

Up: Doppler imaging of stellar
2 Observations
Table 1:
Spectroscopic log and radial velocity data (
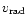 ).
).
| HJD |
Phase |
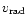 |
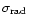 |
Rotation |
Tele- |
| (24+) |
(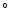 ) ) |
(kms-1) |
cycle |
scope |
| 50391.770 |
90.4 |
-77.5 |
1.5 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50392.661 |
103.3 |
-82.0 |
2.7 |
- |
NSO |
| 50393.748 |
119.0 |
-75.8 |
1.9 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50394.781 |
133.9 |
-78.5 |
1.8 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50395.602 |
145.7 |
-80.5 |
2.0 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50396.648 |
160.8 |
-78.5 |
2.0 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50398.713 |
190.4 |
-82.4 |
2.3 |
- |
NSO |
| 50400.629 |
218.2 |
-81.1 |
1.6 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50401.630 |
232.6 |
-79.6 |
2.4 |
- |
NSO |
| 50404.641 |
276.1 |
-83.2 |
2.0 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50405.617 |
290.1 |
-81.8 |
2.5 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50406.623 |
304.7 |
-80.9 |
1.9 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50408.624 |
333.5 |
-77.3 |
3.0 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50409.617 |
347.8 |
-82.0 |
2.3 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50411.618 |
16.7 |
-79.9 |
1.7 |
map 1 |
NSO |
|
50412.611 |
31.0 |
-80.9 |
1.8 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50413.609 |
45.4 |
-81.2 |
1.7 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50415.610 |
74.3 |
-80.1 |
1.7 |
map 1 |
NSO |
|
50416.623 |
88.9 |
-80.5 |
1.5 |
map 1 |
NSO |
| 50417.710 |
104.4 |
-78.9 |
2.3 |
- |
NSO |
| 50418.683 |
118.6 |
-80.4 |
1.2 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50419.597 |
131.8 |
-80.2 |
1.6 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50420.607 |
146.4 |
-80.3 |
1.8 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50421.690 |
162.0 |
-79.4 |
2.1 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50422.602 |
175.1 |
-79.6 |
1.3 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50423.609 |
189.7 |
-80.6 |
1.5 |
- |
NSO |
| 50424.701 |
205.4 |
-82.8 |
1.3 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50425.674 |
219.4 |
-79.3 |
1.7 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50426.693 |
234.1 |
-80.2 |
2.2 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50429.661 |
276.9 |
-79.4 |
2.1 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50430.682 |
291.7 |
-79.6 |
1.5 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50431.569 |
304.5 |
-81.7 |
2.0 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50432.603 |
319.4 |
-80.8 |
1.6 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50433.593 |
333.7 |
-81.5 |
1.7 |
- |
NSO |
| 50434.599 |
348.2 |
-81.4 |
2.1 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50436.645 |
17.6 |
-80.9 |
1.7 |
- |
NSO |
| 50438.592 |
45.7 |
-80.4 |
2.0 |
map 2 |
NSO |
| 50440.618 |
75.0 |
-79.8 |
2.3 |
map 2 |
NSO |
|
50441.604 |
89.3 |
-80.0 |
2.4 |
- |
NSO |
| 50445.594 |
146.9 |
-80.0 |
2.2 |
- |
NSO |
| 50446.595 |
161.3 |
-81.3 |
2.5 |
- |
NSO |
| 50450.682 |
220.0 |
-81.3 |
1.9 |
- |
NSO |
|
50457.625 |
320.4 |
-81.5 |
1.8 |
- |
NSO |
| 50821.638 |
170.3 |
-78.7 |
1.1 |
- |
KPNO |
| 50826.670 |
243.0 |
-80.0 |
1.0 |
- |
KPNO |
| 50828.628 |
271.4 |
-78.5 |
1.6 |
- |
KPNO |
| 50918.011 |
120.6 |
-79.0 |
1.0 |
- |
KPNO |
| 50921.003 |
163.4 |
-80.3 |
0.7 |
- |
KPNO |
Spectroscopic observations were obtained at the National Solar Observatory
(NSO) with the McMath-Pierce main telescope using the stellar spectrograph
from October 31, 1996 to January 8, 1997. The 800 800-pixel TI CCD
(TI-4 chip, 15
800-pixel TI CCD
(TI-4 chip, 15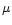 pixels) allowed for a resolving power of
pixels) allowed for a resolving power of  40000
and a useful wavelength range of about 45 Å around 6430 Å.
Two additional spectra in the 6430-Å region plus one spectrum in the
H
40000
and a useful wavelength range of about 45 Å around 6430 Å.
Two additional spectra in the 6430-Å region plus one spectrum in the
H region, along with corresponding reference spectra, were obtained
at Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO) with the coudé feed telescope in
December 1997/January 1998. A very similar 800
region, along with corresponding reference spectra, were obtained
at Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO) with the coudé feed telescope in
December 1997/January 1998. A very similar 800 800 TI CCD (TI-5 chip,
15
800 TI CCD (TI-5 chip,
15 pixels) was used in combination with grating A, camera 5, and the
long collimator. It allowed for a resolving power of 38000 and 22000 in the red
and the blue-wavelength regions, respectively, with a useful wavelength range
of between 50-80 Å. Two more spectra in the 6500-Å region included
H
pixels) was used in combination with grating A, camera 5, and the
long collimator. It allowed for a resolving power of 38000 and 22000 in the red
and the blue-wavelength regions, respectively, with a useful wavelength range
of between 50-80 Å. Two more spectra in the 6500-Å region included
H and were obtained with the same instrumental set-up at the
coudé feed telescope in April 1998 but utilized the 3096
and were obtained with the same instrumental set-up at the
coudé feed telescope in April 1998 but utilized the 3096 1024 CCD
(F3KB chip, 15
1024 CCD
(F3KB chip, 15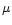 pixels). The resolving power was 28000, and the useful
wavelength range was 300 Å.
Table 1 is a summary of the spectroscopic observations.
Spectra taken after the second rotational cycle in early 1997 and spectra
with signal-to-noise ratios below 100:1 are not used for Doppler imaging
(these spectra are marked with a dash in Table 1).
pixels). The resolving power was 28000, and the useful
wavelength range was 300 Å.
Table 1 is a summary of the spectroscopic observations.
Spectra taken after the second rotational cycle in early 1997 and spectra
with signal-to-noise ratios below 100:1 are not used for Doppler imaging
(these spectra are marked with a dash in Table 1).
All data were reduced using IRAF![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif) and included bias subtraction, flat
fielding, cosmic-ray removal, and an optimal aperture extraction. The
exposure level obtained with an integration time of 30 min corresponds
to a signal-to-noise ratio of approximately 150:1.
Usually twenty flat-field exposures with a Tungsten reference lamp were
taken at the beginning of the night and again at the end of the night. These
forty flat fields were co-added and used to remove the pixel-to-pixel
variations in the stellar spectra. Spectra of bright radial-velocity
standards were obtained several times throughout the night to ensure an
accurate wavelength calibration. Radial velocities for the 1996/97 NSO data
and the two KPNO spectra from JD 2450826 and JD 2450828 were derived
from cross correlations with spectra of the IAU velocity standard
and included bias subtraction, flat
fielding, cosmic-ray removal, and an optimal aperture extraction. The
exposure level obtained with an integration time of 30 min corresponds
to a signal-to-noise ratio of approximately 150:1.
Usually twenty flat-field exposures with a Tungsten reference lamp were
taken at the beginning of the night and again at the end of the night. These
forty flat fields were co-added and used to remove the pixel-to-pixel
variations in the stellar spectra. Spectra of bright radial-velocity
standards were obtained several times throughout the night to ensure an
accurate wavelength calibration. Radial velocities for the 1996/97 NSO data
and the two KPNO spectra from JD 2450826 and JD 2450828 were derived
from cross correlations with spectra of the IAU velocity standard
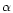 Ari (K2III,
Ari (K2III,
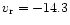 kms-1). The one spectrum from
JD 2450821 was cross correlated with
kms-1). The one spectrum from
JD 2450821 was cross correlated with 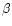 Gem (K0III,
Gem (K0III,
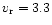 kms-1). 16Vir (K0.5III,
kms-1). 16Vir (K0.5III,
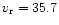 kms-1) was used for the
remaining spectra.
kms-1) was used for the
remaining spectra.
The photometric data in this paper were obtained with the Amadeus 0.75-m
automatic photoelectric telescope (APT), part of the University of Vienna
twin APT at Washington Camp in southern Arizona (Strassmeier et al. 1997).
The observations were made differentially with respect to HD218610 as the
comparison star (
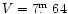 ,
,
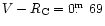 ,
,
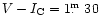 )
and
SAO91066 as the check star. The data cover the time interval
JD 2450395-459 (54 data points, season 1996/97),
JD 2450740-828 (80 data points, season 1997/98), and
JD 2450960-998 (47 data points, season 1998/99).
All photometry was transformed to match the Johnson-Cousins
)
and
SAO91066 as the check star. The data cover the time interval
JD 2450395-459 (54 data points, season 1996/97),
JD 2450740-828 (80 data points, season 1997/98), and
JD 2450960-998 (47 data points, season 1998/99).
All photometry was transformed to match the Johnson-Cousins
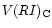 system.
system.


Up: Doppler imaging of stellar
Copyright ESO 2001