All Tables
- Table 1:
Sources of spectroscopic observations: 1 -
Observatory; 2 - code assigned to each combination of telescope + equipment
used throughout this paper; 3 - telescope aperture and spectrograph;
4 - projected spectrograph entrance apertures (the first number is the
slit width, and the second is the slit length); 5 - focus of the
telescope.
- Table 6:
Flux scale factors for optical spectra.
- Table 9:
The wavelength integration intervals and the corresponding NLR contributions.
- Table 10:
Line and continuum fluxes. See the text for the definition of the parameters.
- Table 11:
The wavelength intervals for the
H
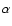 and H
and H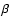 wings and cores.
wings and cores.
- Table 12:
The FWHM and the ratio
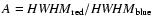 of the
red/blue, for the averaged and rms profiles of
H
of the
red/blue, for the averaged and rms profiles of
H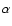 and H
and H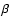 ,
during the three
periods.
,
during the three
periods.
- Table 13:
Time lags and CCF coefficients for the whole monitoring
period, for the three periods based on the profile shapes, and for the division based on the three
values of the
continuum intensity.
- Table 2:
Log of the spectroscopic observations:
Columns: 3 - code according to
Table 1; 4 - projected spectrograph entrance apertures;
5 - wavelength range covered; 6 - spectral resolution; 7 - slit
position angle (PA) in degrees; 8 - mean seeing in arcsec.
- Table 3:
Corrections for the position angle effect.
Columns: 1 - position angle (PA) in degrees; 2 - projected
spectrograph entrance apertures in arcsec; 3 - slit position
angle (PA) corrections for emission lines (kp); 4 -
estimated PA correction error for emission line, e(kp); 5 -
position angle (PA) corrections for continuum flux, kp(cnt); 6 -
the estimated PA correction error for continuum flux, e (kp(cnt)).
- Table 4:
Correction for
seeing effects, for apertures
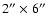 and
and
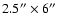 .
Columns: 1 - seeing intervals in arcsec; 2 - mean seeing in arcsec;
3 - our seeing correction for the emission lines fluxes, ks(our);
4 - estimated seeing correction error, e(ks); 5 - Peterson's
seeing correction for the emission lines fluxes from
Peterson et al. (1995), ks(Pet); 6 - our host galaxy seeing
correction for the continuum fluxes, in units of 10-14 erg s-1 cm-2 Å-1, Gs(our); 7 - estimated
host galaxy seeing correction error, e(Gs); 8 - Peterson's host
galaxy seeing correction Gs(Pet) for the continuum fluxes from
Peterson et al. (1995).
.
Columns: 1 - seeing intervals in arcsec; 2 - mean seeing in arcsec;
3 - our seeing correction for the emission lines fluxes, ks(our);
4 - estimated seeing correction error, e(ks); 5 - Peterson's
seeing correction for the emission lines fluxes from
Peterson et al. (1995), ks(Pet); 6 - our host galaxy seeing
correction for the continuum fluxes, in units of 10-14 erg s-1 cm-2 Å-1, Gs(our); 7 - estimated
host galaxy seeing correction error, e(Gs); 8 - Peterson's host
galaxy seeing correction Gs(Pet) for the continuum fluxes from
Peterson et al. (1995).
- Table 5:
Corrections for the seeing effects, for aperture
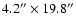 .
Columns: 1 - Seeing intervals in arcsec; 2 -
mean seeing in arcsec; 3 - our seeing correction for the emission
lines fluxes, ks(our); 4 - the estimated seeing correction error,
e(ks); 5 - Peterson's seeing correction ks(Pet) for the emission
lines fluxes from Peterson et al. (1995), ks(Pet); 6 - our host
galaxy seeing correction for the continuum fluxes, in units of
10-14 erg s-1 cm-2 Å-1), Gs(our); 7 -
the estimated host galaxy seeing correction error, e(Gs); 8 -
Peterson's host galaxy seeing correction Gs(Pet) for the
continuum fluxes from Peterson et al. (1995).
.
Columns: 1 - Seeing intervals in arcsec; 2 -
mean seeing in arcsec; 3 - our seeing correction for the emission
lines fluxes, ks(our); 4 - the estimated seeing correction error,
e(ks); 5 - Peterson's seeing correction ks(Pet) for the emission
lines fluxes from Peterson et al. (1995), ks(Pet); 6 - our host
galaxy seeing correction for the continuum fluxes, in units of
10-14 erg s-1 cm-2 Å-1), Gs(our); 7 -
the estimated host galaxy seeing correction error, e(Gs); 8 -
Peterson's host galaxy seeing correction Gs(Pet) for the
continuum fluxes from Peterson et al. (1995).
- Table 7:
Observed continuum, H
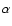 ,
H
,
H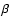 ,
H
,
H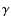 ,
and HeII
,
and HeII
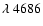 fluxes, reduced to the 6 m telescope
aperture
fluxes, reduced to the 6 m telescope
aperture
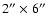 .
The fluxes are corrected for position
angle (to
.
The fluxes are corrected for position
angle (to 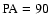 degree), seeing, and aperture effects. Columns: 2 - the continuum flux at 5117 Å
(in units of 10-14 erg s-1 cm-2 Å-1),
and the estimated continuum flux error; 3 -
the H
degree), seeing, and aperture effects. Columns: 2 - the continuum flux at 5117 Å
(in units of 10-14 erg s-1 cm-2 Å-1),
and the estimated continuum flux error; 3 -
the H total flux and the H
total flux and the H flux error; 4 - the
H
flux error; 4 - the
H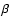 total flux and the H
total flux and the H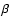 flux error; 5 - the
H
flux error; 5 - the
H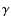 total flux and the H
total flux and the H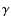 flux error; 6 - the
HeII
flux error; 6 - the
HeII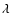 4686 total flux and the HeII
4686 total flux and the HeII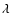 4686 flux error. All line fluxes are in units of
10-12 erg s-1 cm-2.
4686 flux error. All line fluxes are in units of
10-12 erg s-1 cm-2.
- Table 8:
Mean error (uncertainty) of our flux determinations
for continuum, H
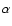 ,
H
,
H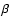 ,
H
,
H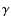 ,
and HeII 4686emission lines in different years, and in the whole (11 years)
observation period. Columns:
2 and 3 - the estimated mean continuum flux error in
% and its sigma;
4 and 5 - the estimated mean H
,
and HeII 4686emission lines in different years, and in the whole (11 years)
observation period. Columns:
2 and 3 - the estimated mean continuum flux error in
% and its sigma;
4 and 5 - the estimated mean H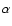 flux
error in % and its sigma; 6 and 7 - the estimated mean
H
flux
error in % and its sigma; 6 and 7 - the estimated mean
H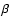 flux error in % and its sigma; 8 and 9 - the estimated mean
H
flux error in % and its sigma; 8 and 9 - the estimated mean
H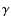 flux error in % and its sigma; 10 and 11 - the
estimated mean flux error in % and its sigma, Bottom - mean error (uncertainty)
in the whole (11 years) observation period.
flux error in % and its sigma; 10 and 11 - the
estimated mean flux error in % and its sigma, Bottom - mean error (uncertainty)
in the whole (11 years) observation period.