| Issue |
A&A
Volume 477, Number 1, January I 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 293 - 298 | |
| Section | The Sun | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078208 | |
| Published online | 06 November 2007 | |
Characteristics of plasma turbulence and radio emission from an interplanetary shock wave
1
Institute of Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, PO Box 291, Irkutsk, Russia e-mail: leden@iszf.irk.ru
2
Space Sciences Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, USA
3
Institute of Laser Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Irkutsk Branch, Russia
Received:
3
July
2007
Accepted:
6
October
2007
Aims.We investigate the characteristics of energetic electron beams, plasma turbulence and radio emission from interplanetary shock waves.
Methods.Numerical calculations of spectra and Landau damping of hot plasma eigen oscillations in the magnetic field are used.
Results.It is shown that the longitudinal wave spectrum, excited in
the solar wind plasma, extends with the increase of the refractive index n over range of values 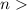 10. This result allows us to explain the broad band of emission, the constant value of the average ratio of frequency-band to radio emission frequency from interplanetary shock wave fronts, and to estimate the electron beam density and amplitude of Langmuir waves at the shock. It is shown that a spectrum of radio emission is determined by the spectrum of Langmuir waves excited upstream of the interplanetary shock wave by heated
electrons escaping from the shock wave front.
10. This result allows us to explain the broad band of emission, the constant value of the average ratio of frequency-band to radio emission frequency from interplanetary shock wave fronts, and to estimate the electron beam density and amplitude of Langmuir waves at the shock. It is shown that a spectrum of radio emission is determined by the spectrum of Langmuir waves excited upstream of the interplanetary shock wave by heated
electrons escaping from the shock wave front.
Key words: Sun: solar wind / Sun: radio radiation / shock waves
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


