All Tables
- Table 1:
Details of the CFDF images used in this study. For the 03 hr and 14 hr
fields, we list the
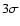 detection limit inside an aperture of
3'' for images convolved to the worst seeing (i.e. 1.3'' for 03 hr
and 1.4'' for 14 hr). For the 22 hr field, we list the
detection limit inside an aperture of
3'' for images convolved to the worst seeing (i.e. 1.3'' for 03 hr
and 1.4'' for 14 hr). For the 22 hr field, we list the 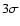 detection limit
inside an aperture of 4'' for un-convolved images.
detection limit
inside an aperture of 4'' for un-convolved images.
- Table 2:
Differential number counts, N, and surface density, n (in
arcmin-2), of Lyman-break galaxies in the CFDF fields, for a
range of IAB-selected slices. The mean surface density,
labelled CFDF, is also given. Errors in the surface density
measurements for each individual field are computed using Poisson
counting statistics; field-to-field variance is used to estimate
the error in the mean.
- Table 3:
Observed and simulated surface densities of objects (in
arcmin-2) recovered using the selection box
(Eq. (1)), based on simulations described in
Sect. 3.3 and observations in the
CFDF-14 hr field. We also estimate the fraction of Lyman-break
galaxies (LBG) recovered using this selection box from the total
galaxy population in this redshift range. Additionally, we present
the fraction of contaminants within this selection box by
interlopers (lower-redshift galaxies) outside our redshift range
(2.9<z<3.4) and by interlopers with z<2 and by stars.
- Table 4:
Comparison for different redshift ranges between objects
falling within Steidel et al.'s selection box and objects selected
in Steidel et al.'s box which also lie within the CFDF selection box
(Eq. (1)) for
IAB<24.5.
- Table 5:
The amplitude of
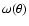 at 1 degree,
at 1 degree,
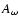 ,
the slope
,
the slope 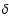 and the comoving correlation length r0 (in h-1 Mpc), for each field and for different magnitude
limited samples considered in this paper. r0 measurements are
computed for three standard cosmological models. To derive r0 we
assume a top-hat redshift distribution centred at
and the comoving correlation length r0 (in h-1 Mpc), for each field and for different magnitude
limited samples considered in this paper. r0 measurements are
computed for three standard cosmological models. To derive r0 we
assume a top-hat redshift distribution centred at
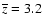 and the best fitted value of the slope. Result marked as CFDF
mean are computed from the mean over all three fields. The error
bars shown correspond to Poisson error bars. An extra systematic
errorbar arising from our uncertainty in the underlying redshift
range of our Lyman-break sources of
and the best fitted value of the slope. Result marked as CFDF
mean are computed from the mean over all three fields. The error
bars shown correspond to Poisson error bars. An extra systematic
errorbar arising from our uncertainty in the underlying redshift
range of our Lyman-break sources of 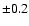 for the entire faint
samples and of
for the entire faint
samples and of 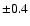 for the bright sample should be added. (Our
principal results are highlighted in bold.)
for the bright sample should be added. (Our
principal results are highlighted in bold.)
- Table 6:
Bias for each field and for each magnitude
limited sample considered in this paper, for
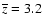 and
for the best fitting value of the slope. The result marked as
"CFDF mean'' is computed from the mean over all three fields. The
error bars shown correspond to Poisson error bars. To account for
our uncertainty in the underlying redshift distribution of our
Lyman-break sources, an extra systematic error of
and
for the best fitting value of the slope. The result marked as
"CFDF mean'' is computed from the mean over all three fields. The
error bars shown correspond to Poisson error bars. To account for
our uncertainty in the underlying redshift distribution of our
Lyman-break sources, an extra systematic error of 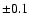 for the
whole and faint samples and of
for the
whole and faint samples and of 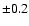 for the bright sample
should be added.
for the bright sample
should be added.