All Tables
- Table 1:
Dense cores covered by the c2d MAMBO survey. The table lists,
from left to right, the core name adopted within the c2d
collaboration, names for the cores adopted by other authors, the
core distance, the type of the core (i.e., starless, YSO,
or VeLLO), the approximate galactic environment of the dense
core, and whether Spitzer data is available for the core. The last
column gives a rough description of the morphology of the subcores (i.e.,
extended substructures; see Sect. 3.2)
within each core using the c2d standard morphology keywords (Enoch et al. 2006, see Sect. 3.3 for a description).
- Table 2:
MAMBO map details. For each core the products ``number of maps''
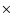 ``array type'' list how often a core was observed with which array (``37'' for MAMBO-1 and ``117'' for MAMBO-2). Several products are given if a dense core was observed with both arrays. The last column lists the minimum noise level in a map after smoothing to
``array type'' list how often a core was observed with which array (``37'' for MAMBO-1 and ``117'' for MAMBO-2). Several products are given if a dense core was observed with both arrays. The last column lists the minimum noise level in a map after smoothing to
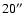 resolution.
resolution.
- Table 6:
IRAS sources in the MAMBO maps that are not detected as MAMBO emission
peaks. For every core in the c2d MAMBO survey the table lists sources from the IRAS Point Source Catalogue and the IRAS Faint Source Catalogue (preceded by an ``F''), and the subcores in which the IRAS sources are located, if applicable. Objects from the IRAS Point Source and Faint Source catalogues present in both catalogues are connected. The last column gives the spectral index between 12 and
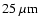 wavelength.
wavelength.
- Table 7:
Properties of MAMBO-detected IRAS sources. For every core in
the c2d MAMBO survey the table lists dust emission peaks and, if
applicable, the related subcore associated with an IRAS source
(Sect. 4.1 discusses the identification of
associated sources; FSC sources are preceded by an ``F''). Associated 2MASS sources are
listed too. The table further lists the spectral index between 12 and
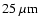 wavelength, the bolometric temperature and luminosity, the submillimetre-to-bolometric luminosity ratio, the mass within a peak-centered aperture of 4200 AU radius,
and the infrared SED class.
wavelength, the bolometric temperature and luminosity, the submillimetre-to-bolometric luminosity ratio, the mass within a peak-centered aperture of 4200 AU radius,
and the infrared SED class.
- Table 8:
Properties of MAMBO detected c2d Spitzer sources. Like Table
7, but now listing sources from Spitzer point
source catalogues and giving the spectral index between 2.2 and
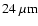 wavelength. VeLLO candidates are marked in the
class designation.
wavelength. VeLLO candidates are marked in the
class designation.
- Table 9:
Prominent YSOs detected in Spitzer data not taken by c2d, and related IRAS sources, if existing.
- Table 10:
Cores in the c2d MAMBO survey with YSOs uncovered by c2d
that were believed to be starless at the beginning of the c2d
survey. Comments on outflows refer to jet-like extended
(
 )
features in IRAC images.
)
features in IRAC images.
- Table 11:
Starless cores that fulfill at least one criteria
for an advanced evolutionary state, as well as VeLLO candidate cores. Brackets for VeLLOs indicate that
 does not fulfill the criterion for evolved cores after correcting for internal luminosity.
does not fulfill the criterion for evolved cores after correcting for internal luminosity.
- Table 12:
YSO offsets from dust emission peaks. For each dust emission peak, and related subcore, associated with a YSO listed in Tables 7 and 8 we give the chosen reference source (preferentially seen by Spitzer) and the observed offset and position angle (i.e., position of star w.r.t. the dust emission peak).
- Table 3:
General data on subcores. Bracketed and starred subcore designations indicate subcores with uncertain properties due to artifacts and subcores with associated YSOs or VeLLOs,
respectively. For every subcore the table lists the position of its ``center of gravity'', the subcore area and effective radius, the integrated flux density and mass for the whole
subcore as well as its area above 50% of its peak intensity, and the maximum signal-to-noise ratio within the subcore boundaries.
- Table 4:
Geometry data for subcores. See Table 4
for an explanation of the subcore designations. For every subcore
the table lists the major and minor axis at the 50% peak intensity
level and their ratio, the position angle of the major axis (east of
north), the filling factor for an ellipse defined by the
aforementioned axis lengths and orientations, and the effective
radius at the 70% peak intensity level.
- Table 5:
Data on dust emission peaks. Bracketed and starred peak
designations indicate peaks with uncertain properties due to
artifacts and peaks with associated YSOs or VeLLOs,
respectively. For every peak the table lists the peak position, the
associated subcore, if applicable, the peak flux density per
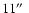 beam (after smoothing to
beam (after smoothing to
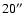 resolution) and
the related column density and extinction, the flux density and
radius for an aperture of
resolution) and
the related column density and extinction, the flux density and
radius for an aperture of
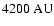 radius, and the flux
densities for the c2d standard apertures between
radius, and the flux
densities for the c2d standard apertures between
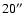 and
and
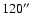 diameter.
diameter.
- Table A.1:
Standard c2d conversion factors for masses and column
densities from dust emission. For each bolometer camera employed by
the c2d collaboration we list the effective wavelength, the half
power beam width, the dust opacity at the effective wavelength (per
gram of ISM), the conversion factors between intensity and column
density, and between integrated flux density and mass (this for a
distance of
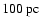 ), respectively.
), respectively.