

Up: Near-infrared surface photometry of
The main results found in this work can be summarized as follows:
- 1.
- The brightness profiles for most objects of our sample
are well fitted by the de Vaucouleurs law.
- 2.
- The infrared effective radii of the galaxies of
our sample are typically one half of its corresponding radius in B band; this can be
interpreted in the sense that
the stellar population dominating the near-infrared emission is more concentrated that
the bluer population.
- 3.
- The color gradients found are very small, and show a general
trend toward bluer colors in the external region.
- 4.
- The infrared colors of the sample are compatible
with stellar populations such as those found in metal-rich Galactic clusters. The galaxies
NGC 7192, NGC 7562 and NGC 7619 are compatible with less metal-rich populations.
- 5.
- The infrared effective radius (
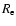 )
and the effective
brightness (
)
and the effective
brightness (
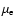 )
of the sample galaxies confirm the Fundamental Plane relation
of elliptical galaxies; the rms scatter of the FP is 0.20 dex for J and H, and
0.23 dex for
)
of the sample galaxies confirm the Fundamental Plane relation
of elliptical galaxies; the rms scatter of the FP is 0.20 dex for J and H, and
0.23 dex for 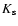 .
The a values (slope in
.
The a values (slope in
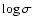 )
are compatible with the
general values found in the literature, while b (slope in
)
are compatible with the
general values found in the literature, while b (slope in
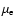 )
is higher by about 20%.
)
is higher by about 20%.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge CNPq and PRONEX/FINEP 76.97.1003.00 for financial support.


Up: Near-infrared surface photometry of
Copyright ESO 2002