

Up: The Hamburg/SAO survey for
Subsections
3 Results of follow-up spectroscopy
In Table 1 we present the results of the observations.
The 209 candidates were selected from our first and second priority
samples introduced in Paper IV.
Of 169 first priority candidates, 141 objects appeared in our list as
new ones. 28 objects were listed in the NED as galaxies or objects
from various catalogs with known redshifts and some of them already had
information on emission lines in earlier publications.
All objects were included in our observing program in order to improve spectral
information.
Comparison of our velocities with those of galaxies with already known
redshift shows acceptable consistency within the uncertainties given.
Another 40 candidates observed were taken from the list of second priority
candidates. As described in Paper IV two samples were created from this list.
A "random selected sample'' containing randomly selected objects from the list
and the "APM selected sample'' which uses additional information for selection.
The "random selected sample'' was created to access the fraction of BCGs in the
second priority list and contains 43 objects. For 26 of them the spectral
data were presented in Paper IV, while for the remaining 17 candidates
observed with the CAHA 2.2 m telescope, the spectral information is presented
here. The results of the analysis for this sample were presented in Paper IV.
We found that the second priority list contains at most 10%
BCG/H II-galaxies.
The second, "APM selected'' sample comprises second priority candidates which
are classified as non-stellar on Palomar Sky Survey plates (PSS) in the APM
database, and have blue color according to the APM color system
((B-R) < 1.0).
Here we give spectral data for 23 objects from this sample. Except one
all are ELGs confirming the efficiency of this selection criterium to
pick up the BCG/H II-galaxies from the second priority list
(cf. Paper IV).
The observed emission line galaxies are listed in Table 3 containing
the following information:
Column 1: The object's IAU-type name with the prefix HS.
Column 2: Right ascension for equinox B1950.
Column 3: Declination for equinox B1950.
The coordinates were measured on direct plates of the HQS
and are accurate to  2
2
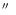 (Hagen et al. 1995).
(Hagen et al. 1995).
Column 4: Heliocentric velocity and its rms uncertainty in
kms-1.
Column 5: Apparent B-magnitude obtained by calibration of the digitized
photoplates with photometric standard stars (Engels et al. 1994),
having an rms accuracy of 
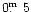 for objects fainter than
mB =
for objects fainter than
mB =
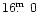 (Popescu et al. 1996).
Since the algorithm to calibrate the objective prism spectra is
optimized for point sources the brightnesses of extended galaxies are
underestimated. The resulting systematic uncertainties are expected to
be as large as 2 mag (Popescu et al. 1996). For about 20%
of our objects, B-magnitudes are unavailable at the moment. We present
for them blue magnitudes obtained from the APM database. They are
marked by a "+'' before the value in the corresponding
column. According to our estimate they are systematically brighter by
(Popescu et al. 1996).
Since the algorithm to calibrate the objective prism spectra is
optimized for point sources the brightnesses of extended galaxies are
underestimated. The resulting systematic uncertainties are expected to
be as large as 2 mag (Popescu et al. 1996). For about 20%
of our objects, B-magnitudes are unavailable at the moment. We present
for them blue magnitudes obtained from the APM database. They are
marked by a "+'' before the value in the corresponding
column. According to our estimate they are systematically brighter by
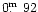 than the B-magnitudes obtained by calibration of the
digitized photoplates (rms
than the B-magnitudes obtained by calibration of the
digitized photoplates (rms
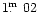 ).
Objects referred to Popescu & Hopp (2000) have
precise B-magnitude in Vennik, et al. (2000).
We do not list them here for the sake of homogeneity.
The B-magnitude for HS 1213+3636A was determined by eye estimate
as 17
).
Objects referred to Popescu & Hopp (2000) have
precise B-magnitude in Vennik, et al. (2000).
We do not list them here for the sake of homogeneity.
The B-magnitude for HS 1213+3636A was determined by eye estimate
as 17
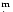 5 and marked by a ":'' as less confident.
5 and marked by a ":'' as less confident.
Column 6: Absolute B-magnitude, calculated from the apparent
B-magnitude and the heliocentric velocity.
The only exception is made for HS 1213+3636B, a super-association in the
nearby galaxy NGC 4214 for which the distance is known from stellar
photometry (see comments below).
No correction for galactic extinction is made because all objects are
located at high galactic latitudes and the corrections are significantly
smaller than the uncertainties of the magnitudes.
Column 7: Preliminary spectral classification type according to
the spectral data presented in this article. BCG means a galaxy
possessing a characteristic H II-region spectrum with low enough
luminosity (
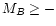 20
20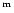 ). SBN and DANS are galaxies of lower
excitation with a corresponding position in line ratio diagrams, as
discussed in Paper I. SBN are the brighter fraction of this type. Here we
follow the notation of Salzer et al. (1989).
Three objects were recognized as Seyfert galaxies.
Two of them (HS 1317+4521B and HS 1616+3627) are Sy1 galaxies due to
the presence of broad Balmer lines and of broad [Fe II] emission.
Our spectrum of HS 1616+3627 has insufficient quality to show this, but
independent spectroscopy data of Grupe et al. (1999) clearly
classify this object as a narrow-line Sy1 galaxy.
The third one (HS 1220+3845) is a narrow-line ELG, which is classified as
a Sy2 galaxy in diagnostic diagrams.
Typical spectra of
low-ionisation nuclear emission-line regions (LINERs) are identified
for 3 galaxies.
SA stands for two probable super-associations in two dwarf spiral
galaxies. Six ELGs are difficult to classify. They are coded as NON.
). SBN and DANS are galaxies of lower
excitation with a corresponding position in line ratio diagrams, as
discussed in Paper I. SBN are the brighter fraction of this type. Here we
follow the notation of Salzer et al. (1989).
Three objects were recognized as Seyfert galaxies.
Two of them (HS 1317+4521B and HS 1616+3627) are Sy1 galaxies due to
the presence of broad Balmer lines and of broad [Fe II] emission.
Our spectrum of HS 1616+3627 has insufficient quality to show this, but
independent spectroscopy data of Grupe et al. (1999) clearly
classify this object as a narrow-line Sy1 galaxy.
The third one (HS 1220+3845) is a narrow-line ELG, which is classified as
a Sy2 galaxy in diagnostic diagrams.
Typical spectra of
low-ionisation nuclear emission-line regions (LINERs) are identified
for 3 galaxies.
SA stands for two probable super-associations in two dwarf spiral
galaxies. Six ELGs are difficult to classify. They are coded as NON.
Column 8: One or more alternative names, according to the
information from NED.
References are given to the other sources of the
redshift-spectral information indicating that a galaxy is an ELG.
The spectra of all emission-line galaxies are shown in Appendix A,
which is available only in the electronic version of the journal.
The results of line flux measurements are given in Table 4.
It contains the following information:
Column 1: The object's IAU-type name with the prefix HS.
By asterisk we note the objects observed during non-photometric
conditions.
Column 2: Observed flux (in
10-16ergs-1cm-2) of the H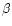 line.
For several objects without H
line.
For several objects without H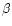 emission line the fluxes are given
for H
emission line the fluxes are given
for H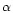 and marked by a "+''.
and marked by a "+''.
Columns 3-5: The observed flux ratios [O II]/H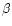 ,
[O III]/H
,
[O III]/H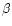 and H
and H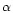 /H
/H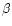 .
.
Columns 6, 7: The observed flux ratios
[N II]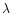 6583 Å/H
6583 Å/H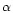 ,
and
([S II]
,
and
([S II]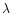 6716 Å +
6716 Å + 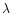 6731 Å)/H
6731 Å)/H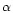 .
.
Columns 8-10: Equivalent widths of the lines
[O II]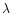 3727 Å, H
3727 Å, H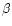 and
[O III]
and
[O III]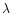 5007 Å.
For several objects without detected H
5007 Å.
For several objects without detected H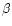 emission line the equivalent
widths are given for H
emission line the equivalent
widths are given for H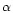 and marked by a "+''.
and marked by a "+''.
Below we give comments on some specific cases:
HS 0948+3723 and HS 1430+4040: H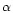 -emission in these
galaxies is affected by cosmic ray hits. The intensity ratio of
H
-emission in these
galaxies is affected by cosmic ray hits. The intensity ratio of
H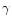 /H
/H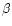 is close to the recombination one with
is close to the recombination one with
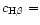 0.
So we accepted for them the recombination H
0.
So we accepted for them the recombination H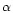 /H
/H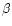 flux
ratio, and corrected respectively the ratios of [N II]/H
flux
ratio, and corrected respectively the ratios of [N II]/H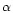 and
[S II]/H
and
[S II]/H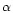 in Table 4.
in Table 4.
HS 1213+3636A:
this is a compact slightly elongated ( 9
9
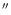 )
object at
)
object at
 60
60
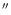 to NW from the center of the star-bursting barred
Magellanic type galaxy (SBm) NGC 4214 (with
to NW from the center of the star-bursting barred
Magellanic type galaxy (SBm) NGC 4214 (with
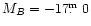 ).
Its radial velocity of
).
Its radial velocity of
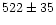 kms-1 is higher by
kms-1 is higher by  220 kms-1 than
the systemic velocity of NGC 4214 and higher by
220 kms-1 than
the systemic velocity of NGC 4214 and higher by  260 kms-1 than
the velocity of H I gas in this place (McIntyre 1997).
This implies that this compact emission region is a kinematically detached
object, either a background dwarf, or more probably, a tiny "satellite''
galaxy, passing by its much more massive neighbouring galaxy.
For the former case its distance from
the Hubble flow is 7 Mpc,
260 kms-1 than
the velocity of H I gas in this place (McIntyre 1997).
This implies that this compact emission region is a kinematically detached
object, either a background dwarf, or more probably, a tiny "satellite''
galaxy, passing by its much more massive neighbouring galaxy.
For the former case its distance from
the Hubble flow is 7 Mpc,
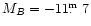 :
and the size
:
and the size  0.3 kpc.
For the latter case, if HS 1213+3636A is located at the same distance as
NGC 4214 (2.64 Mpc, as found through stellar photometry with HST by
Drozdovsky et al. 2001), its
0.3 kpc.
For the latter case, if HS 1213+3636A is located at the same distance as
NGC 4214 (2.64 Mpc, as found through stellar photometry with HST by
Drozdovsky et al. 2001), its
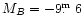 :
and the size
:
and the size
 0.1 kpc. The nature of this tiny galaxy can be checked in
principle by the use of well known luminosity-abundance relationship for
gas-rich galaxies. If it is situated far from NGC 4214 one should
expect that this galaxy should have metallicity
0.1 kpc. The nature of this tiny galaxy can be checked in
principle by the use of well known luminosity-abundance relationship for
gas-rich galaxies. If it is situated far from NGC 4214 one should
expect that this galaxy should have metallicity
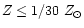 .
On the other hand, if HS 1213+3636A is connected to NGC 4214, one can
speculate that this companion formed of gas pulled out of the parent SBm
galaxy as a result of its strong interaction with other galaxy. In this case the
metallicity of this companion should be close to that of NGC 4214, that
is known to be
.
On the other hand, if HS 1213+3636A is connected to NGC 4214, one can
speculate that this companion formed of gas pulled out of the parent SBm
galaxy as a result of its strong interaction with other galaxy. In this case the
metallicity of this companion should be close to that of NGC 4214, that
is known to be 
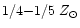 (e.g., Kobulnitsky & Skillman
1996). Thus, metallicity determination of this dwarf with strong
starburst will probably resolve the dilemma.
(e.g., Kobulnitsky & Skillman
1996). Thus, metallicity determination of this dwarf with strong
starburst will probably resolve the dilemma.
HS 1213+3636B:
this well elongated object ( 12
12
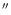 )
is projected onto the middle part
(
)
is projected onto the middle part
( 46
46
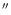 ,
or
,
or  0.6 kpc to NWW from the center) of the same galaxy
NGC 4214. It is at
0.6 kpc to NWW from the center) of the same galaxy
NGC 4214. It is at  25
25
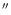 to the South from HS 1213+3636A.
Our velocity differs by only
to the South from HS 1213+3636A.
Our velocity differs by only  60 kms-1 from the NGC 4214 systemic velocity
and is well consistent with the H I velocity of 260 kms-1 at this place from
McIntyre (1997). From our data it follows that HS 1213+3636B
is a super-association (SA) in a spiral arm of NGC 4214. Its
60 kms-1 from the NGC 4214 systemic velocity
and is well consistent with the H I velocity of 260 kms-1 at this place from
McIntyre (1997). From our data it follows that HS 1213+3636B
is a super-association (SA) in a spiral arm of NGC 4214. Its
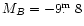 :
and the size
:
and the size  0.15 kpc.
The spectra of both A and B objects were acquired in one slit, so their large
velocity difference is out of doubt.
0.15 kpc.
The spectra of both A and B objects were acquired in one slit, so their large
velocity difference is out of doubt.
HS 1311+3628:
this elongated object ( 11
11
 )
is projected onto the southern edge
(
)
is projected onto the southern edge
( 50
50
 to the South from the center) of Im galaxy UGC 8303
(Holmberg VIII).
A large difference of its radial velocity (
to the South from the center) of Im galaxy UGC 8303
(Holmberg VIII).
A large difference of its radial velocity (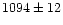 kms-1) with that of
the systemic velocity of the dwarf irregular UGC 8303 (
kms-1) with that of
the systemic velocity of the dwarf irregular UGC 8303 (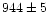 kms-1 from Huchra et al. 1995) and the local H I velocity in this
region (
kms-1 from Huchra et al. 1995) and the local H I velocity in this
region ( 945 kms-1) from the H I map by Thean et al. (1997)
(where this galaxy by error is called UGC 8314),
implies that this object probably does not belongs to UGC 8303 and is
a nearby separate star-forming dwarf.
We observed this object twice on different nights and with different
setups. Both spectra have the same redshifts within the observational
uncertainties.
HS 1311+3628 is therefore not an H II-region in UGC 8303 as
suggested by Popescu et al. (1996).
945 kms-1) from the H I map by Thean et al. (1997)
(where this galaxy by error is called UGC 8314),
implies that this object probably does not belongs to UGC 8303 and is
a nearby separate star-forming dwarf.
We observed this object twice on different nights and with different
setups. Both spectra have the same redshifts within the observational
uncertainties.
HS 1311+3628 is therefore not an H II-region in UGC 8303 as
suggested by Popescu et al. (1996).
HS 1311+3924:
this is the irregular (probably merging) galaxy UGC 8315 and member of a group,
with a radial velocity of 1215 kms-1 according to Garcia et al. (1993).
We got the spectrum of only one of two bright knots in the galaxy elongated
body, namely the NE one. While its velocity 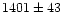 differs by 186 kms-1 from that given by Garcia et al. (1993) the combined uncertainty
of latter value is not well constrained. A long-slit spectrum along
the major axis will be helpful for understanding the nature of this object.
differs by 186 kms-1 from that given by Garcia et al. (1993) the combined uncertainty
of latter value is not well constrained. A long-slit spectrum along
the major axis will be helpful for understanding the nature of this object.
HS 1423+3945: the radial velocity of this object is very close to that
of UGC 9242 (our 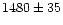 vs.
vs. 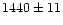 kms-1 in the RC3 catalog) and
therefore the object is very probably an SA in this edge-on dwarf spiral.
kms-1 in the RC3 catalog) and
therefore the object is very probably an SA in this edge-on dwarf spiral.
HS 1242+4058A: The nearby BCG HS 1242+4058B (cf. Paper II) is
separated by  4
4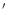 from HS 1242+4058A and the radial velocities
differ by
from HS 1242+4058A and the radial velocities
differ by 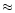 300 kms-1. They are probably not associated with each other.
300 kms-1. They are probably not associated with each other.
HS 1317+4521B: The nearby BCG-candidate ( 10
10
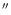 to SW)
HS 1317+4521A is not observed yet.
to SW)
HS 1317+4521A is not observed yet.
HS 1646+4003B: its faint companion ( 30
30
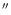 to SSW),
HS 1646+4003A was earlier identified as NON (cf. Paper II).
to SSW),
HS 1646+4003A was earlier identified as NON (cf. Paper II).
HS 0935+4135, HS 0958+3654, HS 1025+3707B, HS 1027+4728, HS 1206+4012,
HS 1236+4532, HS 1433+4245, HS 1514+4602:
In all these galaxies the only emission line suitable for redshift measurement
is H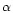 .
A conservative estimate of their radial velocity uncertainty is
300 kms-1.
.
A conservative estimate of their radial velocity uncertainty is
300 kms-1.
For some of the galaxies either the snap-shot spectra had strong enough emission
lines and a well detected [O III]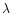 4363Å or they were
reobserved later with better S/N ratio. For these galaxies we determined
metallicities and the following galaxies appeared to have
O/H
4363Å or they were
reobserved later with better S/N ratio. For these galaxies we determined
metallicities and the following galaxies appeared to have
O/H 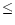 1/10 (O/H)
1/10 (O/H)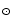 :
HS 1313+4521, HS 1330+3651, HS 1334+3957, HS 1408+4227, HS 1417+4433,
HS 1545+4055, HS 1650+3706, HS 1655+3845.
:
HS 1313+4521, HS 1330+3651, HS 1334+3957, HS 1408+4227, HS 1417+4433,
HS 1545+4055, HS 1650+3706, HS 1655+3845.
For two BCGs (HS 0940+4052 and HS 1311+3628) the blue WR-bump is more
or less evident from the snap-shot spectra, and for 8 more BCGs this
feature is probably present.
Several "BCG?'' were listed in Table 3 with absolute magnitudes
brighter than -20
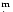 0. In fact, these MB are uncertain, since they come
from the estimates from the Hamburg Quasar Survey plates. Independent
CCD measurements or estimates from alternative sources show that usually they
are fainter by
0. In fact, these MB are uncertain, since they come
from the estimates from the Hamburg Quasar Survey plates. Independent
CCD measurements or estimates from alternative sources show that usually they
are fainter by
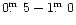 ,
and should fulfill therefore the criterion
,
and should fulfill therefore the criterion
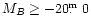 (Kniazev et al. 2001b).
(Kniazev et al. 2001b).
The main criteria applied to search for BCGs are a blue continuum near
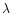 4000 Å and a strong emission line - expected is
[O III]
4000 Å and a strong emission line - expected is
[O III]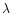 5007 Å - in
the wavelength region between 5000 Å and the sensitivity break of
the Kodak IIIa-J photoemulsion near 5400 Å (see Paper I). For this
reason faint QSOs with Ly
5007 Å - in
the wavelength region between 5000 Å and the sensitivity break of
the Kodak IIIa-J photoemulsion near 5400 Å (see Paper I). For this
reason faint QSOs with Ly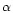
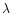 1216 Å redshifted to
1216 Å redshifted to 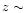 3 or with Mg II
3 or with Mg II 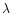 2798 Å
redshifted to z
2798 Å
redshifted to z  0.8 could be selected as
BCG candidates.
In Papers I-IV we already reported on the discovery of a
number of such faint QSOs. They have been missed by the proper Hamburg
Quasar Survey since the latter is restricted to bright
QSOs (
0.8 could be selected as
BCG candidates.
In Papers I-IV we already reported on the discovery of a
number of such faint QSOs. They have been missed by the proper Hamburg
Quasar Survey since the latter is restricted to bright
QSOs (
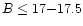 ). Here we report
on the discovery of five high-redshift faint (B > 17.5) QSOs.
For all but one of them, we identified Ly
). Here we report
on the discovery of five high-redshift faint (B > 17.5) QSOs.
For all but one of them, we identified Ly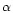
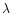 1216 Å redshifted to
1216 Å redshifted to 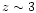 as the line responsible for its selection. One
object (HS 1301+4233) shows a broad emission line tentatively identified with
Mg II
as the line responsible for its selection. One
object (HS 1301+4233) shows a broad emission line tentatively identified with
Mg II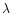 2798 Å.
However this identification remains somewhat uncertain due to low
signal-to-noise of the spectrum.
Two of our new QSOs: HS 1224+4410 and HS 1541+4452, have recently appeared
in the NED as radio sources with no redshift determination (reported as
[HVG99] R17 in Hunter et al. 1999, and B3 1541+448A
in Douglas et al. 1996).
The data for all five quasars are presented in
Table 5. Finding charts and plots of their spectra can be found
on the www-site of the Hamburg Quasar Survey
(http://www.hs.uni-hamburg.de/hqs.html).
2798 Å.
However this identification remains somewhat uncertain due to low
signal-to-noise of the spectrum.
Two of our new QSOs: HS 1224+4410 and HS 1541+4452, have recently appeared
in the NED as radio sources with no redshift determination (reported as
[HVG99] R17 in Hunter et al. 1999, and B3 1541+448A
in Douglas et al. 1996).
The data for all five quasars are presented in
Table 5. Finding charts and plots of their spectra can be found
on the www-site of the Hamburg Quasar Survey
(http://www.hs.uni-hamburg.de/hqs.html).
In total, for 43 candidates no (trustworthy) emission lines were detected.
We divided them into three categories.
For four non-ELG galaxies the signal-to-noise ratio
of our spectra was sufficient to detect absorption lines, allowing
the determination of redshifts. The data are presented in Table 6.
To separate the stars among the objects missing detectable emission
lines we cross-correlated a list of the most common stellar features
with the observed spectra. In total, 21 objects with definite stellar
spectra and redshifts close to zero were identified.
All of them were crudely classified in categories
from definite A-stars to G-stars, with most of them intermediate
between A and F. The data for these stars are presented in Table 7.
There was no possibility of classifying 18 objects without emission lines.
Their spectra have too low signal-to-noise ratio to detect trustworthy
absorption features, or the EWs of their emission lines are too small.


Up: The Hamburg/SAO survey for
Copyright ESO 2001