All Tables
- Table 1:
The XMM-Newton/ 2dFGRS correlation sample. Shown from left to right are sample
identification number, 2dFGRS database name, right ascension and declination for
the X-ray source, offset between X-ray and optical source,
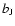 magnitude from
2dFGRS, X-ray flux, redshift from 2dFGRS, logarithm of X-ray luminosity,
logarithmic X-ray-to-optical flux ratio, hardness ratio and error, and, in
the last column, suggested galaxy type. For this column, the following abbreviations
hold: A: absorption line galaxy; F: featureless 2dFGRS spectrum; G: source appears in group; H II: H II nucleus. A question mark indicates
that a classification is not possible. Question marks after a
classification indicate a high degree of uncertainty.
magnitude from
2dFGRS, X-ray flux, redshift from 2dFGRS, logarithm of X-ray luminosity,
logarithmic X-ray-to-optical flux ratio, hardness ratio and error, and, in
the last column, suggested galaxy type. For this column, the following abbreviations
hold: A: absorption line galaxy; F: featureless 2dFGRS spectrum; G: source appears in group; H II: H II nucleus. A question mark indicates
that a classification is not possible. Question marks after a
classification indicate a high degree of uncertainty.
- Table 2:
The Chandra/ 2dFGRS correlation sample. Column details
are as in the previous figure.
- Table 3:
NGs with
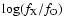 >-2. Groups of rows separated by horizontal
lines correspond to the sample indicated in the first column. 2dFGRS stands for the combined correlation samples 2dFGRS- XMM-Newton and
2dFGRS- Chandra. Each row corresponds to the NG type indicated in the
second column. Each of the last three columns gives the fraction of
NGs with
>-2. Groups of rows separated by horizontal
lines correspond to the sample indicated in the first column. 2dFGRS stands for the combined correlation samples 2dFGRS- XMM-Newton and
2dFGRS- Chandra. Each row corresponds to the NG type indicated in the
second column. Each of the last three columns gives the fraction of
NGs with
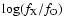 >-2 in the
>-2 in the
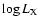 region indicated at the top of
the column. Note that the second of these columns includes NGs from
the
region indicated at the top of
the column. Note that the second of these columns includes NGs from
the
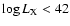 column which also have
column which also have
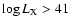 .
Thus, the numerator gives the number of NGs of a given type
in a given sample and a given
.
Thus, the numerator gives the number of NGs of a given type
in a given sample and a given
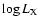 range, and the denominator
the total number of NGs in the same sample and
range, and the denominator
the total number of NGs in the same sample and
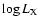 range.
Galaxies for which only upper limit information is available have not
been taken into account. Empty entries indicate that no NGs of this
type have been found. Galaxy labels are as in Tables 1
and 2. Additionally, "sb''rq stands for starburst
and "E'' for
elliptical.
range.
Galaxies for which only upper limit information is available have not
been taken into account. Empty entries indicate that no NGs of this
type have been found. Galaxy labels are as in Tables 1
and 2. Additionally, "sb''rq stands for starburst
and "E'' for
elliptical.