All Tables
- Table 1:
List of observed sources. Columns 2
and 3 give the coordinates used in the observations and for
correlation, Col. 4 gives the source distances in Mpc. Column 5
gives the classification according to Véron-Cetty & Véron (2001).
- Table 2:
Results from the observations. "Tapered'' 6 cm flux
densities were measured using images tapered and restored with the
18 cm beam size. The MERLIN 18 cm and 6 cm positions differ by 35 mas
because the coordinates used at the correlator were changed in an
unknown way and the resulting offset could not be removed
accurately. We have precessed the MERLIN B1950 coordinates to J2000
using NRAO's scheduling software SCHED. Positions are absolute for
observations that were phase-referenced and the phase-referencing
worked; such positions are given in h, m, s (for RA) and
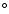 ,
,
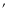 ,
,
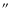 (for Dec). Otherwise the positions are
given in mas relative to the strongest component. The flux density
error estimates represent
(for Dec). Otherwise the positions are
given in mas relative to the strongest component. The flux density
error estimates represent 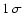 .
.
- Table 3:
All Seyferts observed with VLBI. Column 1 lists the names we
used, Col. 2 the names used by Véron-Cetty & Véron (2001), Col. 3 the
Seyfert types as described by Véron-Cetty & Véron (2001), Col. 4 the linear
resolution in pc, Col. 5 the instrument and frequency used, and Col. 6 the reference to the publication.
- Table 4:
Seyferts from Table 3 that have
dual-frequency (18 cm and 6 cm) VLBI observations with matching beam
sizes, from which the spectral index is derived. Asterisks denote
objects with at least one component with a flat or inverted spectrum.
- Table 5:
Fraction of flat- and inverted-spectrum components in various
Seyfert samples. The column "
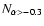 '' gives the number of
components with spectral indices
'' gives the number of
components with spectral indices
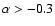 (i.e., components with
flat or inverted spectra). The column "
(i.e., components with
flat or inverted spectra). The column "
 '' gives the
total number of components in each sample. The column % gives
'' gives the
total number of components in each sample. The column % gives
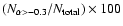 .
The column P gives the
level of significance from a comparison of the fraction of flat- and
inverted-spectrum components in the VLBI sample of this paper (limits
treated as detections), to that of each comparison sample at arcsec
resolution, using the difference-of-two-proportions test with Yates
correction for continuity (e.g., Glanz 1992).
.
The column P gives the
level of significance from a comparison of the fraction of flat- and
inverted-spectrum components in the VLBI sample of this paper (limits
treated as detections), to that of each comparison sample at arcsec
resolution, using the difference-of-two-proportions test with Yates
correction for continuity (e.g., Glanz 1992).
- Table 6:
Comparison of the spectral index distribution of the VLBI
Seyfert sample to various other Seyfert samples. The level of
significance gives the probability that the spectral index
distribution of the comparison sample and the VLBI seyfert sample in
this paper were drawn from the same parent population.
- Table 7:
Subset of sources from Table 3 for which both pc and kpc-scale structures have been observed. The misalignment
angle,
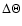 ,
is calculated as
,
is calculated as
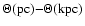 ,
and has then been reflected onto the range of
,
and has then been reflected onto the range of 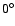 to
to
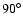 .
For the seven objects at the end of the table, either
the PA information of the kpc scale structure was not completely
reliable or was unavailable. The position angles of the galaxy minor
axes in the last column were drawn from de Vaucouleurs et al. (1991),
except for those marked a taken from Schmitt & Kinney (2000) and those
marked b measured by us from Hubble Space Telescope archival images
(see Sect. 4.3).
.
For the seven objects at the end of the table, either
the PA information of the kpc scale structure was not completely
reliable or was unavailable. The position angles of the galaxy minor
axes in the last column were drawn from de Vaucouleurs et al. (1991),
except for those marked a taken from Schmitt & Kinney (2000) and those
marked b measured by us from Hubble Space Telescope archival images
(see Sect. 4.3).