| Issue |
A&A
Volume 388, Number 1, June II 2002
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 235 - 245 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20020473 | |
| Published online | 28 May 2002 | |
Modelling of the surface magnetic field in neutron stars: Application to radio pulsars
1
Institute of Astronomy, University of Zielona Góra, Lubuska 2, 65-265, Zielona Góra, Poland
2
Center for Plasma Astrophysics, Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory, Al.Kazbegi ave. 2a, Tbilisi 380060, Georgia
3
Max-Planck Institute for Radioastronomy, Auf dem Hügel 69, 53121 Bonn, Germany
Corresponding author: J. A. Gil, jag@astro.ca.wsp.zgora.pl
Received:
27
November
2001
Accepted:
25
March
2002
We propose a vacuum gap (VG) model which can be applied
uniformly for normal and high-magnetic-field pulsars. The model
requires a strong and non-dipolar surface magnetic field near the
pulsar polar cap. We assume that the actual surface magnetic field Bs in pulsars results from the superposition of a global
dipole field Bd and a crust-anchored small scale magnetic
anomaly Bm. We provide a numerical formalism for
modelling such structures of the surface magnetic field and explore it
within the framework of the VG model, which requires strong surface
fields 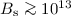 G. Thus, in order to increase the
resultant surface field to values exceeding 1013 G, in low
magnetic field pulsars with
G. Thus, in order to increase the
resultant surface field to values exceeding 1013 G, in low
magnetic field pulsars with 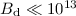 G it is required that
G it is required that
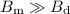 , with the same polarities (orientations) of
Bd and Bm. However, if the polarities are opposite,
the resultant surface field can be lower than the dipolar surface
component inferred from the pulsar spin-down. We propose that
high-magnetic-field pulsars (HBPs) with the inferred global dipole
field Bd exceeding the so-called photon splitting threshold
, with the same polarities (orientations) of
Bd and Bm. However, if the polarities are opposite,
the resultant surface field can be lower than the dipolar surface
component inferred from the pulsar spin-down. We propose that
high-magnetic-field pulsars (HBPs) with the inferred global dipole
field Bd exceeding the so-called photon splitting threshold
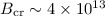 G, can generate observable radio
emission “against the odds”, provided that the surface dipolar
magnetic field Bd is reduced below Bcr by the magnetic
anomaly Bm of the right strength and polarity. We find that
effective reduction is possible if the values of Bd and Bm
are of the same order of magnitude, which would be expected in
HBPs with
G, can generate observable radio
emission “against the odds”, provided that the surface dipolar
magnetic field Bd is reduced below Bcr by the magnetic
anomaly Bm of the right strength and polarity. We find that
effective reduction is possible if the values of Bd and Bm
are of the same order of magnitude, which would be expected in
HBPs with 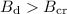 . The proposed VG model of radio emission
from HBPs, in which pair production occurs directly above the polar
cap, is an alternative to the recently proposed lengthened
space-charge-limited-flow (SCLF) model, in which the pair formation
front is
located at relatively high altitudes, where the dipole field is
degraded below Bcr. Our model allows high Bd radio-loud
pulsars not only just above Bcr but even above
. The proposed VG model of radio emission
from HBPs, in which pair production occurs directly above the polar
cap, is an alternative to the recently proposed lengthened
space-charge-limited-flow (SCLF) model, in which the pair formation
front is
located at relatively high altitudes, where the dipole field is
degraded below Bcr. Our model allows high Bd radio-loud
pulsars not only just above Bcr but even above 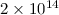 G, which is the upper limit for HBPs within the
lengthened SCLF model.
G, which is the upper limit for HBPs within the
lengthened SCLF model.
Key words: pulsars: general
© ESO, 2002
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


