All Tables
- Table 1:
Observational parameters used. The observations were made with the ISOCAM LW2
(5-8.5
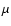 m) and
LW3 (12-18
m) and
LW3 (12-18 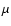 m) filters at their respective reference wavelengths of 6.7
m) filters at their respective reference wavelengths of 6.7 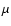 m and 14.3
m and 14.3 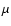 m. On-chip
integration time was always 5.04 seconds and the 3
m. On-chip
integration time was always 5.04 seconds and the 3
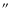 per-pixel-field-of-view was used. M
and N are the
number of steps along each dimension of the raster, while dm and dn are the increments for a raster step. The
sensitivity in
per-pixel-field-of-view was used. M
and N are the
number of steps along each dimension of the raster, while dm and dn are the increments for a raster step. The
sensitivity in 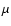 Jy is given at the 5
Jy is given at the 5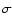 level. The table also includes the total area covered and the
number of readouts per raster step. The rasters were repeated k times. Tot. t is the total time dedicated to
each filter observation.
level. The table also includes the total area covered and the
number of readouts per raster step. The rasters were repeated k times. Tot. t is the total time dedicated to
each filter observation.
- Table 2:
The primary list of sources detected at 15
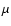 m. The columns are (from left to right):
source identification number in order of increasing Right Ascension; source flux and precision before
calibration (in ADUgs); source flux and precision after calibration (in mJy); Right Ascension and Declination of
the infrared source (J2000); redshift and name of the optical counterpart, if known. The redshift of source
ISO_Cl0024_02 was taken from Schmidt et al. (1986). All other redshifts are from Czoske
et al. (2001) or provided by T. Treu (private communication). The names of the stars are
from HEASARC.
m. The columns are (from left to right):
source identification number in order of increasing Right Ascension; source flux and precision before
calibration (in ADUgs); source flux and precision after calibration (in mJy); Right Ascension and Declination of
the infrared source (J2000); redshift and name of the optical counterpart, if known. The redshift of source
ISO_Cl0024_02 was taken from Schmidt et al. (1986). All other redshifts are from Czoske
et al. (2001) or provided by T. Treu (private communication). The names of the stars are
from HEASARC.
- Table 3:
The supplementary list of 15
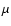 m sources. The meaning of the columns is the same as in
Table 2.
m sources. The meaning of the columns is the same as in
Table 2.
- Table 4:
The list of 7
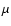 m sources with source flux exceeding 5
m sources with source flux exceeding 5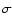 of the local noise, and having
15
of the local noise, and having
15 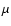 m counterparts. From left to right: 15
m counterparts. From left to right: 15 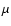 m source identification number as listed in
Table 2; signal and precision of flux in ADU; flux and precision in mJy; Right Ascension, Declination;
nature of the source; and finally the [7
m source identification number as listed in
Table 2; signal and precision of flux in ADU; flux and precision in mJy; Right Ascension, Declination;
nature of the source; and finally the [7 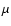 m]/[15
m]/[15 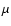 m] colour ratio.
m] colour ratio.
- Table 5:
References to ISOCAM sources in existing archives. The first column lists the source number from
Tables 2 and 3. The key to the references in Cols. 2 to 8 is Dressler & Gunn
(1992, DG), Czoske et al. (2001, CKS), Schneider et al.
(1986, SDG), Smail et al. (1997, SDC), McLean & Teplitz
(1996, MT), Butcher & Oemler (1978, BO), Soucail et al.
(2000, S) and Pickles & van der Kruit (1991, P). The table does not
include the four stars or the quasar PC 0023+1653.
- Table 6:
Results from model SEDs for known cluster galaxies in Cl 0024+1654. The columns list: LW3
identification number; best-fit SED model; number of data points in the observed SED;
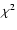 of the fit;
rejection probability of the fit; other acceptable models (rejection probability 95% or less); 15
of the fit;
rejection probability of the fit; other acceptable models (rejection probability 95% or less); 15 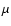 m
k-correction; luminosity at 15
m
k-correction; luminosity at 15 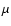 m (h=0.7,
m (h=0.7,
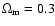 ,
,
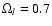 )
using the transformation from
Boselli et al. (1998), and k-corrected using best-fit SED; total infrared luminosity
including the k-correction using the best-fit SED and computed using the transformation from Elbaz et al.
(2002); SFR from total IR luminosity using the transformation of Kennicutt
(1998); position in the V-I vs. I colour-magnitude diagram (Fig. 7) where
"MS'' stands for "Main Sequence'', "BO'' for "Butcher-Oemler'', "U'' for "Unknown''; EW [O II] line from
Czoske et al. (2001); SFR computed from the [O II] emission line using the
transformation to the optical SFR; ratio infrared to optical SFR.
)
using the transformation from
Boselli et al. (1998), and k-corrected using best-fit SED; total infrared luminosity
including the k-correction using the best-fit SED and computed using the transformation from Elbaz et al.
(2002); SFR from total IR luminosity using the transformation of Kennicutt
(1998); position in the V-I vs. I colour-magnitude diagram (Fig. 7) where
"MS'' stands for "Main Sequence'', "BO'' for "Butcher-Oemler'', "U'' for "Unknown''; EW [O II] line from
Czoske et al. (2001); SFR computed from the [O II] emission line using the
transformation to the optical SFR; ratio infrared to optical SFR.
- Table 7:
Summary of ISOCAM observations and results at 15
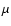 m for five clusters of galaxies. The data was
obtained from Metcalfe et al. (2003) for Abell 370, Abell 2218 and Abell 2390, Fadda et al. (2000) and Duc et al. (2002) for Abell 1689, and this paper for
Cl 0024+1654. The content of the columns in the table are as follows: name and redshift of the cluster, total
area scanned, sensitivity reported at the
m for five clusters of galaxies. The data was
obtained from Metcalfe et al. (2003) for Abell 370, Abell 2218 and Abell 2390, Fadda et al. (2000) and Duc et al. (2002) for Abell 1689, and this paper for
Cl 0024+1654. The content of the columns in the table are as follows: name and redshift of the cluster, total
area scanned, sensitivity reported at the 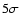 level, flux of the weakest reported source
in
level, flux of the weakest reported source
in 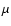 Jy, total
observation time, total number of sources detected including sources without redshifts and stars. Then number of
cluster galaxies, virial radius, virial mass, number of sources with
Jy, total
observation time, total number of sources detected including sources without redshifts and stars. Then number of
cluster galaxies, virial radius, virial mass, number of sources with
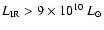 detected and expected. The expected number of sources was obtained by comparison with Cl 0024+1654 as described
in the text. Virial radii and masses are from Girardi & Mezzetti (2001) and King et al.
(2002).
detected and expected. The expected number of sources was obtained by comparison with Cl 0024+1654 as described
in the text. Virial radii and masses are from Girardi & Mezzetti (2001) and King et al.
(2002).