A&A 390, 173-178 (2002)
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20020714
M. O. Mennessier1 - J. Colomé2
1 - Université de Montpellier II and CNRS,
G.R.A.A.L., cc072,
34095 Montpellier Cedex 5, France
2 -
Departament d'Astronomia i Meteorologia,
Universitat de Barcelona,
Avda. Diagonal 647,
8028 Barcelona, Spain
Received 1 February 2002 / Accepted 30 April 2002
Abstract
The Tycho-2 catalogue provides astrometric and photometric data for
the 2.5 million brightest stars in the sky. Therefore it can
provide much larger
samples than the Hipparcos samples used to date in statistical studies.
The object of this paper is the cross-identification of Tycho-2
sources and known variable stars of RR Lyrae type.
The Tycho-2 data of cross-identified sources are added into the
ASTRID specialized database. The present selection almost
doubles the size of the sample of RR Lyrae stars
with available proper motions.
Key words: stars: variables: RR Lyr - catalogs
The Tycho-2 catalogue (Hog et al. 2000)
- hereafter TYC2 -
contains positions, proper motions and two-colour
photometric data for the 2.5 million brightest
stars in the sky.
The completeness is 90![]() to V=11.5 mag and
95
to V=11.5 mag and
95![]() to V=11.0. The main observational basis of the catalogue
is the Tycho star-mapper observations by the
Hipparcos satellite. About 130 observations per object provide homogeneous
photometry from which mean magnitudes in two passbands
close to Johnson B and V,
to V=11.0. The main observational basis of the catalogue
is the Tycho star-mapper observations by the
Hipparcos satellite. About 130 observations per object provide homogeneous
photometry from which mean magnitudes in two passbands
close to Johnson B and V, ![]() and
and ![]() ,
were derived.
,
were derived.
Many statistical results based on kinematic and photometric Hipparcos data, particularly luminosity calibrations, have been published (see for instance: Fernley et al. 1998; Popowski & Gould 1998). The luminosity calibration of RR Lyrae stars is one of the steps in the determination of the Universe distance scale (Luri et al. 1998). Some of these statistical results could be greatly improved by using the TYC2. Indeed TYC2 astrometry and photometry are homogeneous and a larger sample size can compensate for less accurate astrometric data. We present the identification of known RR Lyrae variable stars in the TYC2. Section 2 describes the sample of known RR Lyrae stars. The criteria adopted for the cross-identification are given in Sect. 3. Finally, Sect. 4 describes the sample of RR Lyrae stars identified in the TYC2.
There are
6543 galactic RR Lyrae stars known.
Most of them (6526) are listed in the GCVS
(Durlevich et al. 1996) and NSV (Kazarovets et al. 1998)
catalogues, and in the more recent
Name-list of Variable Stars (Nos. 67-74)
published by Kholopov et al. (1999, 2000) in the IAU Information Bulletin
of Variable Stars. Among the new variable stars discovered
by Hipparcos 17 were identified as RR Lyrae stars (Perryman et al. 1997).
All of them are included in the ASTRID database![]() .
.
The Hipparcos catalogue gives measurements for 202 RR Lyrae stars. All of them are in the TYC2 that indicates the Hipparcos identifiers. Among them, 22 belong to the TYC2-suplement1 and 1 to the TYC2-suplement2; these supplements contain respectively stars without TYC2 data and false or heavily disturbed data. Thus only 179 RR Lyrae stars with an Hipparcos identifier will finally be considered. The properties of these 179 stars will be a guide in checking the criteria adopted for the cross-identification (Sect. 3). Let us remark that two stars (MS Ara = HIP 88402 and TZ Aur = HIP 34743) have no proper motion in TYC2 and so may not be useful for any kinematical applications.
Many RR Lyrae stars in the GCVS and NSV are fainter than the magnitude limit of the TYC2. Thus among the 6341 known RR Lyrae stars that were not observed by Hipparcos, only a few more than 400 can be present in TYC2. They are brighter than 12.5 mag in V and 12.8 mag in Pat their maximum luminosity.
The main criterion is the comparison between the positions of
known RR Lyrae stars possibly observed by Tycho and
the positions of TYC2 sources. The epoch of TYC2 positions is J2000.0.
Only 345 non-Hipparcos RR Lyrae stars have a J2000.0 position
in the SIMBAD database![]() , so we
cannot use this database for our purpose, but it allows us to verify the
agreement with our J2000.0 GCVS position computation.
The comparison of our computed J2000.0 positions and those of SIMBAD
for these 345 stars shows that
60
, so we
cannot use this database for our purpose, but it allows us to verify the
agreement with our J2000.0 GCVS position computation.
The comparison of our computed J2000.0 positions and those of SIMBAD
for these 345 stars shows that
60![]() and 40
and 40![]() of the differences between the two positions
are smaller than 2'' and 1'' respectively, which agrees with
the accuracy of the GCVS positions.
of the differences between the two positions
are smaller than 2'' and 1'' respectively, which agrees with
the accuracy of the GCVS positions.
As a first step, we retain the TYC2 sources closer than 3 times the mean quadratic error on the TYC2 and GCVS J2000.0 positions of one RR Lyrae star. Thus, 482 TYC2 sources are selected as possibly related to 270 known GCVS non-Hipparcos RR Lyrae stars. In some cases one RR Lyrae star has been matched with more than one TYC2 source by this first selection. The criteria described in the next sections refine this selection.
It is very important to check that TYC2 sources positionaly
matched with a RR Lyrae star have physical characteristics
consistent with this type of stars. The
![]() colour should be compatible with the range for
RR Lyrae stars, which can be estimated at [0, 0.7]. The histogram of
the observed
colour should be compatible with the range for
RR Lyrae stars, which can be estimated at [0, 0.7]. The histogram of
the observed
![]() for Hipparcos RR Lyrae stars fulfills this
assumption, as can be seen in Fig. 1.
for Hipparcos RR Lyrae stars fulfills this
assumption, as can be seen in Fig. 1.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=8.8cm,clip]{MS1096f1.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/28/aa1096/Timg8.gif) |
Figure 1:
Histogram of the colour index
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
Since we are dealing with variable stars
the standard error of the mean magnitudes in TYC2 is
large. We denote by
![]() and
and
![]() the
respective accuracy on
the
respective accuracy on ![]() and
and ![]() .
The colour criterion adopted for acceptance of a matched TYC2 star
is:
.
The colour criterion adopted for acceptance of a matched TYC2 star
is:
A second criterion to refine the selection can be defined by
taking into account that the TYC2 magnitude of the star must agree
with the magnitude range for the matching object in the
GCVS. To establish this we define the ratios:
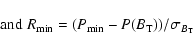
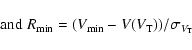
The distribution of the Hipparcos
RR Lyrae stars in the plane
![]() (see Fig. 2,
(see Fig. 2,
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=8.8cm,clip]{MS1096f2.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/28/aa1096/Timg35.gif) |
Figure 2:
Distribution of the Hipparcos
RR Lyrae stars in the plane
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
Thus, looking at the Hipparcos RR Lyrae star behaviour, we adopt
as a criterion for acceptance:
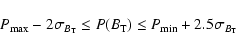
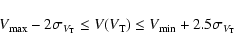
These zones are indicated by bold lines in Fig. 2. Five Hipparcos stars are far out of this area (hip 54694, 67227, 78891, 101545, 112532), thus, their cross-identification with a Tycho source as given in the TYC2 catalogue can be doubtful.
The positions, proper motions, and
![]() magnitudes of TYC2
sources identified
as known RR Lyrae stars (Hipparcos and non-Hipparcos) are
available in the ASTRID database.
magnitudes of TYC2
sources identified
as known RR Lyrae stars (Hipparcos and non-Hipparcos) are
available in the ASTRID database.
Table 1 shows the number of selected sources after the application of each criteria. At the end of the selection process, 172 TYC2 sources are cross-identified with a non-Hipparcos RR Lyrae star. The physical criteria drastically decrease the number of matches deduced only from the position criterion, showing the importance of taking into account physical properties in a cross-identification procedure.
The list of GCVS and TYC2 identifiers of the 172 non-Hipparcos matched RR Lyrae stars is given in Table 4.
Several aspects of the above selection procedure have been checked:
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{MS1096f3.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/28/aa1096/Timg40.gif) |
Figure 3: Distribution of Hipparcos (filled diamonds) and new-identified TYC2 (open circles) RR Lyrae stars in galactic longitude and latitude. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
| Criterion | Selected sources |
| Position | 270 |
| Colour | 216/270 |
| Magnitude | 172/216 |
| Total | 172 |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=8.8cm,clip]{MS1096f4.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/28/aa1096/Timg41.gif) |
Figure 4:
Distribution of the kept non-Hipparcos
RR Lyrae stars in the plane
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=8.8cm,clip]{MS1096f5.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/28/aa1096/Timg42.gif) |
Figure 5:
Comparison of the
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| Interval of |
8-9 | 9-10 | 10-11 | 11-12 | >12 |
| mean
|
|||||
| Hip stars | 0.015 | 0.025 | 0.053 | 0.118 | 0.199 |
| non-Hip stars | 0.156 | 0.220 | |||
| mean
|
|||||
| 0.014 | 0.023 | 0.050 | 0.114 | 0.198 |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=8.8cm,clip]{MS1096f6a.eps}\\ [4mm]
\includegraphics[angle=-90,width=8.8cm,clip]{MS1096f6b.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/28/aa1096/Timg45.gif) |
Figure 6:
Histograms of the colour index
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
| median
|
|
|
| non-HIP | 12.13 | 0.32 |
| HIP | 10.98 | 0.08 |
351 TYC2 sources are identified with known RR Lyrae stars: 179 and 172 with and without Hipparcos measurements, respectively.
Among the 179 Hipparcos RR Lyrae stars, 120 have a Tycho identifier in the SIMBAD database.
Only 8 non-Hipparcos GCVS RR Lyrae stars have a Tycho identifier in the SIMBAD database:
| TYC2 | GCVS | TYC2 | GCVS | TYC2 | GCVS | TYC2 | GCVS |
| 3235 00649 1 | BK And | 7816 01300 1 | V501 Cen | 6027 01044 1 | XX Hya | 6261 02361 1 | V756 Sgr |
| 2773 01607 1 | DM And | 7308 01432 1 | V535 Cen | 5448 00107 1 | DH Hya | 7937 01579 1 | V796 Sgr |
| 9281 01742 1 | BS Aps | 7213 01978 1 | V590 Cen | 6728 01236 1 | FY Hya | 6882 00389 1 | V866 Sgr |
| 9293 01637 1 | LU Aps | 7214 01559 1 | V595 Cen | 0215 01036 1 | GL Hya | 6281 01857 1 | V1025 Sgr |
| 5230 00535 1 | TZ Aqr | 7278 00390 1 | V671 Cen | 5471 00817 1 | IV Hya | 6282 00744 1 | V1055 Sgr |
| 5806 00188 1 | YZ Aqr | 7292 01029 1 | V674 Cen | 9353 00088 1 | SX Hyi | 6278 01906 1 | V1176 Sgr |
| 5814 01330 1 | AA Aqr | 4650 00982 1 | DX Cep | 8444 01013 1 | AO Ind | 7953 01362 1 | V1645 Sgr |
| 5816 00616 1 | BO Aqr | 6482 00328 1 | RT Col | 3204 00101 1 | CQ Lac | 7442 01549 1 | V1646 Sgr |
| 5782 00484 1 | BU Aqr | 1993 02658 1 | RY Com | 1983 00539 1 | RX Leo | 7957 00491 1 | V2277 Sgr |
| 5816 00282 1 | CE Aqr | 1997 00754 1 | BS Com | 0860 00368 1 | AA Leo | 7957 01101 1 | V2281 Sgr |
| 5193 00708 1 | CP Aqr | 7911 01078 1 | WW CrA | 1437 00734 1 | AE Leo | 6866 01681 1 | V3859 Sgr |
| 5228 00828 1 | FY Aqr | 7916 01708 1 | CV CrA | 0270 00519 1 | AN Leo | 7384 00434 1 | V487 Sco |
| 5181 00028 1 | AA Aql | 7913 01356 1 | V592 CrA | 1976 00905 1 | V LMi | 6782 00893 1 | V765 Sco |
| 5739 01986 1 | KM Aql | 7405 01427 1 | V593 CrA | 3000 00744 1 | X LMi | 6427 01515 1 | RV Scl |
| 1057 00788 1 | V672 Aql | 7906 00492 1 | V629 CrA | 8292 01452 1 | VW Lup | 6985 00559 1 | TX Scl |
| 0500 02240 1 | V793 Aql | 6101 00033 1 | SW Crv | 8303 00119 1 | AW Lup | 7507 00715 1 | UZ Scl |
| 9052 01546 1 | CV Ara | 8973 01776 1 | SW Cru | 7313 01084 1 | GZ Lup | 6999 01283 1 | AE Scl |
| 9056 00731 1 | CZ Ara | 2707 00757 1 | DM Cyg | 2960 00958 1 | RW Lyn | 5705 00778 1 | AF Sct |
| 8746 01083 1 | HX Ara | 3171 00285 1 | V830 Cyg | 2641 01678 1 | RZ Lyr | 0366 00711 1 | AV Ser |
| 8369 01766 1 | QU Ara | 3556 02064 1 | V894 Cyg | 2115 02066 1 | AQ Lyr | 1503 00507 1 | AW Ser |
| 8354 00751 1 | V532 Ara | 3609 02052 1 | V1815 Cyg | 2121 02123 1 | CX Lyr | 1489 00510 1 | DF Ser |
| 1217 01508 1 | RW Ari | 2679 01388 1 | V1823 Cyg | 3120 01293 1 | NR Lyr | 5499 00814 1 | RV Sex |
| 1761 01979 1 | TY Ari | 1632 00667 1 | ZZ Del | 7962 01089 1 | TT Mic | 8744 01879 1 | BI Tel |
| 2559 00874 1 | SW Boo | 1078 00034 1 | CK Del | 0163 01482 1 | V535 Mon | 8762 01412 1 | FU Tel |
| 2569 00519 1 | UU Boo | 1647 02135 1 | EG Del | 9253 00898 1 | ET Mus | 8401 00104 1 | GZ Tel |
| 2022 00180 1 | XX Boo | 1640 01518 1 | FF Del | 8724 00541 1 | VW Nor | 8389 01466 1 | HH Tel |
| 7586 00270 1 | U Cae | 8510 01671 1 | VY Dor | 5080 01878 1 | ST Oph | 9027 03628 1 | TT TrA |
| 4339 00474 1 | UU Cam | 9165 00722 1 | XX Dor | 0423 01493 1 | V816 Oph | 8837 00411 1 | YY Tuc |
| 1927 00426 1 | SS Cnc | 3523 01442 1 | AV Dra | 0717 02302 1 | CM Ori | 8470 00493 1 | AO Tuc |
| 0825 00680 1 | AQ Cnc | 4574 01625 1 | BD Dra | 9058 02328 1 | TY Pav | 9345 00132 1 | BK Tuc |
| 3023 00942 1 | Z CVn | 3946 00531 1 | CY Dra | 9077 02070 1 | BH Pav | 7671 02298 1 | AN Vel |
| 0168 01084 1 | X CMi | 0535 01242 1 | RT Equ | 8785 00001 1 | HV Pav | 7735 00975 1 | FS Vel |
| 0172 00642 1 | RV CMi | 7044 01598 1 | DT Eri | 9084 00277 1 | QR Pav | 0282 00632 1 | UV Vir |
| 0192 00043 1 | AL CMi | 6440 00701 1 | Z For | 1685 01784 1 | VV Peg | 0300 00375 1 | VZ Vir |
| 8627 02481 1 | TX Car | 6440 00028 1 | RS For | 1678 00330 1 | CY Peg | 4965 00838 1 | WW Vir |
| 8957 02820 1 | FT Car | 6442 00690 1 | RX For | 1713 01366 1 | DZ Peg | 4981 01329 1 | AD Vir |
| 8548 01214 1 | IU Car | 7560 00526 1 | SW For | 2735 00326 1 | ES Peg | 0321 00306 1 | AE Vir |
| 3677 01213 1 | HU Cas | 7992 00369 1 | RR Gru | 3671 01241 1 | ET Per | 5538 00115 1 | AS Vir |
| 3650 02043 1 | IU Cas | 8451 00553 1 | AO Gru | 7537 00083 1 | TZ Phe | 0306 00647 1 | BC Vir |
| 4015 00150 1 | NO Cas | 2597 00581 1 | CW Her | 0025 00423 1 | SY Psc | 9198 01105 1 | RV Vol |
| 8642 01380 1 | BI Cen | 3063 01333 1 | GY Her | 6007 02820 1 | AK Pup | 9203 01588 1 | SV Vol |
| 7749 01536 1 | KS Cen | 2608 01343 1 | IP Her | 6542 01690 1 | BQ Pup | 1646 00197 1 | FH Vul |
| 7260 00309 1 | V480 Cen | 8062 00084 1 | UU Hor | 8866 01496 1 | X Ret | 1659 00679 1 | FK Vul |
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the PICASSO program PICS 348, by the Programa Nacional de Astronomía y Astrofísica under contract AYA 2000-0937 and by a Socrates-Erasmus grant. We thank A.Gómez and F.Figueras for fruitful comments, and X.Luri for rereading our manuscript.