For comparison we add MRC1138-262 from Nesvadba et al. (2006b). Column (1) - source name.
Column (2) - extent of the optical line emission in kpc along the major and minor axis, respectively. Column (3) - velocity offset between the blue and redshifted bubble in km s-1 in the rest-frame. Column (4) - age of the outflow for constant 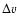 and neglecting projection effects in 107 yrs. Column (5) - energy injection necessary to power the outflow in erg s-1 (``method 1'', see Sect. 5.5 for details), and mass estimates based on the measured H
and neglecting projection effects in 107 yrs. Column (5) - energy injection necessary to power the outflow in erg s-1 (``method 1'', see Sect. 5.5 for details), and mass estimates based on the measured H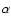 fluxes, uncorrected for extinction. This serves as a strict lower limit to the kinetic energy injection. Column (6) - the same as Col. (5), but using extinction-corrected H fluxes, uncorrected for extinction. This serves as a strict lower limit to the kinetic energy injection. Column (6) - the same as Col. (5), but using extinction-corrected H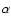 fluxes. Column (7) - energy injection necessary to inflate a hot bubble in erg s-1 (``method 2'', see Sect. 5.5 for details). fluxes. Column (7) - energy injection necessary to inflate a hot bubble in erg s-1 (``method 2'', see Sect. 5.5 for details).
|