![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7cm, angle=-90]{5873fig2.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/48/aa5873-06/Timg92.gif) |
Figure 2:
IRAM/MAMBO Signal-to-Noise map of the field around the M3.5 dwarf GJ 628 at
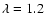 mm. In this map, Signal-to-Noise ratio (S/N) is computed from the intensity map
reduced with the shift-and-add method using the software package mopsic (Zylka 1998)
and smoothed to the angular resolution 12''. The S/N is computed by dividing the intensity
at each pixel by the local rms ( mm. In this map, Signal-to-Noise ratio (S/N) is computed from the intensity map
reduced with the shift-and-add method using the software package mopsic (Zylka 1998)
and smoothed to the angular resolution 12''. The S/N is computed by dividing the intensity
at each pixel by the local rms (
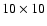 pixels) which is not uniform across this intensity map made by the scanning technique. The local rms pixels) which is not uniform across this intensity map made by the scanning technique. The local rms 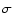 is
is 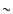 0.4 mJy/11'' beam
in the central region (r < 60'') and degrades towards the edges of the map;
for example, 0.4 mJy/11'' beam
in the central region (r < 60'') and degrades towards the edges of the map;
for example, 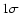 is 0.75 mJy/11'' beam at
is 0.75 mJy/11'' beam at
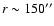 .
The countours are .
The countours are
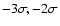 (dotted lines), and
(dotted lines), and
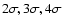 ;
The map pixel size is 3.5''. The West component (MAMBO-W) is associated with a 1.4 GHz radio source ( ;
The map pixel size is 3.5''. The West component (MAMBO-W) is associated with a 1.4 GHz radio source (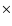 symbol) of the NVSS catalogue and with an optical object of the USNO-B1.1 catalogue (+ symbol), and so it is a background source. The other four MAMBO components (NW, NE, E, SW) may be dust clumps of a large debris disk around GJ 628 but the lack of diffuse emission between them requires additional observations for confirmation. Observed position of GJ 628 at center of the map is
symbol) of the NVSS catalogue and with an optical object of the USNO-B1.1 catalogue (+ symbol), and so it is a background source. The other four MAMBO components (NW, NE, E, SW) may be dust clumps of a large debris disk around GJ 628 but the lack of diffuse emission between them requires additional observations for confirmation. Observed position of GJ 628 at center of the map is 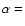 16h 30m 18.0s and
16h 30m 18.0s and
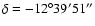 (J2000).
(J2000). |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm, angle=0]{5873fig1.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/48/aa5873-06/Timg72.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7cm, angle=-90]{5873fig2.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/48/aa5873-06/Timg92.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6cm, angle=-90]{5873fig3.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/48/aa5873-06/Timg149.gif)