Table 3:
Effects of the second order contribution of the tidal potential (zonal tides contribution) on nutation angles ( as) and precession (
as) and precession ( as/c) from different studies. MHB 2000Z: values of Mathews et al. (2002) including only the zonal tides contribution; SF99: Souchay & Folgueira (2000).
as/c) from different studies. MHB 2000Z: values of Mathews et al. (2002) including only the zonal tides contribution; SF99: Souchay & Folgueira (2000).
| |
 |
 |
| |
 as as |
 as as |
|
l |
l' |
F |
D |
 |
sin |
cos |
sin |
cos |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
MHB 2000Z |
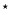 101.3 101.3 |
- |
- |
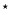 -8.9 -8.9 |
| SF99 |
168.0 |
- |
- |
-9.0 |
| This study |
207.9 |
2.4 |
0.2 |
-9.7 |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
MHB 2000Z |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| SF99 |
4.5 |
- |
- |
-2.8 |
| This study |
5.0 |
0.1 |
0.0 |
-3.2 |
|
0 |
0 |
2 |
-2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
MHB 2000Z |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| SF99 |
3.2 |
- |
- |
0.6 |
| This study |
4.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.4 |
|
Precession in longitude |
 as/c as/c |
|
|
|
MHB 2000Z |
|
- |
|
|
| SF99 |
|
- |
|
|
| This study |
|
-4925.9 |
|
|
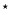 Note that revised values by Mathews (2004) are 194 Note that revised values by Mathews (2004) are 194  as and -10 as and -10  as for the 18.6-year as for the 18.6-year
nutation in longitude and obliquity, respectively.
|
Source LaTeX |
All tables |
In the text