
In the text
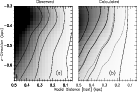 |
Figure 8:
Momentum conserved rotation of the eastern part of the visible
outflow material at the SE side of the disk; plotted as grayscale and lines of
values L = V
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
In the text