| Issue |
A&A
Volume 384, Number 2, MarchIII 2002
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 654 - 665 | |
| Section | Planets and planetary systems | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20020028 | |
| Published online | 15 March 2002 | |
Very Long Baseline Interferometer measurements of turbulence in the inner solar wind
1
Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa 52242, USA
2
Istituto di Radioastronomia del CNR, Via Gobetti 101, 40129 Bologna, Italy
3
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 53121 Bonn, Germany
Corresponding author: S. Spangler, srs@astro.physics.uiowe.edu
Received:
3
July
2001
Accepted:
4
January
2002
Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) observations were made of six sources in
September and 1998. The observations were made at a time when the solar
elongations of five of those sources ranged from 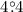 to
to  , so that the
lines of sight to these sources passed at distances of closest approach to the Sun of 16.5 to
25.3
, so that the
lines of sight to these sources passed at distances of closest approach to the Sun of 16.5 to
25.3 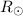 . The solar elongation of the sixth source was
. The solar elongation of the sixth source was  , corresponding
to a distance of
, corresponding
to a distance of  .
The observations were made with the Medicina and Noto antennas of the
Istituto di Radioastronomia, the Matera (Italy) antenna of the Agenzia Spaziale
Italiana, and the Wettzell (Germany) antenna of the Bundesamt für Kartographie und
Geodäsie. On two of the three days of observation (September 24 and
October 15, 1998) simultaneous observations were made at 8.380 (X band) and
2.257 (S band) GHz. In the third observing session (September 25, 1998) observations
were made at 4.981 GHz (C band). Temporal fluctuations in the interferometer phase, induced
by the solar wind, were analysed to yield information on plasma turbulence in the
inner heliosphere. The results of this investigation are as follows.
(1) The measured interferometer phase power spectra are consistent
with a theoretical expression which incorporates independent information on solar wind
turbulence. (2) The values for
.
The observations were made with the Medicina and Noto antennas of the
Istituto di Radioastronomia, the Matera (Italy) antenna of the Agenzia Spaziale
Italiana, and the Wettzell (Germany) antenna of the Bundesamt für Kartographie und
Geodäsie. On two of the three days of observation (September 24 and
October 15, 1998) simultaneous observations were made at 8.380 (X band) and
2.257 (S band) GHz. In the third observing session (September 25, 1998) observations
were made at 4.981 GHz (C band). Temporal fluctuations in the interferometer phase, induced
by the solar wind, were analysed to yield information on plasma turbulence in the
inner heliosphere. The results of this investigation are as follows.
(1) The measured interferometer phase power spectra are consistent
with a theoretical expression which incorporates independent information on solar wind
turbulence. (2) The values for  , the normalization constant of the density power
spectrum, are reasonably consistent with a previously-determined expression for
, the normalization constant of the density power
spectrum, are reasonably consistent with a previously-determined expression for
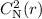 , where r is the heliocentric distance, although the new values for
, where r is the heliocentric distance, although the new values for  are
systematically high with respect to this prior expression. (3) Our estimates for
the speed at which the irregularities move with respect to
the antennas, and in the radial direction from the Sun, are in the range of
190–340 km s-1 for heliocentric distances of 16–26
are
systematically high with respect to this prior expression. (3) Our estimates for
the speed at which the irregularities move with respect to
the antennas, and in the radial direction from the Sun, are in the range of
190–340 km s-1 for heliocentric distances of 16–26 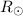 . These values are in
good agreement with observational estimates of the solar wind flow speed in this part of
space based on coronagraph observations. The speeds are lower than the sum of the estimated
solar wind flow speed and the local Alfvén speed. The potential significance of this
result is discussed.
. These values are in
good agreement with observational estimates of the solar wind flow speed in this part of
space based on coronagraph observations. The speeds are lower than the sum of the estimated
solar wind flow speed and the local Alfvén speed. The potential significance of this
result is discussed.
Key words: solar wind / Sun: corona / turbulence
© ESO, 2002
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


