Fig. 4.
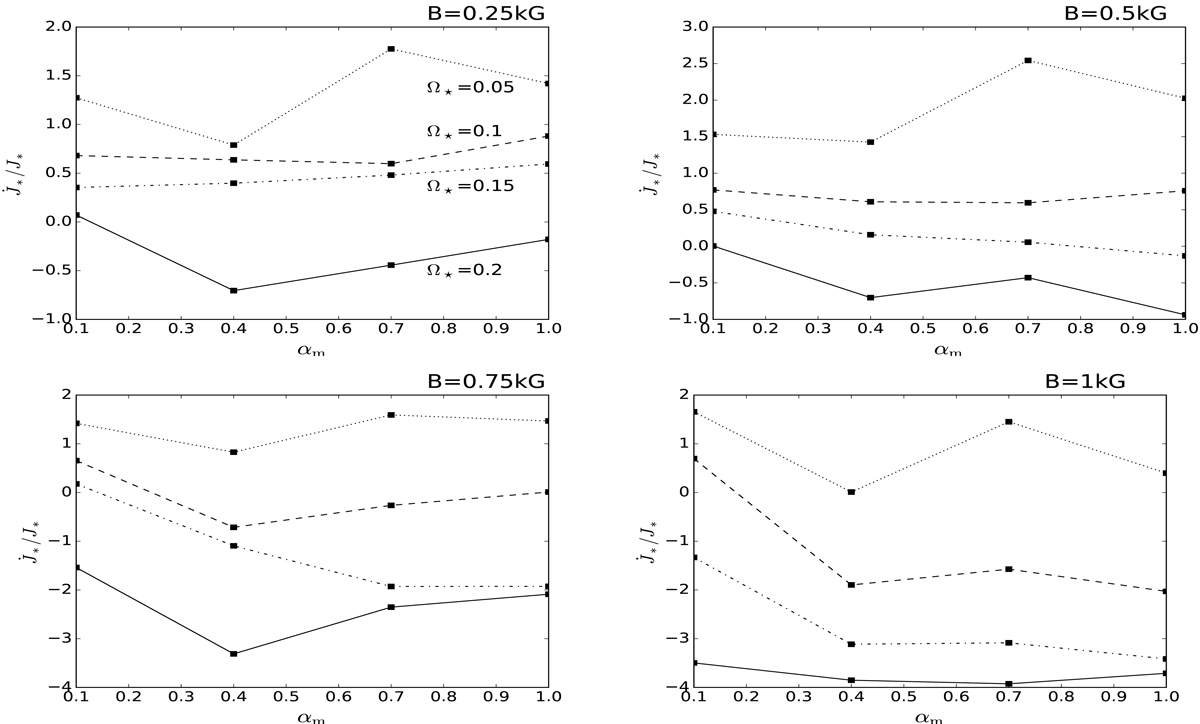
Average angular momentum flux transported onto the stellar surface by the matter in-falling from the disk onto the star through the accretion column. Each panel shows a set of solutions with one stellar magnetic field strength and varying stellar rotation rate and resistivity. Results with Ω⋆/Ωbr = 0.05 (dotted), 0.1 (dashed), 0.15 (dash-dot-dotted), and 0.2 (solid) are shown in units of stellar angular momentum ![]() (with k2 = 0.2 for the typical normalized gyration radius of a fully convective star). A positive flux spins the star up, a negative flux slows it down. With the increase in stellar rotation rate, spin-up of the star by the infalling matter decreases and eventually switches to spin-down.
(with k2 = 0.2 for the typical normalized gyration radius of a fully convective star). A positive flux spins the star up, a negative flux slows it down. With the increase in stellar rotation rate, spin-up of the star by the infalling matter decreases and eventually switches to spin-down.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


