All Tables
- Table 1:
Selected features of the evolution of massive intermediate-mass
stars prior to carbon ignition. The quantities shown are: the maximum
extent of the convective core during the central hydrogen (
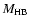 )
and helium (
)
and helium (
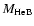 )
burning phases, the mass coordinate of the
base of the convective envelope at its deepest extent during the first
dredge-up (
)
burning phases, the mass coordinate of the
base of the convective envelope at its deepest extent during the first
dredge-up (
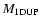 ), the mass of the CO core at carbon ignition
(
), the mass of the CO core at carbon ignition
(
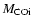 ), the durations of central hydrogen (
), the durations of central hydrogen (
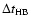 )
and helium (
)
and helium (
 )
burning phases, the time elapsed
between the end of central helium burning and carbon ignition (
)
burning phases, the time elapsed
between the end of central helium burning and carbon ignition (
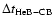 )
and the central
)
and the central
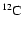 and
and
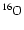 mass
fractions at the end of He core burning. Masses are in solar unit
(
mass
fractions at the end of He core burning. Masses are in solar unit
(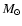 ), times in years (yr).
), times in years (yr).
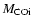 is defined as the mass
coordinate of maximum nuclear energy production in the He burning shell.
is defined as the mass
coordinate of maximum nuclear energy production in the He burning shell.
- Table 2:
Surface abundances mass fractions at the end of the first dredge-up.
- Table 3:
Selected properties of the convective carbon burning zones as a
function of the initial stellar mass. The superscripts 1 and 2 refer to the
flash and flame, respectively. The quantities shown are the time (t) when
convection sets in, the radius (
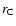 )
and mass (
)
and mass (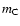 )
coordinates where
it develops, the duration
)
coordinates where
it develops, the duration 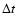 of the convective episode, the maximum
carbon luminosity
of the convective episode, the maximum
carbon luminosity 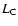 ,
the mass covered by the instability (
,
the mass covered by the instability (
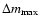 )
and, at the time of peak luminosity, the carbon mass fraction
(
)
and, at the time of peak luminosity, the carbon mass fraction
(
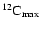 )
in the convective zone.
)
in the convective zone.
- Table 4:
Surface abundances mass fractions at the end of the second dredge-up.
- Table 5:
At the end of the carbon burning phase, stellar mass (
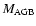 )
and masses of the NeO (
)
and masses of the NeO (
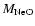 )
and CO cores (
)
and CO cores (
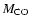 ), defined as the mass coordinate where
), defined as the mass coordinate where
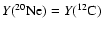 and
and
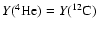 respectively, as a function of the
initial mass
respectively, as a function of the
initial mass
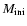 .
.
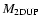 corresponds to the mass
coordinate of the deepest extent of the envelope during the second
dredge-up.
corresponds to the mass
coordinate of the deepest extent of the envelope during the second
dredge-up.