| Issue |
A&A
Volume 414, Number 2, February I 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 777 - 794 | |
| Section | Astronomical instrumentation | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20031489 | |
| Published online | 19 January 2004 | |
The effect of signal digitisation in CMB experiments
1
INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste, Via G. B. Tiepolo 11, 34131, Trieste, Italy
2
Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Milano, Via Celoria 16, 20131, Milano, Italy
3
IASF/CNR, Sezione di Bologna, Via Gobetti 101, 40129, Bologna, Italy
4
IASF/CNR, Sezione di Milano, Via Bassini 15, 20131, Milano, Italy
Corresponding author: M. Maris, maris@ts.astro.it
Received:
2
April
2003
Accepted:
15
September
2003
Signal digitisation may produce significant effects in balloon –
borne or space CMB experiments, when the limited bandwidth for
downlink of data requires loss-less data compression. In fact,
the data compressibility depends on the quantization step q
applied on board by the instrument acquisition chain. In this
paper we present a study of the impact of the quantization error
in CMB experiments using, as a working case, simulated data from
the Planck/LFI 30 and 100 GHz channels.
At TOD level, the effect of the quantization can be approximated
as a source of nearly normally distributed noise, with RMS 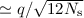 , with deviations from normality
becoming relevant for a relatively small number of repeated
measures
, with deviations from normality
becoming relevant for a relatively small number of repeated
measures 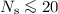 . At map level, the data
quantization alters the noise distribution and the expectation of
some higher order moments. We find a constant ratio,
. At map level, the data
quantization alters the noise distribution and the expectation of
some higher order moments. We find a constant ratio,  , between the RMS of the quantization
noise and RMS of the instrumental noise, σ over the map
(
, between the RMS of the quantization
noise and RMS of the instrumental noise, σ over the map
(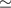 0.14 for
0.14 for 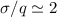 ),
while, for
),
while, for  , the bias on the expectation for
higher order moments is comparable to their sampling variances.
Finally, we find that the quantization introduces a power excess,
, the bias on the expectation for
higher order moments is comparable to their sampling variances.
Finally, we find that the quantization introduces a power excess,
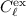 , that, although related to the instrument and
mission parameters, is weakly dependent on the multipole
, that, although related to the instrument and
mission parameters, is weakly dependent on the multipole  at
middle and large
at
middle and large  and can be quite accurately subtracted.
For
and can be quite accurately subtracted.
For 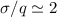 , the residual uncertainty,
, the residual uncertainty, 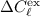 , implied by this subtraction is only
, implied by this subtraction is only
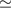 1–2% of the RMS uncertainty,
1–2% of the RMS uncertainty, 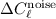 ,
on
,
on  reconstruction due to the noise power,
reconstruction due to the noise power,
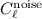 . Only for
. Only for 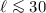 the quantization
removal is less accurate; in fact, the
the quantization
removal is less accurate; in fact, the  noise features,
although efficiently removed, increase
noise features,
although efficiently removed, increase 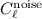 ,
, 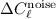 ,
, 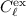 and then
and then 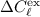 ;
anyway, at low multipoles
;
anyway, at low multipoles 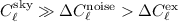 .
This work is based on Planck LFI activities.
.
This work is based on Planck LFI activities.
Key words: methods: data analysis / statistical; cosmology: cosmic microwave background
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


