All Tables
- Table 1:
Observational data and geometrical circumstances. No: Serial number
of the observation. Obs: Observer (DT - Diego Tirelli,
Italian Group of Comet Observers; MJ & GR - Michael Jäger & Gerald Rhemann,
Astrostudio G. Rhemann Ges. m. b. h). Date UT (2004): Time
at midexposure. RA, Dec: right ascension and declination of the comet nucleus,
respectively, measured directly on the CCD images through
astrometric calibration.
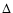 ,
r: Earth-comet and Sun-comet distances.
,
r: Earth-comet and Sun-comet distances.
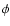 :
Phase angle.
:
Phase angle. 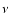 :
True anomaly of the comet nucleus.
:
True anomaly of the comet nucleus.
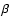 :
Cometocentric latitude of the Earth; it is positive when
the Earth is in the comet north hemisphere.
:
Cometocentric latitude of the Earth; it is positive when
the Earth is in the comet north hemisphere.
- Table 2:
RSS, SWS and NL parameters. No.: serial number of the observation.
PA
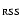 :
measured position angle on the sky of the average orientation
of the RSS. PA
:
measured position angle on the sky of the average orientation
of the RSS. PA
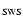 :
measured position angle on the sky of the SWS.
PA
:
measured position angle on the sky of the SWS.
PA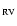 :
computed position angle on the sky of the Sun-comet radius vector.
PA
:
computed position angle on the sky of the Sun-comet radius vector.
PA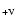 :
computed position angle on the sky of the positive velocity vector.
NLp: NL point sequential number (Fig. 1). (1
:
computed position angle on the sky of the positive velocity vector.
NLp: NL point sequential number (Fig. 1). (1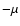 ): radiation pressure acting on
the dust grain.
): radiation pressure acting on
the dust grain. 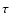 :
days elapsed between ejection of the dust grain from the comet
nucleus and observation. d
:
days elapsed between ejection of the dust grain from the comet
nucleus and observation. d
![$[^{\circ }]$](/articles/aa/full/2005/06/aa1766/img15.gif) ,
d [106 km]: angular (in the plane of the
sky) and linear (in the plane of the comet orbit) distance from the nucleus of the
computed NL point, respectively. PA
,
d [106 km]: angular (in the plane of the
sky) and linear (in the plane of the comet orbit) distance from the nucleus of the
computed NL point, respectively. PA :
position angle of the sky-projected
NL point. oPA
:
position angle of the sky-projected
NL point. oPA :
orbital position angle of
the NL point. Position angles in the plane of the sky are measured from north to east,
as usual, whereas the ones in
the plane of the comet orbit (prefix o) are measured counterclockwise from the
Sun-comet prolonged radius vector
(r').
:
orbital position angle of
the NL point. Position angles in the plane of the sky are measured from north to east,
as usual, whereas the ones in
the plane of the comet orbit (prefix o) are measured counterclockwise from the
Sun-comet prolonged radius vector
(r').