- ... tasks
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The Image Reduction and
Analysis Facility ( IRAF) is distributed by the National Optical
Astronomy Observatories, which is operated by the Association of
Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., under cooperative
agreement with the US National Science Foundation. STSDAS, the
Space Telescope Science Data Analysis System, contains tasks
complementary to the existing IRAF tasks. We used Version 3.5
(March 2006) for the data reduction performed in this paper.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... IDL
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The Interactive
Data Language (IDL) is licensed by Research Systems Inc., of
Boulder, CO, USA.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
tool
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Available from http://stev.oapd.inaf.it/cmd
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... law
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- See http://stev.oapd.inaf.it/cmd
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
estimates
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- It is well known that broad-band SED fitting
results in artefacts in the cluster age distribution. This is
predominantly caused by specific features in the SSP models, such as
the onset and presence of red giant branch or asymptotic giant branch
stars at, respectively,
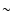 10 and
10 and 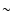 100 Myr (e.g., Bastian et al. 2005). In addition, the peak in Fig. 9 at an age of
100 Myr (e.g., Bastian et al. 2005). In addition, the peak in Fig. 9 at an age of
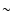 10 Myr may be an artefact caused by the rapid evolution of
stellar populations around
10 Myr may be an artefact caused by the rapid evolution of
stellar populations around 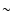 10-30 Myr (e.g., Lee et al. 2005).
10-30 Myr (e.g., Lee et al. 2005).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... evidence
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The apparent
peak in Fig. 9 at an age of
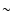 10 Myr is most likely
due to the residual effects of (i) the age-extinction degeneracy
(which is particularly important at these young ages), and (ii) the
fact that the youngest isochrone included in the Analy SED tool
is of an age of
10 Myr is most likely
due to the residual effects of (i) the age-extinction degeneracy
(which is particularly important at these young ages), and (ii) the
fact that the youngest isochrone included in the Analy SED tool
is of an age of
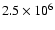 yr, with limited age resolution at
these ages. In addition, we remind the reader that we have adopted a
fixed, solar metallicity, which may also give rise to a small
age-metallicity degeneracy (in view of the variability of the galactic
background and the associated photometric uncertainties, it is
impractical to introduce an additional free parameter in the fits; the
metallicity is expected to be least variable of our choice of possible
free parameters). The consequence of these effects is that the
youngest clusters tend to accumulate close to the lower age cut-off,
and hence this peak should be taken with extreme caution (see, e.g.,
de Grijs et al. 2003a, for a detailed analysis).
yr, with limited age resolution at
these ages. In addition, we remind the reader that we have adopted a
fixed, solar metallicity, which may also give rise to a small
age-metallicity degeneracy (in view of the variability of the galactic
background and the associated photometric uncertainties, it is
impractical to introduce an additional free parameter in the fits; the
metallicity is expected to be least variable of our choice of possible
free parameters). The consequence of these effects is that the
youngest clusters tend to accumulate close to the lower age cut-off,
and hence this peak should be taken with extreme caution (see, e.g.,
de Grijs et al. 2003a, for a detailed analysis).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.