- ...1995
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Note that the Yale group computed the evolution of angular momentum using a simplified description of the action of meridional circulation, which
was considered as a diffusive rather than as an advective process.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... picture
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The potential effect
of internal gravity waves produced by the convective stellar core should be
modest, although it remains to be quantified.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
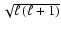
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- This is
the theoretical dependence. Damping can be enhanced by turbulence, which would reduce
the surface amplitude of the mode (see e.g. Andersen 1996).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... coefficient
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The Gaussian we use here is quite thin. Far from a sharp shear layer, the convolution we are using would not alter the turbulent viscosity from that obtained with Eq. (5).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... rotation
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- This
mode does not carry angular momentum.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
species
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- This adds to the indirect effect described above, that is, modification
of the rotation profile which changes rotational mixing.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
applied
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- However, the initial rotation profile has a surface convection
zone rotating slower than the radiative interior.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... moderate
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- This is the same as was used by TKZ.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... smaller
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- In TKZ, the local turbulence was fixed (as in Eq. (4)) and did not depend on the local shear rate.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
models
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- We showed in Talon & Charbonnel (2003)
that in the type of star we consider for this full evolutionary
computation (i.e., Pop I main sequence star with a mass of 1.2
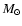 )
the depth and structure of the convective envelope,
and thus the wave characteristics, do not vary significantly
over a main sequence lifetime. It is thus justified to perform the
first test with the spectrum characteristics of the ZAMS models.
)
the depth and structure of the convective envelope,
and thus the wave characteristics, do not vary significantly
over a main sequence lifetime. It is thus justified to perform the
first test with the spectrum characteristics of the ZAMS models.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.