| Issue |
A&A
Volume 422, Number 1, July IV 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 103 - 111 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20047148 | |
| Published online | 06 July 2004 | |
Log-parabolic spectra and particle acceleration in blazars*
II. The BeppoSAX wide band X-ray spectra of Mkn 501
1
Dipartimento di Fisica, Università La Sapienza, Piazzale A. Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy
2
IASF - Sezione di Roma, INAF-CNR, via del Fosso del Cavaliere, 00113 Roma, Italy
3
ASI Science Data Center, ESRIN, 00044 Frascati, Italy
Corresponding author: E. Massaro, enrico.massaro@uniroma1.it
Received:
27
January
2004
Accepted:
13
April
2004
We present the results of a spectral and temporal study of the complete set of
BeppoSAX NFI (11) and WFC (71) observations of the BL Lac object Mkn 501.
The WFC 2–28 keV data, reported here for the first time, were collected over
a period of about five years, from September 1996 to October 2001.
These observations, although not evenly distributed, show that Mkn 501,
after going through a very active phase from spring 1997 to early 1999,
remained in a low brightness state until late 2001.
The data from the LECS, MECS and PDS instruments, covering the wide energy
interval 0.1–150 keV, have been used to study in detail the spectral
variability of the source.
We show that the X-ray energy distribution of Mkn 501 is well described by a
log-parabolic law in all luminosity states.
This model allowed us to obtain good estimates of the SED synchrotron peak
energy and of its associated power.
The strong spectral variability observed, consisting of strictly correlated
changes between the synchrotron peak energy and bolometric flux
(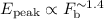 ), suggests that the main physical changes
are not only due to variations of the maximum Lorentz factor of the emitting
particles but that other quantities must be varying as well.
During the 1997 flare the high energy part of the spectrum of Mkn 501
shows evidence of an excess above the best fit log-parabolic law suggesting the
existence of a second emission component that may be responsible for most of the
observed variability.
), suggests that the main physical changes
are not only due to variations of the maximum Lorentz factor of the emitting
particles but that other quantities must be varying as well.
During the 1997 flare the high energy part of the spectrum of Mkn 501
shows evidence of an excess above the best fit log-parabolic law suggesting the
existence of a second emission component that may be responsible for most of the
observed variability.
Key words: radiation mechanisms: non-thermal / galaxies: active / galaxies: BL Lacertae objects: individual: Mkn 501 / X-rays: galaxies
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


