| Issue |
A&A
Volume 475, Number 2, November IV 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 443 - 451 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20077161 | |
| Published online | 17 September 2007 | |
VVDS-SWIRE*
Clustering evolution from a spectroscopic sample of galaxies with redshift 0.2 < z < 2.1 selected from Spitzer IRAC 3.6 μm and 4.5 μm photometry
1
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Marseille, UMR 6110 CNRS-Université de Provence, BP 8, 13376 Marseille Cedex 12, France e-mail: sylvain.delatorre@oamp.fr
2
INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera, via Brera 28, Milan, Italy
3
Department of Astronomy, Cornell University, Space Sciences Building, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA
4
Infrared Processing & Analysis Center, California Institute of Technology, MS 100-22, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA
5
Center for Astrophysics & Space Sciences, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093-0424, USA
6
IASF-INAF, via Bassini 15, 20133 Milano, Italy
7
Astronomy Centre, University of Sussex, Brighton BN1 9QH, UK
8
Geneva Observatory, ch. des Maillettes 51, 1290 Sauverny, Switzerland
9
Spitzer Science Center, California Institute of Technology, Mail Stop 314-6, 1200 East California Boulevard, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA
10
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de l'Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées (UMR 5572), 14 avenue E. Belin, 31400 Toulouse, France
11
IRA-INAF, via Gobetti, 101, 40129 Bologna, Italy
12
INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, via di Frascati 33, 00040 Monte Porzio Catone, Italy
13
INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, via Ranzani, 1, 40127 Bologna, Italy
14
Max Planck Institut fur Astrophysik, 85741, Garching, Germany
15
Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, UMR 7095, 98bis Bvd. Arago, 75014 Paris, France
16
School of Physics & Astronomy, University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham, NG72RD, UK
17
Astrophysical Institute Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany
18
Institute for Astronomy, 2680 Woodlawn Dr., University of Hawaii, Honolulu, 96822, Hawaii
19
Università di Bologna, Dipartimento di Astronomia, via Ranzani 1, 40127 Bologna, Italy
20
Observatoire de Paris, LERMA, 61 avenue de l'Observatoire, 75014 Paris, France
21
Centre de Physique Théorique, UMR 6207 CNRS-Université de Provence, 13288 Marseille, France
22
Integral Science Data Centre, Ch. d'Écogia 16, 1290 Versoix, Switzerland
23
INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, via Moiariello 16, 80131 Napoli, Italy
24
Centro de AstrofÃnsica da Universidade do Porto, Rua das Estrelas, 4150-762 Porto, Portugal
25
Universitá di Milano-Bicocca, Dipartimento di Fisica, Piazza delle Scienze 3, 20126 Milano, Italy
Received:
24
January
2007
Accepted:
26
July
2007
Aims.By combining data from the VIMOS VLT Deep Survey (VVDS) with the Spitzer
Wide-area InfraRed Extragalactic survey (SWIRE), we have built the
currently largest spectroscopic sample of high redshift galaxies selected in
the rest-frame near-infrared. We have obtained 2040 spectroscopic redshifts
of galaxies with 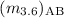 < 21.5 at 3.6 μm, and 1255 spectroscopic
redshifts of galaxies with
< 21.5 at 3.6 μm, and 1255 spectroscopic
redshifts of galaxies with 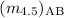 < 21. These allow us to
investigate the clustering evolution of galaxies selected via their
rest-frame near-infrared luminosity in the redshift range 0.2 < z < 2.1.
< 21. These allow us to
investigate the clustering evolution of galaxies selected via their
rest-frame near-infrared luminosity in the redshift range 0.2 < z < 2.1.
Methods.We use the projected two-point correlation function 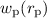 to study the
three dimensional clustering properties of galaxies detected at 3.6 μm
and 4.5 μm with the InfraRed Array Camera (IRAC) in the SWIRE survey
with measured spectroscopic redshifts from the first epoch VVDS. We compare
these properties to those of a larger sample of 16672 SWIRE galaxies for
which we have accurate photometric redshifts in the same field.
to study the
three dimensional clustering properties of galaxies detected at 3.6 μm
and 4.5 μm with the InfraRed Array Camera (IRAC) in the SWIRE survey
with measured spectroscopic redshifts from the first epoch VVDS. We compare
these properties to those of a larger sample of 16672 SWIRE galaxies for
which we have accurate photometric redshifts in the same field.
Results.We find that in the 3.6 μm and 4.5 μm flux limited samples, the
apparent correlation length does not change from redshift ~2 to the
present. The measured correlation lengths have a mean value of r0 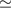 3.9±0.5 h-1 Mpc for the galaxies selected at 3.6 μm and a mean
value of r0
3.9±0.5 h-1 Mpc for the galaxies selected at 3.6 μm and a mean
value of r0 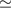 4.4±0.5 h-1 Mpc for the galaxies selected at
4.5 μm, across the whole redshift range explored. These values are
larger than those typicaly found for I-band selected galaxies at
IAB < 24, for which r0 varies from 2.69 h-1 Mpc to
3.63 h-1 Mpc between z = 0.5 to
4.4±0.5 h-1 Mpc for the galaxies selected at
4.5 μm, across the whole redshift range explored. These values are
larger than those typicaly found for I-band selected galaxies at
IAB < 24, for which r0 varies from 2.69 h-1 Mpc to
3.63 h-1 Mpc between z = 0.5 to  . We find that the difference in
correlation length between I-band and 3.6-4.5 μm selected samples
decreases with increasing redshift, becoming comparable at z
. We find that the difference in
correlation length between I-band and 3.6-4.5 μm selected samples
decreases with increasing redshift, becoming comparable at z 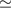 1.5. We
interpret this as evidence that galaxies with older stellar populations and
galaxies actively forming stars reside in comparably over-dense environments
at epochs earlier than z
1.5. We
interpret this as evidence that galaxies with older stellar populations and
galaxies actively forming stars reside in comparably over-dense environments
at epochs earlier than z 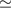 1.5, supporting the recently reported
flattening of the color-density relation at high redshift. The increasing
difference in correlation length with cosmic time observed between
rest-frame UV-optical and near-infrared selected samples could then be an
indication that star formation is gradually shifting to lower density
regions with decreasing redshift, while the older, passively evolving
galaxies remain in the most over-dense peaks.
1.5, supporting the recently reported
flattening of the color-density relation at high redshift. The increasing
difference in correlation length with cosmic time observed between
rest-frame UV-optical and near-infrared selected samples could then be an
indication that star formation is gradually shifting to lower density
regions with decreasing redshift, while the older, passively evolving
galaxies remain in the most over-dense peaks.
Key words: cosmology: observations / cosmology: large-scale structure of Universe / galaxies: evolution / galaxies: high-redshift / galaxies: statistics / infrared: galaxies
Based on data obtained with the European Southern Observatory Very Large Telescope, Paranal, Chile, program 070.A-9007(A), and on data obtained at the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope, operated by the CNRS of France, CNRC in Canada and the University of Hawaii, and observations obtained with MegaPrime/MegaCam, a joint project of CFHT and CEA/DAPNIA, at the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) which is operated by the National Research Council (NRC) of Canada, the Institut National des Science de l'Univers of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) of France, and the University of Hawaii. This work is based in part on data products produced at TERAPIX and the Canadian Astronomy Data Centre as part of the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey, a collaborative project of NRC and CNRS.
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


