- ... enhancement?
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Appendices A and B are only available in electronic form at http://www.aanda.org
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
profile
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Though those authors have since improved their early time
results and parametrisations, we will still use these generic
profile names to deal with inner shapes of profiles, for the sake of
simplicity.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...2007)
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- For further developments on the topic of
triaxiality, asymmetries, as well as on the spin of halos, see e.g.
Zentner et al. (2005); Gustafsson et al. (2006); Bett et al. (2007); Capuzzo-Dolcetta et al. (2006); Moore et al. (2004); Lee & Kang (2006); Gao & White (2006). For the dependence of halo parameters on
the environment, see Ragone-Figueroa & Plionis (2007); Hahn et al. (2007a,b); Maulbetsch et al. (2007).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... substructures
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Small structures, which formed earlier,
are expected to be more spherical (Allgood et al. 2006; Moore et al. 2004).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
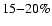
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The concentration is modified when
considering dark energy with various values of
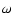 (Dolag et al. 2004), the constant equation of state, but still
remains consistent with B01 model (Wechsler et al. 2006).
(Dolag et al. 2004), the constant equation of state, but still
remains consistent with B01 model (Wechsler et al. 2006).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...Colafrancesco et al. 2006)
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Their figure corresponds to
slightly modified B01 and ENS01, which are not retained here.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... parameters
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- See
discussion in Sect. 3.3 for the consequences of
varying
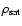 and considering different inner profiles
(e.g. a Moore inner profile).
and considering different inner profiles
(e.g. a Moore inner profile).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... paper
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Let us say it
again: should the first option have been retained, we would have ended up
with boost factors smaller than one!
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
coefficient
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- So that
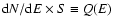 ,
as used
in Sect. 4.
,
as used
in Sect. 4.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... model
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- This
differs from the convention used in Lavalle et al. (2007) for which
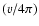 is included in S.
is included in S.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
uncorrelated
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- We remind that tidal disruption of a clump in the
Galactic centre depends either on its mass and on its location, which
induces a small correlation between the mass and the space distributions.
Nevertheless, we have checked that it could be neglected for this purpose.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... distributions)
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The integration volume V is the DM halo
volume, but in practical calculations, we reduce it to the diffusion volume.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
flux
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- An analysis of these effective volumes has been presented and
discussed in great details in Maurin & Taillet (2003), for both
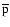 and
and 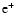 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.