

Up: Integrated spectroscopy of bulge fields
- 1.
- We present for the first time the full set of Lick indices for a
sample of metal-rich globular clusters in the Galactic bulge.
- 2.
- The Mg2 and
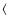 Fe
Fe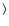 indices of the most
metal-rich globular clusters (NGC 5927, NGC 6528, and NGC 6553) are
similar to those of the bulge, indicating that cluster and bulge
fields have a similar [Fe/H] ratio.
indices of the most
metal-rich globular clusters (NGC 5927, NGC 6528, and NGC 6553) are
similar to those of the bulge, indicating that cluster and bulge
fields have a similar [Fe/H] ratio.
- 3.
- The CN index is clearly stronger in metal-rich globular
clusters, compared to the stellar population in the Galactic bulge.
- 4.
- All the metallicity-sensitive indices are tightly correlated
with the
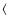 Fe
Fe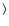 index (Spearman rank coefficient
index (Spearman rank coefficient
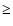 0.87).
0.87).
- 5.
- We provide empirical calibrations of several indices versus
[Fe/H] in the range
![$-2.29\leq\rm [Fe/H]\leq-0.17$](/articles/aa/full/2002/43/aa2781/img260.gif) .
We find that the
Mg2 and the [MgFe] index are the best metallicity indicators with a
rms of 0.15 dex.
.
We find that the
Mg2 and the [MgFe] index are the best metallicity indicators with a
rms of 0.15 dex.
- 6.
- The H
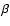 index shows a large scatter as a function of
galactocentric distance which can be explained by the changing
horizontal branch morphology.
index shows a large scatter as a function of
galactocentric distance which can be explained by the changing
horizontal branch morphology.
- 7.
- All other indices decrease with galactocentric radius and have
constant low values beyond the radius of
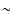 10 kpc.
10 kpc.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the use of the Lick standard star database which is
maintained by Guy Worthey. THP gratefully acknowledges the support
of the German Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft,
DFG under the project number Be 1091/10-1. We would like to
thank the anonymous referee for a careful and constructive report.


Up: Integrated spectroscopy of bulge fields
Copyright ESO 2002