Fig. 3
Download original image
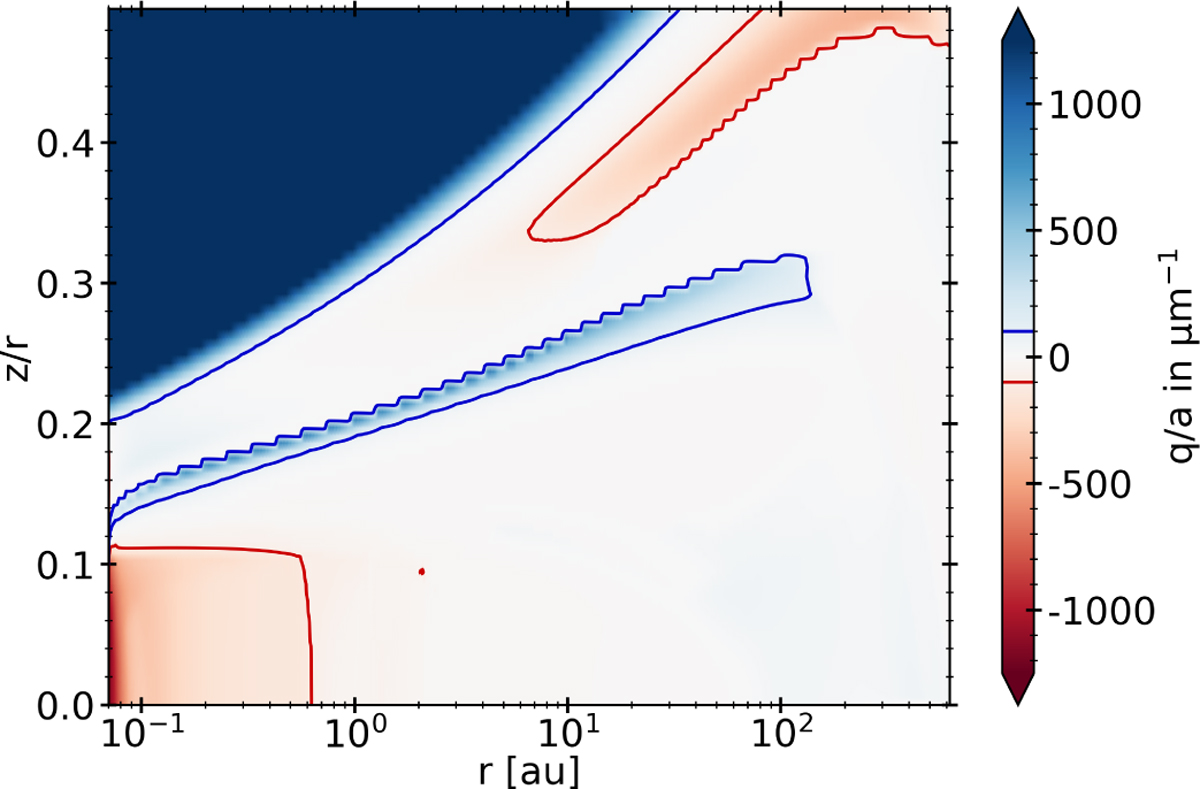
Illustration of how the charge per dust grain radius (q/a) [μm−1 ] changes within the whole disk. For large areas of the disk, the dust is mostly neutral. In the upper areas that are largely affected by photodissociation, we find that dust charges very positively (> 100, blue contour lines). In the areas of the midplane closest to the star, we find that the dust charges very negatively (< −100, red contour lines).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


