| Issue |
A&A
Volume 417, Number 2, April II 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 401 - 409 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20034365 | |
| Published online | 19 March 2004 | |
The importance of dust in cooling and heating the InterGalactic Medium
Centre d'Études Spatiales des Rayonnements, 9 avenue du Colonel Roche, 31022 Toulouse, France
Corresponding author: L. A. Montier, montier@cesr.fr
Received:
19
September
2003
Accepted:
18
December
2003
Recent observations at low and high redshift seem to confirm the
presence of dust in the InterGalactic Medium (IGM) and especially in
the IntraCluster Medium (ICM), at very low abundances. We have studied
the impact of this dust on the IGM conditions, in terms of heating and
cooling. Firstly we have described the dust emission by an analytical model, and we have proved that the dust IR emission can be
considered as the dominant cooling
agent of the ICM, when the temperature is greater than 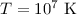 and the dust-to-gas mass ratio exceeds a value of
and the dust-to-gas mass ratio exceeds a value of  . This cooling process is more efficient for small grains, and
fills the gap between the cooling by free-free emission at
. This cooling process is more efficient for small grains, and
fills the gap between the cooling by free-free emission at 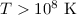 and other cooling processes
such as recombination, collisional ionisation and collisional
excitation at
and other cooling processes
such as recombination, collisional ionisation and collisional
excitation at 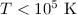 . Secondly, when the UV
Background is strong
enough,
. Secondly, when the UV
Background is strong
enough, 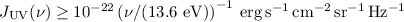 , and the
temperature is low enough,
, and the
temperature is low enough, 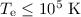 , dust grains
become an efficient heating agent of the IGM. Moreover these two opposite
processes due to dust have opposite impact on the IGM at different
scales: the cooling should be dominant at large scale (in the ICM),
whereas the heating
is efficient at small scale (near quasars or star formation
regions). The issue of the dust replenishment of the IGM is also
considered, taking into account the process of galactic dust ejection and
intergalactic dust production. The recent
observations of an intergalactic star population and the estimate of
the reionisation (pop III stars) at
, dust grains
become an efficient heating agent of the IGM. Moreover these two opposite
processes due to dust have opposite impact on the IGM at different
scales: the cooling should be dominant at large scale (in the ICM),
whereas the heating
is efficient at small scale (near quasars or star formation
regions). The issue of the dust replenishment of the IGM is also
considered, taking into account the process of galactic dust ejection and
intergalactic dust production. The recent
observations of an intergalactic star population and the estimate of
the reionisation (pop III stars) at 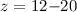 , both point toward dust
pollution of the IGM early in the cosmic history,
with possible important consequences for the evolution scenarii of the
Universe.
, both point toward dust
pollution of the IGM early in the cosmic history,
with possible important consequences for the evolution scenarii of the
Universe.
Key words: galaxies: intergalactic medium / ISM: dust extinction / galaxies: cluster: general
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


