All Tables
- Table 3:
Power law indices of the mass spectrum of the clumps, d
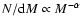 ,
for different mass ranges. The
mass of the clumps has been derived either from the dust continuum or from gas emission. The arrows indicate the whole mass
range for which the fit to the mass spectrum has been done.
,
for different mass ranges. The
mass of the clumps has been derived either from the dust continuum or from gas emission. The arrows indicate the whole mass
range for which the fit to the mass spectrum has been done.
- Table 1:
Observed IRAS sources, alongside with source type, H(igh) or L(ow) according to the classification of Palla et al. (1991), position (precessed to J2000 coordinates), kinematic distance, and luminosity. The last column shows the sum
of the mass estimated from the 1.2 mm continuum for clumps located at <90'' from the IRAS position. The luminosities and the masses
have been estimated assuming the near distance,
 ,
except where noted.
,
except where noted.
- Table 2:
Offset position, angular diameter, linear diameter, integrated flux density at 1.2 mm, mass, and density of the clumps
detected towards each IRAS source. The offset positions are relative to the nominal IRAS point source positions. The last column
indicates whether the clump is associated with MSX emission, either point-like or diffuse, or not. Linear diameters, masses, and densities of the
clumps have been estimated assuming the near kinematic distance when the distance ambiguity could not be resolved, except where
noted.