All Tables
- Table 1:
Log of observations for RXS J1131-1231 with HST.
- Table 2:
Relative astrometry, flux ratio (with respect to image A) and absolute photometry in filters F555W, F814W and F160W of the lensed QSO images A, B, C, D, as derived from PSF fitting (see Sect. 4.2). After the Einstein ring has been subtracted, relative astrometry and absolute photometry are derived for the lensing galaxy G from the best fit of the Sérsic model (see Sect. 4.3). After subtracting the lens, the astrometry of component X is derived from a Gaussian fitting and its magnitude from aperture photometry (corrected for infinite aperture). Theoretical magnification ratios
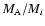 and the (unobserved) AGN position are derived from our fiducial lens model (see Sect. 4.4). Magnitudes of the host are calculated in Sect. 4.5. Quoted errors are standard errors on the mean, computed from the results on the NExp individual frames, including the systematics estimated in Sects. 2.2 and 2.3. Boldface indicates the final, weighed average astrometry derived from all bands.
and the (unobserved) AGN position are derived from our fiducial lens model (see Sect. 4.4). Magnitudes of the host are calculated in Sect. 4.5. Quoted errors are standard errors on the mean, computed from the results on the NExp individual frames, including the systematics estimated in Sects. 2.2 and 2.3. Boldface indicates the final, weighed average astrometry derived from all bands.
- Table 3:
Best values of the Sérsic and de Vaucouleurs (dVc) profiles fitted to the lensing galaxy (see Sect. 4.3 for details). Quoted errors are the 1
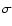 dispersion of the results on the NExp individual frames. The number of d.o.f. is about 3120 for F555W and F814W frames, and about 1100 for F160 frames.
dispersion of the results on the NExp individual frames. The number of d.o.f. is about 3120 for F555W and F814W frames, and about 1100 for F160 frames.
- Table 4:
Fitted values of the parameters of simple mass models (see text for details). For each model, the first (resp. second) line gives the results when fitting (resp. not fitting) the lens position (LF; resp. NLF).
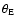 is the angular Einstein radius,
is the angular Einstein radius,
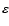 the intrinsic ellipticity,
the intrinsic ellipticity, 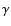 the external shear,
the external shear,
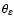 and
and
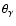 the position angles,
the position angles,
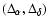 the differences between the modeled and the observed lens positions in
the differences between the modeled and the observed lens positions in 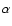 and in
and in 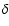 .
.
- Table 5:
Fitted values of the parameters of best SIE +
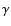 model after introducing an m=4 multipole (
model after introducing an m=4 multipole (
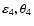 ). The lens position is fitted. Same notations as in Table 4.
). The lens position is fitted. Same notations as in Table 4.
- Table 6:
Best values of parameters of the Sérsic profile fitted on the reconstructed host galaxy.
- Table 7:
Observed evolution of the lens, as a function of the underlying assumption on
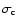 :
FJ or GL model with possible correction for central velocity dispersion (
:
FJ or GL model with possible correction for central velocity dispersion (
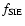 )
and typical environment (Env).
)
and typical environment (Env).