A&A 404, 93-111 (2003)
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20030170
I. D. Karachentsev 1 - E. K. Grebel 2 - M. E. Sharina 1,10 - A. E. Dolphin 3 - D. Geisler 4 - P. Guhathakurta 5 - P. W. Hodge 6 - V. E. Karachentseva 7 - A. Sarajedini 8 - P. Seitzer 9
1 - Special Astrophysical Observatory, Russian Academy
of Sciences, N. Arkhyz, KChR, 369167, Russia
2 - Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117
Heidelberg, Germany
3 - Kitt Peak National Observatory, National Optical Astronomy
Observatories, PO Box 26732, Tucson, AZ 85726, USA
4 - Departamento de Física, Grupo de Astronomía, Universidad de
Concepción, Casilla 160-C, Concepción, Chile
5 - UCO/Lick Observatory, University of California at Santa Cruz, Santa
Cruz, CA 95064, USA
6 - Department of Astronomy, University of Washington, Box 351580,
Seattle, WA 98195, USA
7 - Astronomical Observatory of Kiev University, 04053, Observatorna 3,
Kiev, Ukraine
8 - Department of Astronomy, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
32611, USA
9 - Department of Astronomy, University of Michigan, 830 Dennison
Building, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA
10 - Isaac Newton Institute, Chile, SAO Branch
Accepted 9 December 2002 / Accepted 31 January 2003
Abstract
We present an analysis of Hubble Space Telescope/WFPC2 images of nine
nearby galaxies in Sculptor. We derive their distances from the luminosity
of the tip of the red giant branch stars with a typical accuracy of
![]() 12%. Their distances are 4.21 Mpc (Sc 22), 4.92 Mpc (DDO 226),
3.94 Mpc (NGC 253), 3.40 Mpc (KDG 2), 3.34 Mpc (DDO 6), 3.42 Mpc (ESO 540-030),
4.43 Mpc (ESO 245-05), 4.27 Mpc (UGCA 442), and 3.91 Mpc (NGC 7793). The
galaxies are concentrated in several spatially separated loose groups around
NGC 300, NGC 253, and NGC 7793. The Sculptor galaxy complex together with
the CVn I cloud and the Local Group form a 10 Mpc filament, apparently
driven by the free Hubble flow.
12%. Their distances are 4.21 Mpc (Sc 22), 4.92 Mpc (DDO 226),
3.94 Mpc (NGC 253), 3.40 Mpc (KDG 2), 3.34 Mpc (DDO 6), 3.42 Mpc (ESO 540-030),
4.43 Mpc (ESO 245-05), 4.27 Mpc (UGCA 442), and 3.91 Mpc (NGC 7793). The
galaxies are concentrated in several spatially separated loose groups around
NGC 300, NGC 253, and NGC 7793. The Sculptor galaxy complex together with
the CVn I cloud and the Local Group form a 10 Mpc filament, apparently
driven by the free Hubble flow.
Key words: galaxies: dwarf - galaxies: distances and redshifts - galaxies: kinematics and dynamics
The association of five bright spiral galaxies in the Sculptor constellation,
NGC 55, NGC 247, NGC 253, NGC 300, and NGC 7793, has been considered by many
authors as the galaxy group closest to the Local Group (LG), at a distance of
![]() 2 Mpc. Over the past decades, a number of dwarf irregular galaxies
in this area have been found by van den Bergh (1959: DDO 6, DDO 226), Nilsen
(1974: UGCA 438, UGCA 442), and Lauberts (1982: ESO sky survey objects).
Special searches for fainter irregular (dIrr) and spheroidal (dSph)
dwarf galaxies in the Sculptor group were undertaken by Côté et al.
(1997), Karachentseva & Karachentsev (1998, 2000), and Jerjen et al. (1998, 2000). In their paper entitled,
"Discovery of numerous dwarf galaxies in the two nearest
groups of galaxies'', Côté et al. (1997) reported on the discovery of
five new dwarf members of the Sculptor group: Sc 2, Sc 18, Sc 22, Sc 24,
and Sc 42. However, all of them, except Sc 22, were found then to be
background galaxies (see the CCD images in Whiting et al. 2002),
whose H I velocities were confused with galactic high velocity clouds
in the velocity range from +60 to +160 km s-1. Recent H I surveys
of the Sculptor region by Staveley-Smith et al. (1998), Barnes et al. (2001),
de Blok et al. (2002) have not yet led to the discovery of new dwarf members
of the group. Jerjen et al. (1998) measured distances to five dwarf galaxies
in Sculptor from fluctuations of their surface brightness and showed that
the so-called "Sculptor group'' turns out to be a loose filament of galaxies
extended along a line of sight over
2 Mpc. Over the past decades, a number of dwarf irregular galaxies
in this area have been found by van den Bergh (1959: DDO 6, DDO 226), Nilsen
(1974: UGCA 438, UGCA 442), and Lauberts (1982: ESO sky survey objects).
Special searches for fainter irregular (dIrr) and spheroidal (dSph)
dwarf galaxies in the Sculptor group were undertaken by Côté et al.
(1997), Karachentseva & Karachentsev (1998, 2000), and Jerjen et al. (1998, 2000). In their paper entitled,
"Discovery of numerous dwarf galaxies in the two nearest
groups of galaxies'', Côté et al. (1997) reported on the discovery of
five new dwarf members of the Sculptor group: Sc 2, Sc 18, Sc 22, Sc 24,
and Sc 42. However, all of them, except Sc 22, were found then to be
background galaxies (see the CCD images in Whiting et al. 2002),
whose H I velocities were confused with galactic high velocity clouds
in the velocity range from +60 to +160 km s-1. Recent H I surveys
of the Sculptor region by Staveley-Smith et al. (1998), Barnes et al. (2001),
de Blok et al. (2002) have not yet led to the discovery of new dwarf members
of the group. Jerjen et al. (1998) measured distances to five dwarf galaxies
in Sculptor from fluctuations of their surface brightness and showed that
the so-called "Sculptor group'' turns out to be a loose filament of galaxies
extended along a line of sight over ![]() 5 Mpc.
5 Mpc.
In this paper we present new distance measurements for nine galaxies in the Sculptor region, derived from their tip of the red giant branch (TRGB). Together with earlier published TRGB distances to four other galaxies (Karachentsev et al. 2000, 2002) and the distance to NGC 300 from Cepheids (Freedman et al. 1992), this gives us a basis for a more detailed study of the structure of the Sculptor complex.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=12cm,clip]{Fig1.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg4.gif) |
Figure 1:
Digital Sky Survey images of 9 nearby galaxies in Sculptor.
The field size is 8
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
Images of nine galaxies were obtained with the Wide Field and Planetary
Camera (WFPC2) aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) between August 24,
1999 and June 28, 2001 as part of our HST snapshot survey of nearby galaxy
candidates (Seitzer et al. 1999; Grebel et al. 2000). The galaxies were
observed with 600-second exposures taken in the F606W and F814W filters
for each object. Digital Sky Survey (DSS) images of these galaxies are
shown in Fig. 1 with the HST WFPC2 footprints superimposed. The field size
of the red DSS-II images is 8
![]() .
Small galaxies were usually
centered on the WF3 chip, but for some bright objects the WFPC2
position was shifted towards the galaxy periphery to decrease
stellar crowding. The WFPC2 images of the galaxies are presented
in the upper panels of Fig. 2, where both filters are combined.
.
Small galaxies were usually
centered on the WF3 chip, but for some bright objects the WFPC2
position was shifted towards the galaxy periphery to decrease
stellar crowding. The WFPC2 images of the galaxies are presented
in the upper panels of Fig. 2, where both filters are combined.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=13.5cm,clip]{Fig2_1.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg5.gif) |
Figure 2: Top: WFPC2 images of nine galaxies: Sc 22, DDO 226, NGC 253, KDG 2, DDO 6, ESO 540-032, ESO 245-05, UGCA 442, and NGC 7793 produced by combining the two 600s exposures obtained through the F606W and F814W filters. The arrows point to the North and the East. Bottom left: The color-magnitude diagrams from the WFPC2 data for the nine galaxies in Sculptor. Bottom right: The Gaussian-smoothed I-band luminosity function restricted to red stars (top), and the output of an edge-detection filter applied to the luminosity function for the nine galaxies. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14.5cm,clip]{Fig2_2.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg6.gif) |
Figure 2: continued. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14.5cm,clip]{Fig2_3.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg7.gif) |
Figure 2: continued. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14.5cm,clip]{Fig2_4.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg8.gif) |
Figure 2: continued. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14.5cm,clip]{Fig2_5.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg9.gif) |
Figure 2: continued. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14.5cm,clip]{Fig2_6.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg10.gif) |
Figure 2: continued. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14.5cm,clip]{Fig2_7.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg11.gif) |
Figure 2: continued. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14.5cm,clip]{Fig2_8.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg12.gif) |
Figure 2: continued. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=14.5cm,clip]{Fig2_9.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg13.gif) |
Figure 2: continued. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
For photometric measurements we used the HSTphot stellar photometry
package developed by Dolphin (2000a). The package has been optimized
for the undersampled conditions present in the WFPC2 to work in
crowded fields. After removing cosmic rays,
simultaneous photometry was performed on the F606W and F814W frames
using multiphot, with corrections to an aperture with a
radius of
![]() .
Charge-transfer efficiency (CTE) corrections and
calibrations were then applied, which are based on the Dolphin (2000b)
formulae, producing V, I photometry for all stars detected in both
images. Additionally, stars with a signal-to-noise ratio S/N < 3,
.
Charge-transfer efficiency (CTE) corrections and
calibrations were then applied, which are based on the Dolphin (2000b)
formulae, producing V, I photometry for all stars detected in both
images. Additionally, stars with a signal-to-noise ratio S/N < 3,
![]() > 2.0, or
> 2.0, or ![]() sharpness
sharpness
![]() in each
exposure were eliminated from the final photometry list. The uncertainty
of the photometric zero point is estimated to be within
in each
exposure were eliminated from the final photometry list. The uncertainty
of the photometric zero point is estimated to be within
![]() (Dolphin 2000b).
(Dolphin 2000b).
The tip of red giant branch (TRGB) method provides an efficient tool
to measure galaxy distances. The TRGB distances agree with those given by
the Cepheid period-luminosity relation to within 5%. As shown by
Lee et al. (1993), the TRGB is relatively independent
of age and metallicity. In the I band the TRGB for low-mass stars
is found to be stable within ![]()
![]() (Salaris & Cassisi 1997;
Udalski et al. 2001) for metallicities, [Fe/H], encompassing the entire
range from -2.1 to -0.7 dex found in galactic globular clusters.
According to Da Costa & Armandroff (1990), for metal-poor systems the TRGB
is located at
(Salaris & Cassisi 1997;
Udalski et al. 2001) for metallicities, [Fe/H], encompassing the entire
range from -2.1 to -0.7 dex found in galactic globular clusters.
According to Da Costa & Armandroff (1990), for metal-poor systems the TRGB
is located at
![]() .
Ferrarese et al. (2000) calibrated the
zero point of the TRGB from galaxies with Cepheid distances and estimated
.
Ferrarese et al. (2000) calibrated the
zero point of the TRGB from galaxies with Cepheid distances and estimated
![]() .
A new TRGB calibration,
.
A new TRGB calibration,
![]() ,
was made by Bellazzini et al. (2001) based on
photometry and on the distance estimate from a detached eclipsing binary in the
galactic globular cluster
,
was made by Bellazzini et al. (2001) based on
photometry and on the distance estimate from a detached eclipsing binary in the
galactic globular cluster ![]() Centauri. For this paper we use
Centauri. For this paper we use
![]() .
The lower left panels of Fig. 2 show
I, (V-I) color-magnitude diagrams (CMDs) for the nine
observed galaxies.
.
The lower left panels of Fig. 2 show
I, (V-I) color-magnitude diagrams (CMDs) for the nine
observed galaxies.
Table 1: New distances to galaxies in Sculptor region.
We determined the TRGB using a Gaussian-smoothed I-band luminosity
function (LF) for red stars with colors V-I within
![]() of the mean
of the mean
![]() expected for red giant branch stars. Following
Sakai et al. (1996), we applied a Sobel edge-detection filter.
The position of the TRGB was identified with the peak in the
filter response function. The resulting LFs and the Sobel-filtered LFs
are shown in the lower right corners of Fig. 2. The results are
summarized in Table 1. There we list:
(1) galaxy name; (2) equatorial coordinates of the galaxy center;
(3) galaxy major diameter and axial ratio; (4) apparent integrated blue
magnitude from the NASA Extragalactic Database (NED) and galactic
extinction in the B-band from Schlegel et al. 1998; (5) morphological
type in de Vaucouleurs' notation; (6) heliocentric radial velocity and
radial velocity with respect to the LG centroid
(Karachentsev & Makarov 1996); (7) position of the TRGB and its
uncertainty as derived with the Sobel filter; (9) true distance modulus
with its uncertainty, which takes into account the uncertainty in the TRGB,
as well as uncertainties of the HST photometry zero point (
expected for red giant branch stars. Following
Sakai et al. (1996), we applied a Sobel edge-detection filter.
The position of the TRGB was identified with the peak in the
filter response function. The resulting LFs and the Sobel-filtered LFs
are shown in the lower right corners of Fig. 2. The results are
summarized in Table 1. There we list:
(1) galaxy name; (2) equatorial coordinates of the galaxy center;
(3) galaxy major diameter and axial ratio; (4) apparent integrated blue
magnitude from the NASA Extragalactic Database (NED) and galactic
extinction in the B-band from Schlegel et al. 1998; (5) morphological
type in de Vaucouleurs' notation; (6) heliocentric radial velocity and
radial velocity with respect to the LG centroid
(Karachentsev & Makarov 1996); (7) position of the TRGB and its
uncertainty as derived with the Sobel filter; (9) true distance modulus
with its uncertainty, which takes into account the uncertainty in the TRGB,
as well as uncertainties of the HST photometry zero point (![]()
![]() ),
the aperture corrections (
),
the aperture corrections (![]()
![]() ), and the crowding effects
(
), and the crowding effects
(![]()
![]() )
added quadratically; the uncertainties in the extinction and
reddening are taken to be 10% of their values from Schlegel et al. (1998);
(for more details on the total budget of internal and external systematic
errors for the TRGB method see Mendez et al. 2002); and (9) linear distance
in Mpc and its uncertainty.
)
added quadratically; the uncertainties in the extinction and
reddening are taken to be 10% of their values from Schlegel et al. (1998);
(for more details on the total budget of internal and external systematic
errors for the TRGB method see Mendez et al. 2002); and (9) linear distance
in Mpc and its uncertainty.
Given the distance moduli of the galaxies, we can estimate their
mean metallicity from the mean color of the TRGB measured at an
absolute magnitude
MI = -3.5, as recommended by Da Costa & Armandroff
(1990). Based on a Gaussian fit to the color distribution of the giant
stars in a corresponding I-magnitude interval
![]() ,
we derived
their mean colors,
(V - I)-3.5, which lie in the range of 1.18 mag to
1.54 mag
after correction for galactic reddening. Following the relation of Lee et al.
(1993), this provides us with mean metallicities
-1.1 dex
,
we derived
their mean colors,
(V - I)-3.5, which lie in the range of 1.18 mag to
1.54 mag
after correction for galactic reddening. Following the relation of Lee et al.
(1993), this provides us with mean metallicities
-1.1 dex ![]() [Fe/H]
[Fe/H]
![]() dex,
listed in the last column of Table 1. With a typical statistical scatter
of the mean color (
dex,
listed in the last column of Table 1. With a typical statistical scatter
of the mean color (![]()
![]() ), and uncertainties of the HST photometry
zero point we expect the uncertainty in metallicity to be about 0.3 dex.
Therefore within the measurement accuracy the metallicity of the galaxies
satisfy the required limitation, [Fe/H] < -0.7 dex. Below, some
individual properties of the galaxies are briefly discussed.
), and uncertainties of the HST photometry
zero point we expect the uncertainty in metallicity to be about 0.3 dex.
Therefore within the measurement accuracy the metallicity of the galaxies
satisfy the required limitation, [Fe/H] < -0.7 dex. Below, some
individual properties of the galaxies are briefly discussed.
Sc 22. This dwarf spheroidal galaxy of very low surface brightness
was discovered by Côté et al. (1997). Surface photometry of Sc 22
was carried
out by Jerjen et al. (1998, 2000), who determined its integrated apparent
magnitude, BT = 17.73 mag, integrated color, (B-R)T = 0.79 mag, and
central
surface brightness,
![]() in the B band. Using the method of
surface
brightness fluctuations (SBF), they estimated the distance to Sc 22 to be
2.67
in the B band. Using the method of
surface
brightness fluctuations (SBF), they estimated the distance to Sc 22 to be
2.67 ![]() 0.16 Mpc. The galaxy was not detected in the H I line by
Côté et al. (1997), neither was it detected in the "blind'' HIPASS survey
by Staveley-Smith et al. (1998) and Barnes et al. (2001). The color-magnitude
diagram of Sc 22 (see Fig. 2) is populated predominantly by red stars.
The application of the Sobel filter yields I(TRGB) =
0.16 Mpc. The galaxy was not detected in the H I line by
Côté et al. (1997), neither was it detected in the "blind'' HIPASS survey
by Staveley-Smith et al. (1998) and Barnes et al. (2001). The color-magnitude
diagram of Sc 22 (see Fig. 2) is populated predominantly by red stars.
The application of the Sobel filter yields I(TRGB) =
![]() ,
which corresponds to a linear distance of 4.21
,
which corresponds to a linear distance of 4.21 ![]() 0.43 Mpc. This is
much larger than the SBF distance.
0.43 Mpc. This is
much larger than the SBF distance.
DDO 226 = IC 1574 = UGCA 9. This dIrr galaxy has a relatively
high radial velocity,
![]() = 408 km s-1. The CMD of DDO 226 shows
blue and red stellar populations. Due to large number of red stars, which
probably belong to the asymptotic giant branch (AGB), the location of the
TRGB is determined with a low level
of confidence. According to the data in Fig. 2, I(TRGB) = 24
= 408 km s-1. The CMD of DDO 226 shows
blue and red stellar populations. Due to large number of red stars, which
probably belong to the asymptotic giant branch (AGB), the location of the
TRGB is determined with a low level
of confidence. According to the data in Fig. 2, I(TRGB) = 24
![]() ,
which yields a linear distance of 4.92
,
which yields a linear distance of 4.92 ![]() 0.58 Mpc.
0.58 Mpc.
NGC 253. NGC 253 is the brightest galaxy in the Sculptor group.
With a size of 27
![]() ,
NGC 253 extends far beyond
the WFPC2 field. Surprisingly, this prominent Sc galaxy has so far no
reliable distance estimate, apart from a rough estimate of D = 2.77 Mpc
derived by Puche & Carignan (1988) from the Tully-Fisher relation.
In our HST observations the WFPC2 was pointed to the NE part of the
galaxy, where stellar the crowding is lower. The HST photometry detects
a total of about 27 000 stars, mostly of red colors. The TRGB is located at
I = 23
,
NGC 253 extends far beyond
the WFPC2 field. Surprisingly, this prominent Sc galaxy has so far no
reliable distance estimate, apart from a rough estimate of D = 2.77 Mpc
derived by Puche & Carignan (1988) from the Tully-Fisher relation.
In our HST observations the WFPC2 was pointed to the NE part of the
galaxy, where stellar the crowding is lower. The HST photometry detects
a total of about 27 000 stars, mostly of red colors. The TRGB is located at
I = 23
![]() ,
corresponding to a distance of 3.94
,
corresponding to a distance of 3.94 ![]() 0.37 Mpc.
With this distance, the resulting absolute integrated magnitude of NGC 253,
MB = -20.14 mag, turns out to be comparable with the absolute magnitudes of
the Milky Way and other brightest members of the nearest groups.
0.37 Mpc.
With this distance, the resulting absolute integrated magnitude of NGC 253,
MB = -20.14 mag, turns out to be comparable with the absolute magnitudes of
the Milky Way and other brightest members of the nearest groups.
KDG 2 = ESO 540-030 = KK 09. This dSph galaxy of low surface
brightness was found by Karachentseva (1968) and then selected as
the Local Volume member candidate by Karachentseva & Karachentsev (1998).
According to the surface photometry carried out by Jerjen et al. (1998,
2000), KDG 2 has an integrated magnitude of BT = 16.37 mag, an integrated
color of (B-R)T = 0.83 mag, and a central surface brightness of
24.1
![]() in the B-band. Jerjen et al. (1998) determined its
distance via SBF to be 3.19
in the B-band. Jerjen et al. (1998) determined its
distance via SBF to be 3.19 ![]() 0.13 Mpc. The HST photometry detects
about 1900 predominantly red stars. We derived the TRGB to be located at
0.13 Mpc. The HST photometry detects
about 1900 predominantly red stars. We derived the TRGB to be located at
![]() ,
which corresponds to D = 3.40
,
which corresponds to D = 3.40 ![]() 0.34 Mpc, in good
agreement with the previous estimate. Apart from red stars, we also found
a number of blue stars, which occupy the central part of the galaxy.
Probably, KDG 2 is not a dSph galaxy, but belongs to a transition
dSph/dIrr type, like LGS-3 and Antlia. Huchtmeier et al. (2000) did not
detect it in the H I line.
0.34 Mpc, in good
agreement with the previous estimate. Apart from red stars, we also found
a number of blue stars, which occupy the central part of the galaxy.
Probably, KDG 2 is not a dSph galaxy, but belongs to a transition
dSph/dIrr type, like LGS-3 and Antlia. Huchtmeier et al. (2000) did not
detect it in the H I line.
DDO 6 = UGCA 15 = ESO 540-031. This dIrr galaxy of drop-like shape
has a radial velocity of
![]() = 348 km s-1. In Fig. 2 the CMD
shows the presence of mixed blue and red populations, in particular,
a prominent population
of RGB stars. We determined I(TRGB) to be
= 348 km s-1. In Fig. 2 the CMD
shows the presence of mixed blue and red populations, in particular,
a prominent population
of RGB stars. We determined I(TRGB) to be
![]() ,
yielding
D = 3.34
,
yielding
D = 3.34 ![]() 0.24 Mpc.
0.24 Mpc.
ESO 540-032 = FG 24 = KK 10. Like KDG 2, FG 24 (Feitzinger & Galinski
1985) has a reddish color and a low surface brightness, typical of dSph
or dSph/dIrr galaxies. The galaxy was not detected in H I by Huchtmeier
et al. (2000). Surface photometry of FG 24, performed by Jerjen et al. (1998,
2000), yields an integrated magnitude of BT = 16.44 mag, an integrated color
(B-R)T = 1.08 mag, and a central surface brightness 24.5
![]() in the B-band. Most of the stars detected by us in FG 24 (see Fig. 2) are
likely RGB stars, although some faint blue stars are present in the galaxy's
central
part. The TRGB I-band magnitude derived by us,
in the B-band. Most of the stars detected by us in FG 24 (see Fig. 2) are
likely RGB stars, although some faint blue stars are present in the galaxy's
central
part. The TRGB I-band magnitude derived by us,
![]() ,
corresponds to a distance
of 3.42
,
corresponds to a distance
of 3.42 ![]() 0.27 Mpc, which exceeds the distance 2.21
0.27 Mpc, which exceeds the distance 2.21 ![]() 0.14 Mpc
estimated by Jerjen et al. (1998) from SBF, but agrees excellently with
the new distance estimate, 3.4
0.14 Mpc
estimated by Jerjen et al. (1998) from SBF, but agrees excellently with
the new distance estimate, 3.4 ![]() 0.2 Mpc, obtained by Jerjen & Rejkuba
(2001) from the TRGB.
0.2 Mpc, obtained by Jerjen & Rejkuba
(2001) from the TRGB.
ESO 245-005. This irregular galaxy of Magellanic type has an angular
dimension of
![]()
![]()
![]() and a radial velocity of
and a radial velocity of
![]() = 308 km s-1. In
the WFPC2 image of its central bar-like part we detected about 11 000 blue and red stars. We determined the I-band TRGB to be at
24
= 308 km s-1. In
the WFPC2 image of its central bar-like part we detected about 11 000 blue and red stars. We determined the I-band TRGB to be at
24
![]()
![]()
![]() ,
yielding a distance of 4.43
,
yielding a distance of 4.43 ![]() 0.45 Mpc.
0.45 Mpc.
UGCA 442 = ESO 471-06. This is an edge-on galaxy of Im type with a
radial velocity
![]() = 299 km s-1 and angular dimension
6
= 299 km s-1 and angular dimension
6
![]() ,
much larger than the WFPC2 field. The galaxy seems to be well resolved
into stars. Our HST photometry reveals about 5600 stars, both blue and red
ones. The derived TRGB,
,
much larger than the WFPC2 field. The galaxy seems to be well resolved
into stars. Our HST photometry reveals about 5600 stars, both blue and red
ones. The derived TRGB,
![]() ,
corresponds to a distance
of 4.27
,
corresponds to a distance
of 4.27 ![]() 0.52 Mpc.
0.52 Mpc.
NGC 7793. This is a bright spiral galaxy with a dimension of
9
![]() and with a radial velocity
and with a radial velocity
![]() = 252 km s-1. The WFPC2 was pointed
at its eastern side. There are about 22 000 stars detected by us in both the
filters. The CMD shows a mixture of young and old stellar populations.
The TRGB magnitude, 23
= 252 km s-1. The WFPC2 was pointed
at its eastern side. There are about 22 000 stars detected by us in both the
filters. The CMD shows a mixture of young and old stellar populations.
The TRGB magnitude, 23
![]() ,
yields a galaxy distance of
3.91
,
yields a galaxy distance of
3.91 ![]() 0.41 Mpc, in satisfactory agreement with the distance 3.27
0.41 Mpc, in satisfactory agreement with the distance 3.27 ![]() 0.08 Mpc
derived by Puche & Carignan (1988) from the Tully-Fischer relation.
0.08 Mpc
derived by Puche & Carignan (1988) from the Tully-Fischer relation.
Table 2: List of 21 nearby galaxies in the Sculptor group region.
To study the 3D structure of the Sculptor complex, we collected the most complete sample of data on all known nearby galaxies situated in this sky region. Table 2 presents the following characteristics of the 21 galaxies of our sample: (1) galaxy name; (2) equatorial (upper line), and Supergalactic (lower line) coordinates; (3) major angular diameter in arcmin and apparent axial ratio; (4) apparent integrated magnitude from NED and galactic extinction from Schlegel et al. (1998) in the B-band; (5) morphological type; (6) heliocentric radial velocity in km s-1 and velocity in the Local Group rest frame (Karachentsev & Makarov 1996); (7) the H I line width (in km s-1) at the 50% level of the maximum from LEDA (Paturel et al. 1996) or HIPASS, corrected for galaxy inclination (upper line), and absolute magnitude of the galaxy, corrected for galactic extinction (lower line); (8) distance to the galaxy in Mpc from the Milky Way (upper line), and from the Local Group centroid (lower line), respectively. The last column gives the method used for distance measurement ("Cep'' - from Cepheids, "RGB'' - from TRGB, "SBF'' - from surface brightness fluctuations, and "TF'' - from the Tully-Fisher relation), and the distance data reference.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=12cm,clip]{Fig3.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg54.gif) |
Figure 3: Sky distribution of nearby galaxies in the direction of the Sculptor group. Filled and open circles indicate dwarf irregular and dwarf spheroidal galaxies, respectively. Large squares correspond to the most luminous galaxy in each group. Their probable companions are connected to the principal galaxies with straight lines. Radial velocities of the galaxies relative to the Local Group centroid are indicated by small numbers. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Apart from four dSph galaxies with known distances but unknown radial velocities (KK 3, Sc 22, KDG 2, and FG 24), we included in Table 2 also a low surface brightness galaxy KK 258 with unknown distance and velocity, which looks like a nearby semi-resolved system at CCD image derived by Whiting et al. (2002). In comparison with the TRGB distances, the distance estimates of Sc 22, KDG 2 and FG 24 from SBF (Jerjen et al. 1998) have systematically lower distances, which is why we corrected their original SBF distance to NGC 59, D = 4.4 Mpc, by +0.9 Mpc.
Table 3: Properties of nearby groups in Sculptor.
The distribution of the 21 galaxies from Table 2 is presented in Fig. 3 in
equatorial coordinates. Three of the brightest spiral galaxies are shown
as filled squares, and dIrr and dSph galaxies are shown as filled and
open circles, respectively. Radial velocities of the galaxies with respect
to the LG centroid are indicated by numbers. As can be seen, the distribution
of galaxies in Sculptor exhibits the absence of any distinct center, and
it does not show a sharp boundary either.
Most of the galaxies are situated at low supergalactic latitudes,
![]() SGB
SGB![]()
![]() ,
where projection effects makes it difficult
to restore the 3-D structure of the group. Referring to Table 3, we
recognize that the spiral galaxy NGC 253 surpasses all
other galaxies in this group by more than a factor of five in
luminosity. Therefore, we consider NGC 253 as the
dynamical center of the Sculptor group.
,
where projection effects makes it difficult
to restore the 3-D structure of the group. Referring to Table 3, we
recognize that the spiral galaxy NGC 253 surpasses all
other galaxies in this group by more than a factor of five in
luminosity. Therefore, we consider NGC 253 as the
dynamical center of the Sculptor group.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=12cm,clip]{Fig4.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg63.gif) |
Figure 4: Tully-Fisher relation for eight galaxies in Sculptor with accurate distances. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Puche & Carignan (1988) estimated the distance to NGC 253 and some other
galaxies in Sculptor, based on the Tully-Fisher relation. However, for
its calibration, they used old data on galaxy distances. A revised relation
"absolute magnitude - H I line width'' for 6 galaxies in Sculptor
with new distance estimates is presented in Fig. 4. Here, the line width is
corrected for galaxy inclination to the line of sight. Using the regression
line,
MB = -7.0 log
![]() ,
we estimated the distances to five
galaxies:
NGC 55, NGC 247, NGC 625, ESO 349-031, and ESO 149-03, presented in
Col. 8 of Table 2.
,
we estimated the distances to five
galaxies:
NGC 55, NGC 247, NGC 625, ESO 349-031, and ESO 149-03, presented in
Col. 8 of Table 2.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=13cm,clip]{Fig5.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg66.gif) |
Figure 5:
Radial velocity-distance relation for 20 nearby galaxies
in Sculptor. The galaxies with accurate distance estimates are shown
as filled circles, and galaxies with T-F distances are shown as
crosses. Four dSph galaxies without radial velocities are indicated
by vertical bars. The brightest galaxy, NGC 253, is indicated by a square.
The solid line corresponds to the Hubble relation with H = 75 km s-1 Mpc-1,
curved at small distances assuming a decelerating gravitational action
of the Local Group with a total mass of
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
The Hubble diagram showing velocity versus distance for 20 galaxies
in Sculptor
is given in Fig. 5. Galaxies with accurate distance estimates ("Cep'',
"RGB"'', "SBF'') are shown as filled circles, while galaxies with distances
from the T-F relation are indicated by crosses, and the brightest spiral
galaxy NGC 253 is shown as a square. Four dSph galaxies without velocities
are shown conditionally by vertical bars. The solid line corresponds
to the Hubble parameter H = 75 km s-1 Mpc-1. At small distances the line
deviates from a straight line due to a decelerating gravitational action
of the Local Group, the total mass of which is adopted to be
![]() (Karachentsev et al. 2002).
(Karachentsev et al. 2002).
Based on the data in Figs. 3 and 5, we can describe the structure of the galaxy complex in Sculptor in the following way.
a) Three galaxies with
![]() 400 km s-1 (ESO 149-03, NGC 59, and DDO 226)
apparently are background objects. NGC 59 and DDO 226 probably form
a wide pair with a linear projected distance of 580 kpc and a radial
velocity difference of 13 km s-1.
400 km s-1 (ESO 149-03, NGC 59, and DDO 226)
apparently are background objects. NGC 59 and DDO 226 probably form
a wide pair with a linear projected distance of 580 kpc and a radial
velocity difference of 13 km s-1.
b) In front of the complex there is a pair of bright galaxies, NGC 300 and NGC 55, with two dSph companions, ESO 410-05 and ESO 294-10. The mean distance to this loose quartet is 1.95 Mpc. This is only 0.6 Mpc more distant than to another known loose quartet: NGC 3109, Sex A, Sex B, and Antlia, located at the LG edge. Possibly, two other dIrr galaxies, UGCA 438 and IC 5152, are associated with the NGC 300 group, too.
c) The brightest spiral galaxy NGC 253 together with its companions, NGC 247, DDO 6, Sc 22, KDG 2 and FG 24, can be considered as the Sculptor complex' core. The last three dSph galaxies do not have radial velocities so far. Apart from the NGC 253 group, there is a galaxy triplet, NGC 7793, UGCA 442, and ESO 349-031. The radial distances of NGC 253 and NGC 7793 are almost the same within the measurement errors.
d) Among the remaining galaxies, NGC 625 and ESO 245-05 have an angular
separation of 2![]() and a radial velocity difference of only 27 km s-1.
However, their distance estimates differ significantly. Because
NGC 625 deviates essentially from the Hubble regression line in Fig. 5,
we assume its T-F distance to be underestimated by approximately 2 Mpc.
This assumption can be easily proven by measuring the TRGB distance
to this poorly studied galaxy.
and a radial velocity difference of only 27 km s-1.
However, their distance estimates differ significantly. Because
NGC 625 deviates essentially from the Hubble regression line in Fig. 5,
we assume its T-F distance to be underestimated by approximately 2 Mpc.
This assumption can be easily proven by measuring the TRGB distance
to this poorly studied galaxy.
The total mass of each group can be estimated from the virial balance
of kinetic and potential energies (Limber & Mathews 1960),
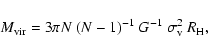 |
(1) |
Another way to estimate the total mass of group was proposed by
Bahcall & Tremaine (1981). Assuming the motions of dwarf galaxies around the
main group member to be closed Keplerian motions with orbit eccentricity
e, in the case of random orientation of galaxy orbits we obtain
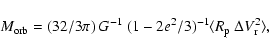 |
(2) |
The basic dynamical parameters of the three mentioned groups in Sculptor
are presented in Table 3. In the case of orbital mass estimates the mean
eccentricity e= 0.7 is adopted. As seen from these data, the
virial/orbital mass-to-luminosity ratios of the groups lie in the range
of 45 to 260
![]() .
However, for all the groups their crossing
time, 6-18 Gyr, is comparable to the time of cosmic expansion, 1/H0,
which makes the derived mass estimates too unreliable.
.
However, for all the groups their crossing
time, 6-18 Gyr, is comparable to the time of cosmic expansion, 1/H0,
which makes the derived mass estimates too unreliable.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=13cm,clip]{Fig6.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/22/aa3395/Timg78.gif) |
Figure 6: The distribution of the radial velocity difference and of the space distance of nearby galaxies with respect to NGC 253. These data yield a radius of the zero-velocity surface of R0= 0.7 Mpc. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
According to Lynden-Bell (1981) and Sandage (1986), in the expanding
universe any dense enough group with a total mass M0 may be
characterized by a "zero-velocity surface'', which separates the group
from the Hubble flow. In the case of spherical symmetry, the radius of
this surface, R0, is expressed via the total mass of the group and
the Hubble constant, H0, by a simple relation
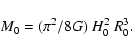 |
(3) |
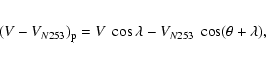
Measurements of accurate distances to 9 galaxies in Sculptor led to
essential clarifying of the structure and kinematics of this nearby complex
of galaxies. However, nine other presumably nearby galaxies in the same area
(with
![]() 500 km s-1 or D < 5 Mpc) still remain without reliable
distance estimates (NGC 55, NGC 625, NGC 247, SDIG, and ESO 149-03)
or radial velocity estimates (ESO 410-05, KDG 2, FG 24, and Sc 22).
Our new data on galaxy distances confirm the conclusion drawn by Jerjen
et al. (1998) that the so-called group in Sculptor is a loose
"cloud'' of galaxies of 1
500 km s-1 or D < 5 Mpc) still remain without reliable
distance estimates (NGC 55, NGC 625, NGC 247, SDIG, and ESO 149-03)
or radial velocity estimates (ESO 410-05, KDG 2, FG 24, and Sc 22).
Our new data on galaxy distances confirm the conclusion drawn by Jerjen
et al. (1998) that the so-called group in Sculptor is a loose
"cloud'' of galaxies of 1 ![]() 6 Mpc in size, extended along the line of sight.
Apparently, the near and the far parts of this "cigar'' are not gravitationally
bound each other, but take part in the general Hubble flow. In this sense, the
Sculptor cloud looks like another nearby cloud, Canes Venatici I
(Karachentsev et al. 2003b). Both these loose clouds are populated mostly
by dwarf galaxies, and their luminosity function has a flat "primordial''
shape. As seen from Fig. 7 in Karachentsev et al. (2003a), the Galaxy
complexes in Sculptor and Canes Venatici together with the Local Group
form a filament extending over
6 Mpc in size, extended along the line of sight.
Apparently, the near and the far parts of this "cigar'' are not gravitationally
bound each other, but take part in the general Hubble flow. In this sense, the
Sculptor cloud looks like another nearby cloud, Canes Venatici I
(Karachentsev et al. 2003b). Both these loose clouds are populated mostly
by dwarf galaxies, and their luminosity function has a flat "primordial''
shape. As seen from Fig. 7 in Karachentsev et al. (2003a), the Galaxy
complexes in Sculptor and Canes Venatici together with the Local Group
form a filament extending over ![]() 10 Mpc.
10 Mpc.
The nearby galaxy complex in Sculptor seems to us a suitable case to study
the "anatomy'' of virial mass excess. In projection onto the sky, the Sculptor
filament has a rather high overdensity, and can be easely identified
as a usual group by the "friend of friends'' algorithm
(Huchra & Geller 1982) or by the method of hierarchical trees (Materne 1978).
In his Nearby Galaxy Catalog, Tully (1988) denotes the Sculptor group by
the number "14-13''. Based on radial velocities and projected separations
of 11 members of the group, Tully (1987) estimated its virial
mass-to-luminosity ratio to be
![]() .
There the
galaxies NGC 55, NGC 253, NGC 7793, and DDO 226 were considered as
members of a single group. Apart from real and probable members of the
Sculptor complex, Tully included in the group also the galaxy PGC 71145, whose
radial velocity is +16 km s-1 (instead of +1600 km s-1 as a result of
a misprint in Longmore et al. 1982). Comparing the ratio
.
There the
galaxies NGC 55, NGC 253, NGC 7793, and DDO 226 were considered as
members of a single group. Apart from real and probable members of the
Sculptor complex, Tully included in the group also the galaxy PGC 71145, whose
radial velocity is +16 km s-1 (instead of +1600 km s-1 as a result of
a misprint in Longmore et al. 1982). Comparing the ratio
![]() from Tully (1987) with our estimate of the total mass-to-luminosity ratio,
29
from Tully (1987) with our estimate of the total mass-to-luminosity ratio,
29 ![]() 11
11
![]() ,
we conclude that the usage of the more reliable
and precise
observational data that are now available, as well as our new approach to
the determination of mass
can decrease the total mass estimate of the group by one order of magnitude.
,
we conclude that the usage of the more reliable
and precise
observational data that are now available, as well as our new approach to
the determination of mass
can decrease the total mass estimate of the group by one order of magnitude.
Acknowledgements
Support for this work was provided by NASA through grant GO-08601.01-A from the Space Telescope Science Institute, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., under NASA contract NAS5-26555. This work was partially supported by RFBR grant 01-02-16001 and DFG-RFBR grant 02-02-04012. D.G. gratefully acknowledges support from the Chile Centro de Astrofísica FONDAP No. 15010003.The Digitized Sky Surveys were produced at the Space Telescope Science Institute under U.S. Government grant NAG W-2166. The images of these surveys are based on photographic data obtained using the Oschin Schmidt Telescope on the Palomar Mountain and the UK Schmidt Telescope. The plates were processed into the present compressed digital form with permission of these institutions.
This project made use of the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED), which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Caltech, under contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.