Free Access
Fig. 11
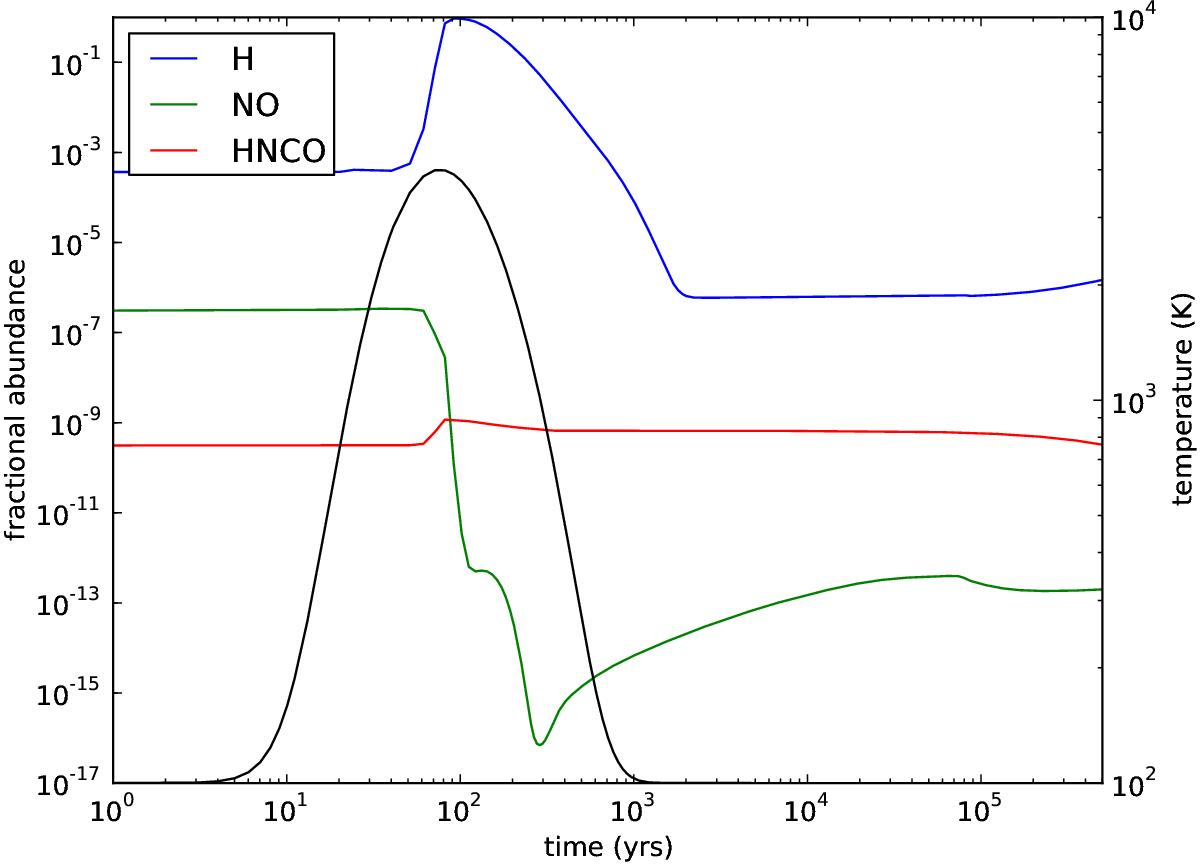
Chemical shock modelling showing H, NO, and HNCO. This is fast (60 km s-1) shock model 7. The rapid decrease in NO is due to reaction with H. HNCO requires NO to form and therefore does not increase in abundance after the shock, in contrast to what is found in both slow (20 km s-1) and non shocked models.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


