| Issue |
A&A
Volume 413, Number 2, January II 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 465 - 476 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20034172 | |
| Published online | 18 December 2003 | |
Analysis of two-point statistics of cosmic shear
II. Optimizing the survey geometry
1
Institut f. Astrophysik u. Extr. Forschung, Universität Bonn, Auf dem Hügel 71, 53121 Bonn, Germany
2
Max-Planck-Institut f. Astrophysik, Postfach 1317, 85741 Garching, Germany
Corresponding author: M. Kilbinger, kilbinge@astro.uni-bonn.de
Received:
8
August
2003
Accepted:
30
September
2003
We present simulations of a cosmic shear survey and show how
the survey geometry influences the accuracy of determination of
cosmological parameters. We numerically calculate the full covariance
matrices  of two-point statistics of cosmic shear, based on the
expressions derived in the first paper of this series. The individual
terms are compared for two survey geometries with large and small cosmic variance.
We use analyses based on maximum likelihood of
of two-point statistics of cosmic shear, based on the
expressions derived in the first paper of this series. The individual
terms are compared for two survey geometries with large and small cosmic variance.
We use analyses based on maximum likelihood of  and the Fisher
information matrix in order to derive expected constraints on
cosmological parameters. As an illustrative example, we simulate various
survey geometries consisting of 300 individual fields of
and the Fisher
information matrix in order to derive expected constraints on
cosmological parameters. As an illustrative example, we simulate various
survey geometries consisting of 300 individual fields of 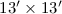 size, placed (semi-)randomly into patches
which are assumed to be widely separated on the sky and therefore uncorrelated.
Using the aperture mass statistics
size, placed (semi-)randomly into patches
which are assumed to be widely separated on the sky and therefore uncorrelated.
Using the aperture mass statistics 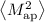 , the optimum
survey consists of 10 patches with 30 images in each patch. If
, the optimum
survey consists of 10 patches with 30 images in each patch. If 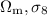 and Γ are supposed to be extracted from the data, the
minimum variance bounds on these three parameters are 0.17, 0.25 and
0.04 respectively. These variances increase slightly when the initial power
spectrum index ns is also to be determined from the data. The
cosmological constant is only poorly constrained.
and Γ are supposed to be extracted from the data, the
minimum variance bounds on these three parameters are 0.17, 0.25 and
0.04 respectively. These variances increase slightly when the initial power
spectrum index ns is also to be determined from the data. The
cosmological constant is only poorly constrained.
Key words: cosmology: observations / gravitational lensing / cosmology: large-scale structure of Universe
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


