- ... variables
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Based on
observations obtained at the German-Spanish Astronomical Center, Calar
Alto, operated by the Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie,
Heidelberg, jointly with the Spanish National Commission for
Astronomy,
on observations made at the 1.2 m telescope, located at Kryoneri
Korinthias, and owned by the National Observatory of Athens, Greece, and
on observations made with the OGS telescope, operated on
the island of Tenerife by the European Space Agency, in the
Spanish Observatorio del Teide of the IAC.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Table 1 is only available in electronic form at http://www.edpsciences.org
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...IRAF.
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- IRAF is distributed by the National
Optical Astronomy Observatories.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... range
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The classification of Ritter & Kolb (2003)
is somewhat confusing, as their use of the UX UMa type disagrees with
the more common definition of systems charcterised by persistent broad
Balmer absorption lines.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... properties
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- With one
exception: HS 0229+8016 was observed in August 1992 in a
somewhat fainter state,
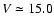 ,
compared to its typical
brightness near 14 mag. On that occasion, the Balmer and
He I absorption lines were absent/weak, and the strength of the
emission lines had markedly increased.
,
compared to its typical
brightness near 14 mag. On that occasion, the Balmer and
He I absorption lines were absent/weak, and the strength of the
emission lines had markedly increased.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.