All Tables
- Table 1:
GPS sources. Columns 1 through 13 provide source name, optical identification (G: galaxy,
Q: quasar, EF: empty field), optical magnitude ("V'',"R'' are the
bands in the optical, "r'' band-defined by Stanghellini et al.
1993), redshift (those with * are a photometric estimate by
Heckman et al. 1994), linear scale factor pc/mas [
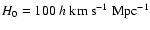 and q0=0.5 have been assumed],
maximum VLBI angular size fromPapers I, II or this observation,
maximum VLBI linear size, 5 GHz total flux density measured at
Effelsberg, low frequency spectral index, high frequency spectral
index, turnover frequency, peak flux density and references for
the spectral information (Refs. 1, de Vries et al. 1997; 2,
Stanghellini et al. 1998; 3, Dallacasa et al. 2000; 4, O'Dea et
al. 1996; 5, Spoelstra et al. 1985).
and q0=0.5 have been assumed],
maximum VLBI angular size fromPapers I, II or this observation,
maximum VLBI linear size, 5 GHz total flux density measured at
Effelsberg, low frequency spectral index, high frequency spectral
index, turnover frequency, peak flux density and references for
the spectral information (Refs. 1, de Vries et al. 1997; 2,
Stanghellini et al. 1998; 3, Dallacasa et al. 2000; 4, O'Dea et
al. 1996; 5, Spoelstra et al. 1985).
- Table 2:
Integrated properties of the sources from the WSRT
data, values of EVPA are likely to be meaningless for objects with
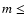 0.4%.
0.4%.
- Table 3:
Parameters of the components in the VLBI images at 5 GHz. The columns give: (1)
source name and possible classification (CSOc: Compact Symmetric
Object candidate, cj: core-jet); (2) total image intensity
measured with IMEAN at 5 GHz; (3) component identification labled
to Xiang et al. (2002, 2005); (4), (5) peak (per beam) and integral
intensity of component at 5 GHz measured with JMFIT; (6),(7)
major/minor axes (with error
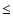 10%) and position angle of
component at 5 GHz measured with JMFIT; (8), (9) distance and
position angle relative to the first component; (10) brightness
temperature of component; (11) integrated fractional polarization
in source.
10%) and position angle of
component at 5 GHz measured with JMFIT; (8), (9) distance and
position angle relative to the first component; (10) brightness
temperature of component; (11) integrated fractional polarization
in source.