Fig. 2
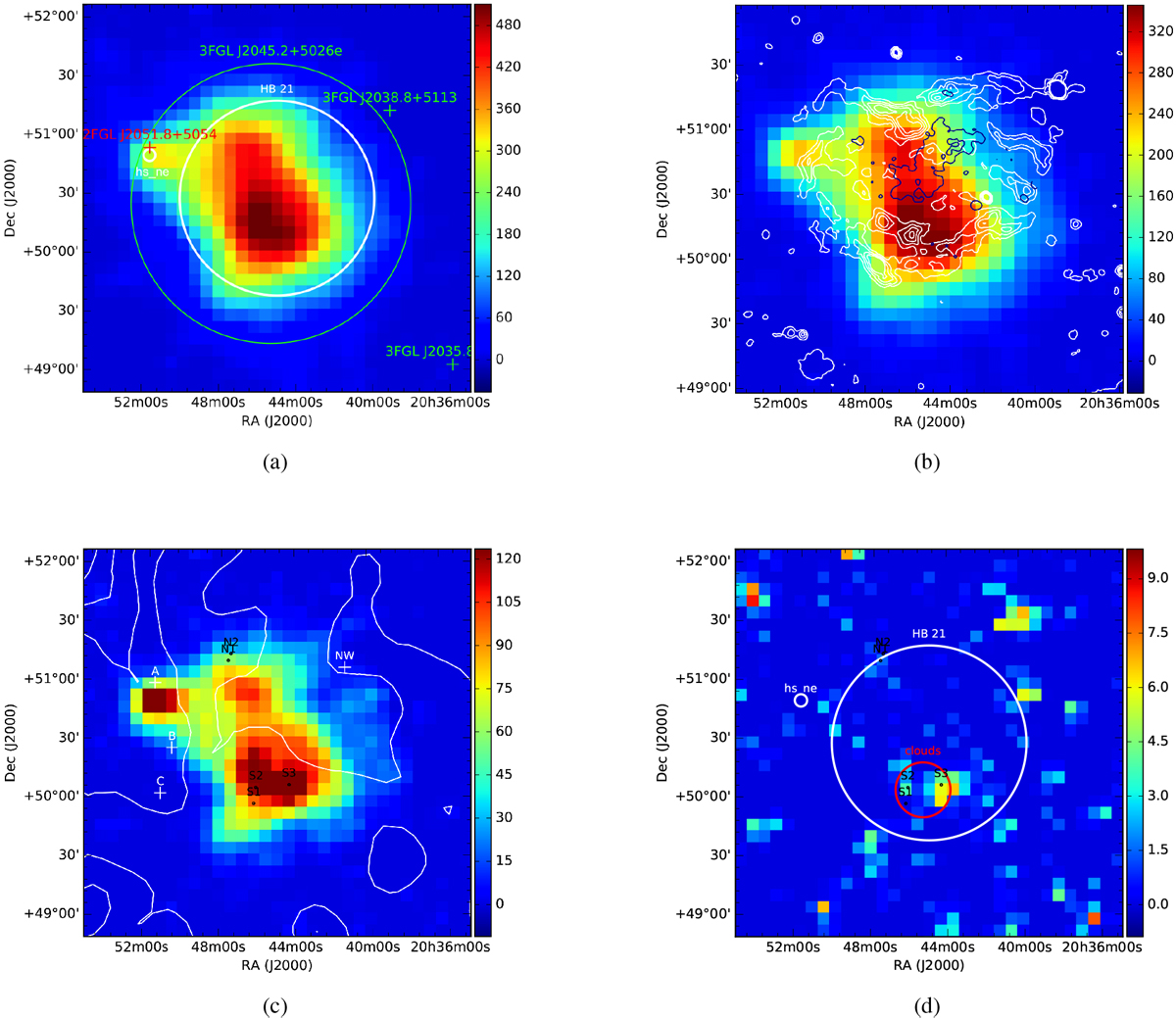
Test statistic map of the selected ROI around the SNR HB 21. The map in panel a is computed in the whole energy interval considered for the analysis, i.e., above 60 MeV. Overlaid to this map, the 3FLG sources are reported; 3FGL J2045.2+5026e is also included and defined in the catalog as a disk-type geometry with a radius of 1°.19 (green markers). The best-fit model for the SNR HB 21 as found in this work is also shown (disk-type geometry with a radius of 0°.83), together with the nearby hotspot hs_ne (white regions). The position of the point source 2FGL J2051.8+5054 is presented as well (red cross). Panel b: TS map above 500 MeV is presented, together with the contours of radio continuum emission at 4850 MHz (white) and the ROSAT X-ray (dark blue) contours. The ROSAT data are available at https://skyview.gsfc.nasa.gov/current/cgi/titlepage.pl. Panel c: for energies above 1 GeV. On top of the TS map, the CO contours are reported in white. The CO distribution are taken from Dame et al. (2001) and integrated between −20 and 10 km s−1: six contour levels are linearly spaced from 1.5 to 28 K km s−1. We also show the position of the shocked CO clumps S1, S2, S3, N1, N2 (black circles; Koo et al. 2001) and clouds A, B, C (Tatematsu et al. 1990) and NW (Byun et al. 2006; white crosses). Panel d: TS map of the residual emission of the best modeling of the SNR and the hotspot (white regions) is shown above 1 GeV. In addition, the position of the shocked CO clumps is reported, together with the estimated cloud region (red region).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


