| Issue |
A&A
Volume 419, Number 2, May IV 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 527 - 531 | |
| Section | Galactic structure, stellar clusters, and populations | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20035947 | |
| Published online | 03 May 2004 | |
The contribution of halo red giant mass loss to the high-velocity gas falling onto the Milky Way disk
Sternwarte, Universität Bonn, Auf dem Hügel 71, 53121 Bonn, Germany
Corresponding author: deboer@astro.uni-bonn.de
Received:
24
December
2003
Accepted:
10
February
2004
The origin of gas falling from the halo
toward the disk of the Milky Way is still largely unclear.
Here the amount of gas shed by the (older) halo red giants is estimated.
The distribution of red giants (RGs) in the halo is not known
but that of a subset of stars in the post RG phase,
the sdB stars of the horizontal-branch (HB), is.
Using the mid-plane density and z-distribution of sdB stars,
the ratio of sdB stars to all HB stars, and the RG mass loss,
the infall due to total mass lost by all halo RG stars at 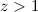 kpc
is calculated.
For the extended halo component
kpc
is calculated.
For the extended halo component
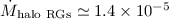
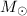 kpc-2 yr-1
while the thick disk component RGs contribute
kpc-2 yr-1
while the thick disk component RGs contribute
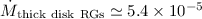
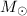 kpc-2 yr-1,
each with an uncertainty of a factor 4.
The total rate of infall due to RG mass-loss is
kpc-2 yr-1,
each with an uncertainty of a factor 4.
The total rate of infall due to RG mass-loss is
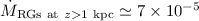
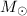 kpc-2 yr-1,
a sizeable fraction
of the equally uncertain observed rate of infall of material.
Since most of the RG stars in the extended halo are old,
their mass loss is predominantly metal-poor,
while that of the disk RGs is more metal-rich.
The galactic fountain flow provides additional metal-rich infall
and small galaxies being accreted contribute to the infall of gas as well.
kpc-2 yr-1,
a sizeable fraction
of the equally uncertain observed rate of infall of material.
Since most of the RG stars in the extended halo are old,
their mass loss is predominantly metal-poor,
while that of the disk RGs is more metal-rich.
The galactic fountain flow provides additional metal-rich infall
and small galaxies being accreted contribute to the infall of gas as well.
Key words: Galaxy: halo / Galaxy: structure / Galaxy: evolution
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


