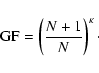- ... viscosity
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
-
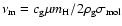 with
with 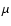 and
and
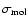 ,
respectively, the mean molecular weight and mean molecular cross-section of the gas molecules.
,
respectively, the mean molecular weight and mean molecular cross-section of the gas molecules.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... is
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The Epstein limit holds for particles with sizes smaller than the mean-free-path of the gas,
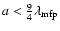 .
If this limit is exceeded, friction times increase by a factor
.
If this limit is exceeded, friction times increase by a factor
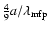 and quadratically scale with radius (Schräpler & Henning 2004; Whipple 1972; Weidenschilling 1977).
and quadratically scale with radius (Schräpler & Henning 2004; Whipple 1972; Weidenschilling 1977).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... read
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Dullemond & Dominik (2005) note that the second expression in Eq. (5) may not exceed v0.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... particles
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The reader should note that the words "particle'', "agglomerate'' and "aggregate'' are frequently interchanged throughout this and other paragraphs.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... present
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Note that we start compaction already at
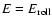 instead of
instead of
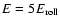 .
We have found, however, that the simulations are insensitive to the precise energy at which compaction starts.
.
We have found, however, that the simulations are insensitive to the precise energy at which compaction starts.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
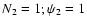 )
)![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Here we take
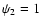 as the enlargement factor of single monomers.
as the enlargement factor of single monomers.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... equation
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Which reads:
describing losses of m due to all collisions with m (first term on right hand side) and gains in the distribution of m due to collisions between m' and m-m' (second term), where the factor
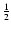 ensures collisions are not twice accounted for. Ossenkopf (1993) provides a general extension of the Smoluchowski equation including source and sink terms.
ensures collisions are not twice accounted for. Ossenkopf (1993) provides a general extension of the Smoluchowski equation including source and sink terms.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... needed
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Due to the duplication, the mean mass of the system increases with a factor (N+1)/N. The growth factor after
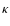 -steps then becomes
-steps then becomes
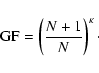 |
(24) |
Thus,
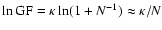 if
if 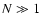 and
and
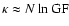 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... is
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The mean mass of the population is inversely proportional to the number of particles per unit volume.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... unity
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The Schmidt number measures the ratio of the gas to particle diffusivity; it is supposed to be close to unity if
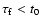 .
(Schräpler & Henning 2004).
.
(Schräpler & Henning 2004).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... line
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- References to colours only apply to the electronic version of this paper.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.