

Up: The runaway black hole J1655-40
From the proper motion and radial velocity of GRO J1655-40 - irrespective
of the uncertainties in the distance - we conclude the following:
- 1.
- The X-ray binary has a runaway velocity of 112
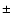 18 km s-1,
probably imparted by a natal explosion during the formation of the black hole.
18 km s-1,
probably imparted by a natal explosion during the formation of the black hole.
- 2.
- The linear momentum of the binary system is
538
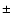 100
100 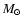 km s-1, which is comparable to that found
in solitary neutron stars and millisecond pulsars. This suggests that the
relatively low-mass black hole (
km s-1, which is comparable to that found
in solitary neutron stars and millisecond pulsars. This suggests that the
relatively low-mass black hole (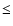 6
6 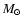 )
in GRO J1655-40
may have been formed through a neutron star phase.
)
in GRO J1655-40
may have been formed through a neutron star phase.
- 3.
- The kinetic energy of the system is (5.8
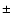 0.4)
0.4) 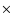 1047 ergs, namely,
1047 ergs, namely, 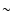 6
6  10-4, that of a typical supernova.
10-4, that of a typical supernova.
- 4.
- The galactocentric orbital plane is almost parallel to the Galactic
disk and the Galactic pericentre
 3 kpc, which indicates that the
black hole in GRO J1655-40 is the remnant of a massive star born
in the Galactic disk.
3 kpc, which indicates that the
black hole in GRO J1655-40 is the remnant of a massive star born
in the Galactic disk.
- 5.
- Contrary to the binary XTE J1118+480 which harbors a black hole
born in the halo (Mirabel et al. 2001),
in the case of GRO J1655-40 there is unambigous kinematical evidence
that the black hole was born in the disk and received a natal kick, most
likely from a supernova explosion (Israelian et al. 1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Casares, P. Podsiadlowski,
M.E. Beer, J.-P. Lasota, S. Corbel, P. Benaglia, A. Piatti, and E. Gourgoulhon
for help and discussions on different aspects of this work. J.A.C. and
I.F.M. are members of the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones
Científicas y Técnicas of Argentina, and I.R. is a fellow of the
Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cienífico e Tecnológico of
Brazil. I.F.M. acknowledges support from PIP 0049/98 and Fundación
Antorchas.


Up: The runaway black hole J1655-40
Copyright ESO 2002