- ... spectra
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Appendix A, Figs. 3-5 are only available in electronic form at http://www.aanda.org
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... fluxes
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- I.e., where the source extent was
smaller than the largest angular scale which can be mapped by the VLA
in the given configuration and frequency band.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... 22.5 GHz
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Note, however, that a steeper power-law fit to the high frequency radio data would not fit the
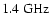 and
and
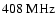 data points.
data points.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
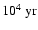
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Type 1b and type II SNe are thought to be the source of the synchrotron emission in ULIRGs, and occur by the core-collapse of stars more massive than
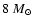 .
The difference in lifetime between a star of
.
The difference in lifetime between a star of
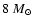 and a star of
and a star of
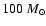 is
is  5
5 
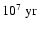 .
Therefore, for a normal initial mass function, even if the stars formed instantaneously, the SN rate cannot show large variations on timescales as short as
.
Therefore, for a normal initial mass function, even if the stars formed instantaneously, the SN rate cannot show large variations on timescales as short as
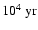 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.