All Tables
- Table 1:
Summary of observations: each mask is named with the identification
number of its primary target. The number of slitlets, of IR-peakers included, and
of measured spectroscopic redshifts are reported.
- Table 2:
Data for IR-peak sources included in slit, sorted by field: basic photometric information,
photometric flag, spectroscopic classification and redshift are listed.
See Table 5 for more details on flags.
- Table 3:
Detected lines for IR-peak targets, sorted by mask (first night). For each source, we
report the observed wavelength, equivalent width (EW), full width at half maximum (FWHM, corrected for
the instrumental resolution) and identification of
the detected spectral features. For each detected line, the spectroscopic
redshift is computed (last column).
- Table 4:
Detected lines for IR-peak targets, sorted by mask (second night).
- Table 7:
Results of spectro-photometric fitting for sources with no AGN component.
The five columns on the right contain the stellar masses of galaxies, their ongoing (within the last 108 yr)
star formation rate, two values of the intrinsic extinction,
and the IR (8-1000
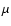 m restframe) luminosity produced by the
ongoing starburst, estimated assuming an M 82-like template. The two
m restframe) luminosity produced by the
ongoing starburst, estimated assuming an M 82-like template. The two 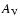 values are computed by averaging over the whole galaxy life
and over the last 108 yr (representing the amount of dust affecting the ongoing burst). In parenthesis
the 3
values are computed by averaging over the whole galaxy life
and over the last 108 yr (representing the amount of dust affecting the ongoing burst). In parenthesis
the 3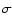 ranges derived from the exploration of the parameter space are reported.
ranges derived from the exploration of the parameter space are reported.
- Table 8:
Results of SED fitting for IR-peakers requiring an AGN component. The fit consists in the
combination of a simple stellar population and a torus model (Fritz et al. 2006). The 3
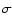 ranges for
the main geometrical and dust properties of the torus are reported, as well as stellar population ages, extinctions and masses.
ranges for
the main geometrical and dust properties of the torus are reported, as well as stellar population ages, extinctions and masses.
- Table 9:
Summary of results.
- Table 5:
Results for first night. For each target, the number of detected
absorption and emission lines is reported, as well as a photometric and spectroscopic
(see footnotes) classification. The measured spectroscopic redshift is in Col. 6,
while Col. 7 lists the photometric estimate of z, as obtained with the
Hyper-z code (Bolzonella et al. 2000).
- Table 6:
Results for second night.