| Issue |
A&A
Volume 481, Number 3, April III 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 651 - 659 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078285 | |
| Published online | 18 February 2008 | |
Star formation and bar instability in cosmological halos
1
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di Torino, Strada Osservatorio 20, 10025 Pino Torinese, Torino, Italy e-mail: curir@oato.inaf.it
2
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova, Vicolo Osservatorio 5, 35122 Padova, Italy
Received:
16
July
2007
Accepted:
1
February
2008
Context. This is the third in a series of papers presenting the first attempt to analyse the growth of the bar instability in a consistent cosmological scenario. In the previous two articles, we explored the role of the cosmology on stellar disks and the impact of the gaseous component on a disk embedded in a cosmological dark matter halo.
Aims. The aim of this paper is to point out the impact of the star formation on the bar instability inside disks having different gas fractions.
Methods. We performed cosmological simulations of the same disk-to-halo mass systems as in the previous works where the star formation was not triggered. We compared the results of the new simulations with the previous ones to investigate the effect of the star formation by analysing the morphology of the stellar components, the bar strength, the behaviour of the pattern speed. We followed the gas and the central mass concentration during the evolution and their impact on the bar strength.
Results. A stellar bar, lasting 10 Gyr,
is still living at 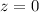 in all our cosmological simulations.
The central mass concentration of gas and of the new stars has a mild effect
on the ellipticity of the bar but is not able to destroy it, and at
in all our cosmological simulations.
The central mass concentration of gas and of the new stars has a mild effect
on the ellipticity of the bar but is not able to destroy it, and at 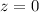 the
stellar bar strength is enhanced by the star formation.
The bar pattern speed decreases with the disk evolution.
the
stellar bar strength is enhanced by the star formation.
The bar pattern speed decreases with the disk evolution.
Key words: galaxies: spiral / galaxies: structure / galaxies: evolution / galaxies: halos / galaxies: kinematics and dynamics
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


