A&A 403, 587-591 (2003)
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20030418
The metallicity range of variables in M 3
J. Jurcsik
Konkoly Observatory of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences,
PO Box 67, 1525 Budapest, Hungary
Received 3 December 2002 / Accepted 13 March 2003
Abstract
The recently published spectroscopic metallicities of RR Lyrae
stars in M 3 (Sandstrom et al. 2001) show a relatively wide range of the
measured [Fe/H] values.
As no dependence of the metallicities on either minimum temperature or period
was found,
they concluded that no real metallicity spread was detected.
Comparing these spectroscopic metallicities with the [Fe/H] values
calculated from the Fourier parameters of the light curves of the variables
a correlation between the results of the two metallicity determinations emerges.
As a consequence of the complete independence of the spectroscopic and
photometric metallicities, this correlation points to a real
metallicity spread in M 3.
The absolute magnitudes of the variables follow a similar trend
with both the spectroscopic and photometric metallicities as the
general
![$M_V - {\rm [Fe/H]}$](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/img5.gif) relation predicts.
This fact supports that the detected range in the metallicities of the
variables is real.
relation predicts.
This fact supports that the detected range in the metallicities of the
variables is real.
Key words: globular clusters: individual: M 3 -
stars: abundances -
stars: variables: RR Lyr -
stars: horizontal-branch -
stars: population II
Nearly every globular cluster contains stars of homogeneous metallicity.
The most prominent exception is 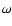 Cen with its considerably large,
Cen with its considerably large,
 1 dex spread in the [Fe/H] content of giants and subgiants.
Slight [Fe/H] inhomogeneity in M 92 (King et al. 1998; Langer et al. 1998) has also
been detected. Concerning the other elemental abundances, detailed chemical
composition analysis of globular cluster stars have revealed that complicate
patterns of abundance inhomogeneity exist in many clusters.
1 dex spread in the [Fe/H] content of giants and subgiants.
Slight [Fe/H] inhomogeneity in M 92 (King et al. 1998; Langer et al. 1998) has also
been detected. Concerning the other elemental abundances, detailed chemical
composition analysis of globular cluster stars have revealed that complicate
patterns of abundance inhomogeneity exist in many clusters.
M 3 is one of the reference clusters of the globular cluster metallicity scale.
Spectroscopically, [Fe/H] has been already derived from high
dispersion studies of about 10 giant stars (Bell & Dickens 1980; Kraft et al. 1992; Cavallo & Nagar 2000; Kraft & Ivans 2002)
which do not show any evidence of a [Fe/H] spread.
The latest result gives an average [Fe/H] value of -1.5 dex
on a metallicity scale based on measurements of FeII lines in order to
avoid the non-negligible bias of
overionization effects in FeI lines (Kraft & Ivans 2002). The first spectroscopic
data on direct [Fe/H] measurements of the cluster RR Lyrae variables
have been recently published by Sandstrom et al. (2001, hereafter SPS).
Using moderate resolution spectra taken with the Hydra
multifiber spectrograph they conclude that the RR Lyrae variables are
also uniform in composition as no dependence on either minimum temperature
or period can be found based on data of 29 RR Lyrae
variables. Although the scatter in SPS's [Fe/H] values
(
![${\rm [Fe/H]_{mean}}=-1.43, s.dev.=\pm 0.12$](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/img8.gif) and
and
![${\rm [Fe/H]_{mean}}=-1.21, s.dev.=\pm 0.22$](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/img9.gif) from FeI and FeII lines, respectively) can be explained by uncertainties of
model parameters and equivalent widths, it does not exclude the possibility
of some real star to star [Fe/H] abundance differences either.
from FeI and FeII lines, respectively) can be explained by uncertainties of
model parameters and equivalent widths, it does not exclude the possibility
of some real star to star [Fe/H] abundance differences either.
In Jurcsik & Kovács (1996) it has been shown that the [Fe/H] of RRab stars calculated from the period (P) and the 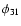 Fourier phase-difference of the light curve
is as accurate as most of the spectroscopic results.
With this formula the spectroscopic [Fe/H] of the 81 calibrating RRab stars
could be reproduced with 0.14 dex standard deviation.
Fourier phase-difference of the light curve
is as accurate as most of the spectroscopic results.
With this formula the spectroscopic [Fe/H] of the 81 calibrating RRab stars
could be reproduced with 0.14 dex standard deviation.
In a preliminary investigation it has been found that the
metallicities of the RRab stars in M 3 calculated according to this photometric
method show larger spread than expected if the [Fe/H] of the variables
is homogeneous (Bakos & Jurcsik 2000).
The aim of the present Paper is to check the reality of any possible [Fe/H]
inhomogeneity of the M 3 variables comparing their spectroscopic and
photometric metallicity values.
The two metallicity determination methods - namely, a) spectroscopic;
b) utilizing light curve parameters (photometric) -, are completely
independent,
therefore any correlation between these metallicities
would indicate that the observed metallicity spread is real.
During the last few years strong arguments were raised against metallicity
determinations using FeI lines (Lambert et al. 1996; Thévenin & Idiart 1999; Kraft & Ivans 2002) because of the non-negligible
departures from LTE in metal-poor stellar atmospheres resulting
overionization of iron. Based on these results for the comparison purposes
we use exclusively the
FeII metallicities of SPS, which have unexpectedly large, >0.6 dex range.
The signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of the spectroscopic observations
varies between 28 and 76 whereas the number of spectra (NS) of individual
stars are between 10 and 41. For V 9 both the S/N and NS have one of the
lowest values,
30 and 10, respectively. Therefore we have decided to omit this star from the
spectroscopic sample. The
![${\rm [Fe/H]_{FeII}=-0.87~dex}$](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/img11.gif) seems to be
unreliably large
for this star based on the comparison of its light curve with a large sample
of RRab light curves compiled in Jurcsik (1998).
A field RR Lyrae star (UW Gru) has been found to show light changes very
similar to M 3/V 9.
seems to be
unreliably large
for this star based on the comparison of its light curve with a large sample
of RRab light curves compiled in Jurcsik (1998).
A field RR Lyrae star (UW Gru) has been found to show light changes very
similar to M 3/V 9.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.5cm,clip]{H4268f1.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/Timg12.gif) |
Figure 1:
Phased V light curves of M 3/V 9 (dots) and UW Gru (crosses).
The magnitudes of UW Gru are shifted to match the magnitudes of M 3/V 9. The identity of the light curves' shapes indicates
close similarity of the objects that have similar periods and colours.
Consequently, no significant metallicity
difference between these stars can be real. |
| Open with DEXTER |
Figure 1 shows the phased light curves of M 3/V 9 and UW Gru using
the observations of Corwin & Carney (2001) and Benko et al. (2003) for M 3/V 9, and Bernard (1982) for UW Gru.
The light curves of these two stars
can be hardly separated, within photometric uncertainties they can be
regarded as identical. We suppose that such equality of the light
curves with similar pulsation periods can only happen if there is
no significant difference in any of the basic physical properties of the two
stars. The periods of these variables are very similar and their mean
colours are also the same within the range limited by the photometric
uncertainties as given in Table 1.
The metallicity of UW Gru was given as -1.68 dex in (Layden 1994)
which was transformed to -1.41 dex metallicity value on a common [Fe/H] scale used in Jurcsik & Kovács (1996). As a consequence of
the absolute equality of the light curves
of M 3/V 9 and UW Gru the spectroscopic
![${\rm [Fe/H]=-0.87~dex}$](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/img13.gif) value
cannot be correct for M 3/V 9. It validates our decision to omit V 9 from the
spectroscopic sample.
value
cannot be correct for M 3/V 9. It validates our decision to omit V 9 from the
spectroscopic sample.
Table 1:
Parameters of M 3/V 9 and UW Gru.
Reliable photometric [Fe/H] can be determined for 19 RRab stars among
the spectroscopic sample of SPS (29 stars). The following stars
are omitted:
- stars showing strong Blazhko modulation that makes
[Fe/H]
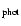 incorrect (V 20, V 39, V 52, V 61, V 63, V 66, V 78).
incorrect (V 20, V 39, V 52, V 61, V 63, V 66, V 78).
- no or poor quality published light curves are available (V 113, V 115).
- V 202, which cannot be regarded as a normal RRab star based on its
long period (0
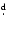 77), light curve shape, and low amplitude
(
77), light curve shape, and low amplitude
(
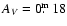 ).
).
In order to increase the small sample size
those Blazhko stars are also used in the comparison which
exhibit only slight light curve modulations (V 10, V 59 and V 62).
The small amplitude modulations are supposed not to
affect significantly the calculated
photometric metallicities.
For most of the stars photometries are available from different
sources.
In these cases the data have been merged with
necessary zero-point offsets (
0.01-0.05 mag) and a single
[Fe/H]
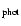 is calculated from the combined data set.
In each case the magnitude correction has been determined
relative to the Corwin & Carney (2001) data.
All the data have been cleaned from outlying points.
The large number of the photometric measurements (
is calculated from the combined data set.
In each case the magnitude correction has been determined
relative to the Corwin & Carney (2001) data.
All the data have been cleaned from outlying points.
The large number of the photometric measurements (
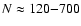 )
makes the separation of discrepant data unambiguous in
most of the cases.
The formal errors of the [Fe/H]
)
makes the separation of discrepant data unambiguous in
most of the cases.
The formal errors of the [Fe/H]
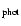 values are between 0.03 and 0.07 dex.
values are between 0.03 and 0.07 dex.
The spectroscopic and photometric metallicities, the intensity averaged
mean magnitudes according to Corwin & Carney (2001), and the used photometries
of the variables are listed in Table 2.
Table 2:
Spectroscopic and photometric metallicities and
observed mean magnitudes of the SPS RRab sample.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.4cm,clip]{H4268f2.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/Timg27.gif) |
Figure 2:
Spectroscopic vs. photometric [Fe/H] of 18 RRab stars in M 3.
Dotted lines are the direct and inverse linear regression fits to the data. The
correlation between the
spectroscopic and photometric metallicities seems to be significant.
As the two different measures of the metallicities are basically
independent, their correlation indicates that a metallicity range of
the M 3 variables is indeed detected. |
| Open with DEXTER |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{H4268f3.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/Timg28.gif) |
Figure 3:
Histogram of correlation coefficients (r) of 10 000 Monte-Carlo simulations
of 18 [Fe/H]
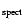 and
[Fe/H]
and
[Fe/H]
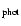 pairs.
a) No metallicity spread is assumed, the standard deviations of the data
are 0.22 and 0.13 dex, respectively.
b) The data range over 0.34 dex in metallicity with 0.18 and 0.11 dex
standard
deviations.
Arrows indicate the regression coefficient between the measured
spectroscopic and photometric metallicities.
pairs.
a) No metallicity spread is assumed, the standard deviations of the data
are 0.22 and 0.13 dex, respectively.
b) The data range over 0.34 dex in metallicity with 0.18 and 0.11 dex
standard
deviations.
Arrows indicate the regression coefficient between the measured
spectroscopic and photometric metallicities. |
| Open with DEXTER |
The final sample of stars with [Fe/H] reliably determined both
spectroscopically and photometrically
consists of a limited number of 18 variables.
Figure 2 shows these data, with the direct and inverse regression fits
overplotted.
The linear Pearson correlation coefficient between the two data sets is 0.54,
with 0.021 probability value. The small number of data
makes it difficult to estimate the statistical significance
of this result. Therefore, Monte-Carlo simulation has been performed
in order to decide whether
the correlation between the metallicities is real, or it is only
an artifact due to the large errors of the data.
The Monte-Carlo simulation was realized as follows.
Two artificial data sets were generated. First, the 0.22 and 0.13 dex
standard deviations of the [Fe/H]
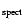 and [Fe/H]
and [Fe/H]
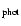 data were supposed to arise merely from the scatters of the observations
around a single metallicity value.
Secondly, it was assumed that a 0.34 dex [Fe/H] range was real, and the
standard deviations of the spectroscopic and photometric data were smaller,
0.18 and 0.11 dex, respectively (these values are the residual
scatters of the regressions, see Fig. 2).
In both cases 10 000 [Fe/H]
data were supposed to arise merely from the scatters of the observations
around a single metallicity value.
Secondly, it was assumed that a 0.34 dex [Fe/H] range was real, and the
standard deviations of the spectroscopic and photometric data were smaller,
0.18 and 0.11 dex, respectively (these values are the residual
scatters of the regressions, see Fig. 2).
In both cases 10 000 [Fe/H]
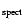 and [Fe/H]
and [Fe/H]
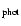 data sets with 18 elements were generated.
The histograms of the correlation coefficients (r) of the simulated data
sets are shown in Fig. 3. While the observed r=0.54 correlation
occurs marginally in case a,
it has significant occurrence frequency in case b.
We can therefore draw the conclusion that in our sample the r=0.54correlation is indeed significant.
data sets with 18 elements were generated.
The histograms of the correlation coefficients (r) of the simulated data
sets are shown in Fig. 3. While the observed r=0.54 correlation
occurs marginally in case a,
it has significant occurrence frequency in case b.
We can therefore draw the conclusion that in our sample the r=0.54correlation is indeed significant.
As the two metallicity determinations
are completely independent, the fact that a correlation between these quantities
is found points to the reality of the observed metallicity spread.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{H4268f4.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/Timg31.gif) |
Figure 4:
Absolute magnitudes versus spectroscopic and photometric metallicities of
M 3 RRab stars.
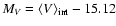 mag (Harris 1996).
Lines indicate one of the theoretical ZAHB relations (Caloi et al. 1997).
For the [Fe/H] mag (Harris 1996).
Lines indicate one of the theoretical ZAHB relations (Caloi et al. 1997).
For the [Fe/H]
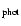 values at the different metallicities the
faintest stars (which are likely on the ZAHB) indicate a similar trend of MV with metallicity as expected, if the metallicity range is real.
The brightest star V 60 has the longest period (0.77 d) and possibly is already in
an evolved stage of the HB evolution. The second brightest among the spectroscopic
sample is V 202 which RR Lyrae classification is uncertain.
The less convincing evidence of an MV - [Fe/H] relation for the spectroscopic values
is possibly due to the larger errors in the [Fe/H]
values at the different metallicities the
faintest stars (which are likely on the ZAHB) indicate a similar trend of MV with metallicity as expected, if the metallicity range is real.
The brightest star V 60 has the longest period (0.77 d) and possibly is already in
an evolved stage of the HB evolution. The second brightest among the spectroscopic
sample is V 202 which RR Lyrae classification is uncertain.
The less convincing evidence of an MV - [Fe/H] relation for the spectroscopic values
is possibly due to the larger errors in the [Fe/H]
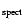 values.
values. |
| Open with DEXTER |
The metallicity dependence of the absolute magnitudes of horizontal
branch (HB) stars is well known, and is proven both from theoretical
and observational points of view. Although the uniqueness, the slope
and the zero point of this relation are still controversial,
the reality of the detected metallicity spread can be justified by
checking the connection between the measured absolute magnitudes and
metallicities of the variables.
A strict connection between the luminosities and metallicities of HB stars
is only valid for zero age HB (ZAHB) stars, as the luminosity of stars
evolving off the ZAHB sequence increases, and this results a true internal
scatter of any measured MV - [Fe/H] plot. The lower boundary of these
plots have to follow the MV - [Fe/H] relation valid for ZAHB stars
within the limits of the observational uncertainties.
It is stressed that the brightness of the stars has no influence on
either of the [Fe/H] determinations, which rules out any a priori
connection between the values. If the metallicity spread of the variables is
real, than the faintest magnitudes at the different
metallicities have to follow the global trend valid for ZAHB stars.
In Fig. 4 the absolute magnitudes
of the RRab sample are plotted versus their spectroscopic and photometric
metallicities. For the [Fe/H]
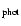 values, the faintest stars at different
metallicities follow the trend predicted by ZAHB models closely.
Selecting ZAHB stars from the photometric sample by taking into account only the two
faintest stars of each 0.1 dex [Fe/H] bins a correlation with
0.84 correlation coefficient and a 0.20 slope can be yield.
This slope agrees extremely well with the model predictions which
typically yield slopes within the 0.18-0.26 range.
values, the faintest stars at different
metallicities follow the trend predicted by ZAHB models closely.
Selecting ZAHB stars from the photometric sample by taking into account only the two
faintest stars of each 0.1 dex [Fe/H] bins a correlation with
0.84 correlation coefficient and a 0.20 slope can be yield.
This slope agrees extremely well with the model predictions which
typically yield slopes within the 0.18-0.26 range.
The less convincing result for the spectroscopic metallicities is possibly due
to the larger errors in the spectroscopic data.
This result provides further
evidence that a metallicity spread of about 0.3-0.4 dex of the M 3 RRab stars has
been in fact detected.
The statistically significant
correlation between the spectroscopic and photometric metallicities
of the RRab variables in M 3, which have  0.6, and 0.4 dex ranges, respectively,
leads to the conclusion
that a true spread in the metallicities of the variables exists.
This is in contrast with the strictly homogeneous iron content of the cluster
red giants, though, it is also worth noting that in an early study CaI overabundance of about 0.6 dex of a cluster giant (vZ1397) was found (Cohen 1978).
This result has been neither confirmed nor rejected still today.
Although some systematic difference between the
metallicity scales of the red giants and the variables
may exist,
the comparison of the observed metallicities
indicates that the variables show a metallicity range
spanning to about 0.3-0.4 dex more metal rich values.
0.6, and 0.4 dex ranges, respectively,
leads to the conclusion
that a true spread in the metallicities of the variables exists.
This is in contrast with the strictly homogeneous iron content of the cluster
red giants, though, it is also worth noting that in an early study CaI overabundance of about 0.6 dex of a cluster giant (vZ1397) was found (Cohen 1978).
This result has been neither confirmed nor rejected still today.
Although some systematic difference between the
metallicity scales of the red giants and the variables
may exist,
the comparison of the observed metallicities
indicates that the variables show a metallicity range
spanning to about 0.3-0.4 dex more metal rich values.
Spectroscopic observations and chemical composition determinations
of cluster variables, apart from some 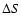 measurements showing
large scatter most probably due to observational errors,
exist only of two clusters,
measurements showing
large scatter most probably due to observational errors,
exist only of two clusters, 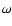 Cen and M 3.
In
Cen and M 3.
In 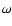 Cen as the iron abundances of the red giants have larger
than 1.0 dex range,
the result that the RR Lyrae metallicities are not homogeneous either
is not surprising.
It is important to repeat, however, that no spectroscopic
observations of any other globular cluster variables exist.
The photometric metallicities as compiled in Kovács & Walker (2001) show unaccountable
large scatter in many clusters where no metallicity
spread of red giants is observed. This warns that a similar
result, an observable metallicity spread of the variables
might possibly occur in other clusters as well.
Cen as the iron abundances of the red giants have larger
than 1.0 dex range,
the result that the RR Lyrae metallicities are not homogeneous either
is not surprising.
It is important to repeat, however, that no spectroscopic
observations of any other globular cluster variables exist.
The photometric metallicities as compiled in Kovács & Walker (2001) show unaccountable
large scatter in many clusters where no metallicity
spread of red giants is observed. This warns that a similar
result, an observable metallicity spread of the variables
might possibly occur in other clusters as well.
Table 3:
Mean meatallicity values of M 3 variables within smaller and larger radial
distances.
Corwin & Carney (2001) have found that there are 12 RR Lyrae stars in the inner 81'' region lying
0.1-0.2 mag below the ZAHB. They excluded the possibility that
these stars were too faint because of photometric
inaccuracies, however, they could not give any
plausible reason for their low luminosities.
As shown in Fig. 4 metallicity effect may partly explain the
faintness of these stars.
The variables discussed in the present paper
although do not show clear evidence of correlation between their metallicities and
radial distances from the cluster center, the innermost stars have
systematically larger metallicities than the outer variables as is shown in
Table 3.
Radial differences of the HB type and of the frequency of blue straggler stars (BSS)
have been also detected in M 3, namely the horizontal branch of the inner region is
bluer and its BSS population is more numerous (Catelan et al. 2001; Ferraro et al. 1997).
Though these phenomena still lack explanation,
all of them indicate that there is a dynamical segregation
within the cluster. Fitting the luminosity function of M 3, Rood et al. (1999)
have also found that the lower mass stars (
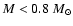 ;
stars below the turnoff point)
do not have a uniform radial distribution as well.
If the stellar composition, and central density of the
stars nearer to the cluster's center are in some degree different,
this might explain our finding, supposing that all the spectroscopically
measured cluster red giants with homogeneous metallicities belong to
the outskirt of the cluster.
;
stars below the turnoff point)
do not have a uniform radial distribution as well.
If the stellar composition, and central density of the
stars nearer to the cluster's center are in some degree different,
this might explain our finding, supposing that all the spectroscopically
measured cluster red giants with homogeneous metallicities belong to
the outskirt of the cluster.
If the iron content is indeed not homogeneous in HB stars,
its explanation could probably be found in the early
star formation and chemical evolution history of the system.
Recent investigations indicate that self-pollution
could have been efficient
during the first some hundred million years of the cluster lifetime,
just before its first crossing of the galactic plane,
which removed all the intracluster gas from the cluster.
As a manifestation of self-pollution, both the then existing stars accreted
processed material, and the composition of the intracluster gas
which formed to stars later, was altered (Thoul et al. 2002; D'Antona et al. 2002).
Models show that in M 3, 11% of the mass of a 1 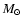 star
may originate from the mass loss of the first generation, large mass, evolved stars,
and not from the uncontaminated protocluster gas according to the accretion scenario
(Thoul et al. 2002).
Shustov & Wiebe (2000) modeled supernova explosions in globular clusters,
and concluded that self-pollution
via SN ejetion could also happen in globular
clusters, that might be a clue to explain any detected metallicity
spread. They also argue that SN self-pollution results in smaller scatter of the
observed iron abundances than in any of the lighter elements.
This helps to interpret why [Fe/H] values seem to be homogeneous in most of the
globular clusters.
star
may originate from the mass loss of the first generation, large mass, evolved stars,
and not from the uncontaminated protocluster gas according to the accretion scenario
(Thoul et al. 2002).
Shustov & Wiebe (2000) modeled supernova explosions in globular clusters,
and concluded that self-pollution
via SN ejetion could also happen in globular
clusters, that might be a clue to explain any detected metallicity
spread. They also argue that SN self-pollution results in smaller scatter of the
observed iron abundances than in any of the lighter elements.
This helps to interpret why [Fe/H] values seem to be homogeneous in most of the
globular clusters.
The question why [Fe/H] dispersion only of RR Lyrae stars is detected,
while red giants seem to be uniform in their iron content
is difficult to answer on the bases of the presently available observational data.
Because of the small sample
size and the large uncertainties especially in the spectroscopic data
of RR Lyrae stars,
good quality detailed spectroscopic measurements of a much larger RR Lyrae
sample is needed to confirm and to find the correct interpretation of the
suggested metallicity dispersion of RR Lyrae stars in M 3.
Similar studies of other globular clusters are also encouraged.
Acknowledgements
This research has made use of the SIMBAD database, operated at CDS
Strasbourg, France. This work has been supported by OTKA grants T30954 and T43504.
- Bakos, G., & Jurcsik, J. 2000, ASPCS, 203,
255
In the text
- Benko, J., et al. 2003, in preparation
In the text
- Bell, R. A., & Dickens, R. J. 1980, ApJ, 242,
657
In the text
NASA ADS
- Bernard, A. 1982, PASP, 94, 700
In the text
NASA ADS
- Caloi, V., D'Antona, F., & Mazzitelli, I. 1997,
A&A,
320, 823
In the text
NASA ADS
- Carretta, E., Cacciari, C., Ferraro, F. R., Fusi Pecci, F., &
Tessicini, G. 1998, MNRAS, 298, 1005
NASA ADS
- Catelan, M., Ferraro, E. R., & Rood, R. T. 2001, ApJ, 560,
970
In the text
NASA ADS
- Cavallo, R. M., & Nagar, N. M. 2000, AJ, 120, 1364
In the text
NASA ADS
- Cohen, J. 1978, ApJ, 223, 487
In the text
NASA ADS
- Corwin, T. M., & Carney, B. W. 2001, AJ, 122, 3183
In the text
NASA ADS
- D'Antona, F., Caloi, V., Montalbán, J., Ventura, P., &
Gratton, R.
2002, A&A, 395, 69
In the text
NASA ADS
- Ferraro, F. R., Paltrinieri, B., Fusi Pecci, F.,
et al. 1997, A&A, 324, 915
In the text
NASA ADS
- Harris, W. E. 1996, AJ, 112, 1487,
In the text
http://physun.physics.mcmaster.ca/Globular.html
NASA ADS
- Jurcsik, J. 1998, A&A, 333, 571
In the text
NASA ADS
- Jurcsik, J., & Kovács, G. 1996, A&A, 312, 111
In the text
NASA ADS
- Kaluzny, J., Hilditch, R. W., Clement, C., & Rucinski, S. M. 1998,
MNRAS, 296, 347
NASA ADS
- King, J. R., Stephens, A., Boesgaard, A. M., &
Deliyannis, C. 1998, AJ, 115,
666
In the text
NASA ADS
- Kovács, G., & Walker, A. 2001, A&A, 374, 264
In the text
NASA ADS
- Kraft, R. P., Sneden, C., Langer, G. E., & Prosser, C. 1992, AJ,
104, 645
In the text
NASA ADS
- Kraft, R. P., & Ivans, I. I. 2003, PASP, 115, 143
In the text
NASA ADS
- Lambert, D. L., Heath, J. E., Lemke, M., & Drake, J. 1996,
ApJS, 103, 183
In the text
NASA ADS
- Langer, G. E., Fischer, D., Sneden, C., & Bolte, M. 1998, AJ,
115, 685
In the text
NASA ADS
- Layden, A. 1994, AJ, 108, 1016
In the text
NASA ADS
- Rood, R. T., Carretta, E., Paltrinieri, B., et al. 1999, ApJ,
523, 752
In the text
NASA ADS
- Sandstrom, K., Pilachowski, C. A., & Saha, A. 2001, AJ, 122,
3212
In the text
NASA ADS
- Shustov, B. M., & Wiebe, D. S. 2000, MNRAS, 319,
1047
In the text
NASA ADS
- Thévenin, F., & Iidart, T. P. 1999, ApJ, 521, 753
In the text
NASA ADS
- Thoul, A. Jorissen, A., Goriely, S., et al. 2002, A&A, 383, 491
In the text
NASA ADS
Copyright ESO 2003
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.5cm,clip]{H4268f1.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/Timg12.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.4cm,clip]{H4268f2.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/Timg27.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{H4268f4.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2003/20/aah4268/Timg31.gif)