- ... survey
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Based on observations obtained with XMM-Newton, an ESA science
mission with instruments and contributions directly funded by ESA Member
States and the USA (NASA). The majority of the newoptical
spectroscopy data used here have been obtained using thefacilities of the
Italian "Telescopio Nazionale Galileo'' (TNG) and of the European Southern
Observatory (ESO).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Tables 2-4 and Appendices are only available in
electronic form at
http://www.edpsciences.org
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... Centre
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The XMM-Newton Survey
Science Centre is an international collaboration involving a consortium of 10
institutions appointed by ESA to help the SOC in developing the software
analysis system, to pipeline process all the XMM-Newton data, and to exploit
the XMM-Newton serendipitous detections, see http://xmmssc-www.star.le.ac.uk
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... mission
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- One of
the responsibilities of the XMM-Newton SSC is the production of
the XMM-Newton Source Catalogue. This catalogue will provide a
rich and unique resource for generating well-defined samples for
specific studies, using the fact that X-ray selection is a highly
efficient way of selecting certain types of objects, like for
instance AGN, clusters of galaxies and active stars. The first
XMM-Newton Serendipitous Source Catalogue (1XMM), released on 2003
April 7, contains source detections drawn from 585 XMM-Newton EPIC
observations and a total of
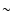 30 000 individual X-ray sources
having a likelihood value above 8 and good quality flags. The
median flux (in the total photon energy band 0.2-12 keV) of the
catalogue sources is
30 000 individual X-ray sources
having a likelihood value above 8 and good quality flags. The
median flux (in the total photon energy band 0.2-12 keV) of the
catalogue sources is
 erg cm-2 s-1, with
erg cm-2 s-1, with
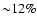 of them having fluxes below
of them having fluxes below
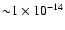 erg cm-2 s-1, see
http://xmmssc-www.star.le.ac.uk/
erg cm-2 s-1, see
http://xmmssc-www.star.le.ac.uk/
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... catalogue
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- http://www.ast.cam.ac.uk/~apmcat/
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... interval
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The good-time interval is
defined as the on-axis exposure time taken from the exposure map
produced in the XMM-Newton pipeline processing system.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... sample
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The fraction of MOS2 images with a thin, medium and
thick filter used here are
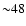 %,
%, 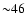 % and
% and 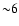 %, respectively.
%, respectively.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... extragalactic
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Since we are primarily interested in
the extragalactic number-flux relationship we have excluded from
the computation the sources classified as stars (see Sect. 3.2).
Based on the results presented in Sect. 3.5 we are confident that the large
majority of the unidentified sources are associated to extragalactic objects.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...positions
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Using the optical position of the sources
classified as type 1 AGN we have evaluated that the
90% confidence level error circle
has a radius equal to
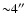 ;
about 99% of the type 1 AGN are within
;
about 99% of the type 1 AGN are within
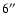 from the X-ray position. This is consistent with what found
in other XMM-Newton surveys (Barcons et al. 2002; Fiore et al.
2003).
from the X-ray position. This is consistent with what found
in other XMM-Newton surveys (Barcons et al. 2002; Fiore et al.
2003).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... 2.6 m
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- As part of the AXIS (An XMM-Newton
International Survey) project, see http://www.ifca.unican.es/~xray/AXIS
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... (XBS J014100.6-675328
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- XBS J014100.6-675328 (BL Hyi), also belonging to
the HBSS sample, is a well known AM Herculis object (a polar)
i.e. a binary system composed of a magnetic white dwarf and a low-mass star
(see Caccianiga et al. 2004, and references therein).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... HBSS sample
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- On the basis of the results presented in Sect. 3.5 we are
confident that the bulk of unidentified sources both in the BSS and HBSS
samples are associated with extragalactic objects and we know that XBS J014100.6-675328 is an accreting binary system
(see Caccianiga et al. 2004).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... processing
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- We have not used here the
"pipeline processing product'' HR1 which is defined using the
corrected count rate in the (0.15-0.5) keV and in the (0.5-2) keV energy band since the measured count rate in the (0.15-0.5) keV band
is a strong function of the Galactic
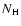 along the line of sight. Note that the effect on HR2 and HR3 due
to the different
along the line of sight. Note that the effect on HR2 and HR3 due
to the different
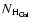 for the objects in the sample
(which ranges between
for the objects in the sample
(which ranges between
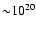 to 1021 cm-2) is
negligible.
to 1021 cm-2) is
negligible.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... survey
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- We note that in the HBS28 sample discussed in Caccianiga et al.
(2004) none of the 19 type 1 AGN is absorbed with
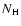 in excess to 1022
cm-2, implying that the fraction of X-ray absorbed type 1 AGN is less
than 10% of the total type 1 AGN population. This result is also confirmed
by the present HBSS sample since at most 4 (out of 39) broad line AGN are
characterized by HR2 values typical of absorbed (
in excess to 1022
cm-2, implying that the fraction of X-ray absorbed type 1 AGN is less
than 10% of the total type 1 AGN population. This result is also confirmed
by the present HBSS sample since at most 4 (out of 39) broad line AGN are
characterized by HR2 values typical of absorbed (
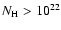 cm-2)
AGN. See also Sect. 3.4.
cm-2)
AGN. See also Sect. 3.4.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
stars
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The two sources that are outside the "stellar'' HR2
locus are XBS J014100.6-675328 and XBS J215323.7+173018.
The first object, XBS J014100.6-675328, has been already
discussed in footnote 9.
The XMM spectrum, discussed in Caccianiga et
al. (2004), is well fitted by a unabsorbed power-law model with
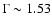 plus a thermal component having a temperature
plus a thermal component having a temperature
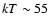 eV and an emission line at
eV and an emission line at 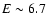 keV. The second
object (XBS J215323.7+173018) is a star having an XMM spectrum
described by a thermal component with
keV. The second
object (XBS J215323.7+173018) is a star having an XMM spectrum
described by a thermal component with
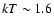 keV and a possible hard tail.
keV and a possible hard tail.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
sample
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- This latter estimate is consistent with the fact that in the
HBS28 sample
discussed in Caccianiga et al. (2004) there is
only one type 2 AGN with HR2
between -0.75 and -0.35 out of 8 type 2 objects.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.