Fig. 1
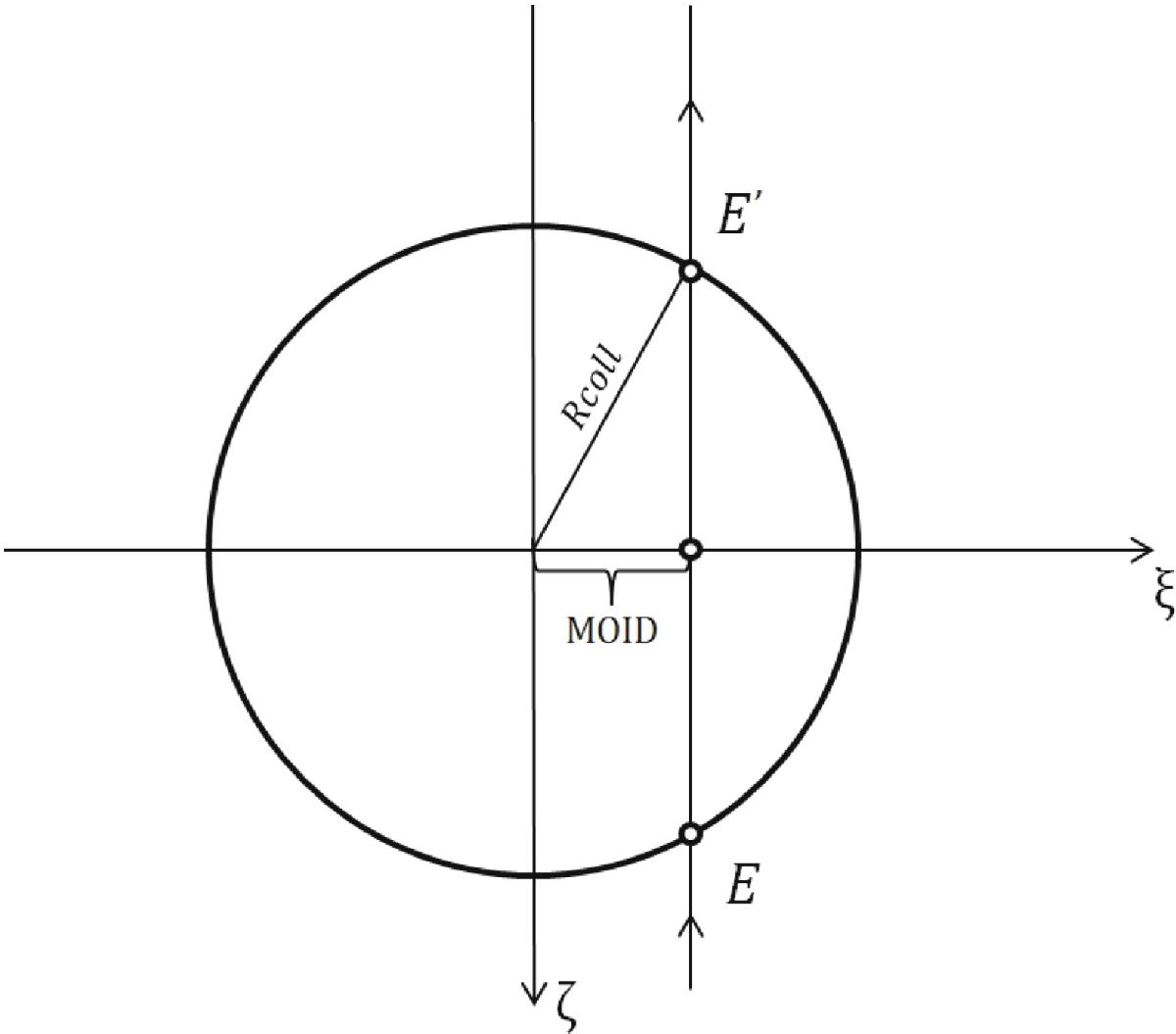
Illustration of the MOID-chord method of calculating the random probability of collision with a target planet, given a known value of the minimum orbit intersection distance (MOID). The target’s collisional radius defines a circle in the b-plane, and the time it takes for the target’s projection to move the distance EE′ divided by its orbital period gives the probability. From Rickman et al. (2014) with permission.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


