Table 2:
Magnetic phenomena in NGC 6946 and their probable origins.
Total magnetic energy density  turbulent energy density in inner galaxy
turbulent energy density in inner galaxy |
Field amplification by turbulent gas flows |
| Total magnetic energy density dominates in outer galaxy |
Magneto-rotational instability ? |
| Low degrees of polarization in gas spiral arms |
Field tangling due to star-formation activity |
| Large-scale pattern in Faraday rotation |
Coherent fields |
| Magnetic arms with regular, almost completely aligned fields |
Efficient dynamo action in interarm regions |
| Two inner magnetic arms |
Superposition of dynamo modes m=0 and m=2 |
| No large-scale field reversals |
Higher dynamo modes weak or absent in inner galaxy |
| Outer magnetic arms |
Higher dynamo modes or shear flows in outer galaxy |
| Alignment of ordered fields along spiral structure |
Interaction between gas flow and magnetic field |
| Magnetic arms are phase-shifted images of gas arms |
Magnetic field may trigger the formation of gas spiral arms |
| North-south asymmetry in Faraday rotation |
Spiral field points inwards in both inner magnetic arms |
| Enhanced magnetic field along inner edge of inner gas spiral arm |
Compression or shear by density waves |
| Smooth turning of field lines into inner gas spiral arm |
No shock |
| Mild field compression in inner gas spiral arm |
Magnetic field connected to warm, diffuse gas |
| Anti-correlation of RM and field pitch angle |
Helical fields |
| RM structure function flat until 6 kpc scale |
Uncorrelated field structures below 6 kpc scale |
| RM structure function rising for scales larger than 6 kpc |
Large-scale coherent fields |
Depolarization rings at
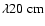 |
Differential Faraday rotation in
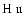 complexes
complexes |
Strong Faraday depolarization at
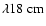 and
and
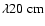 |
Faraday dispersion by random fields |
| Large-scale asymmetry in Faraday depolarization |
Helical fields ? |